A Tapestry of Wealth: Unraveling Africa’s Natural Resources
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Wealth: Unraveling Africa’s Natural Resources
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Wealth: Unraveling Africa’s Natural Resources. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Wealth: Unraveling Africa’s Natural Resources
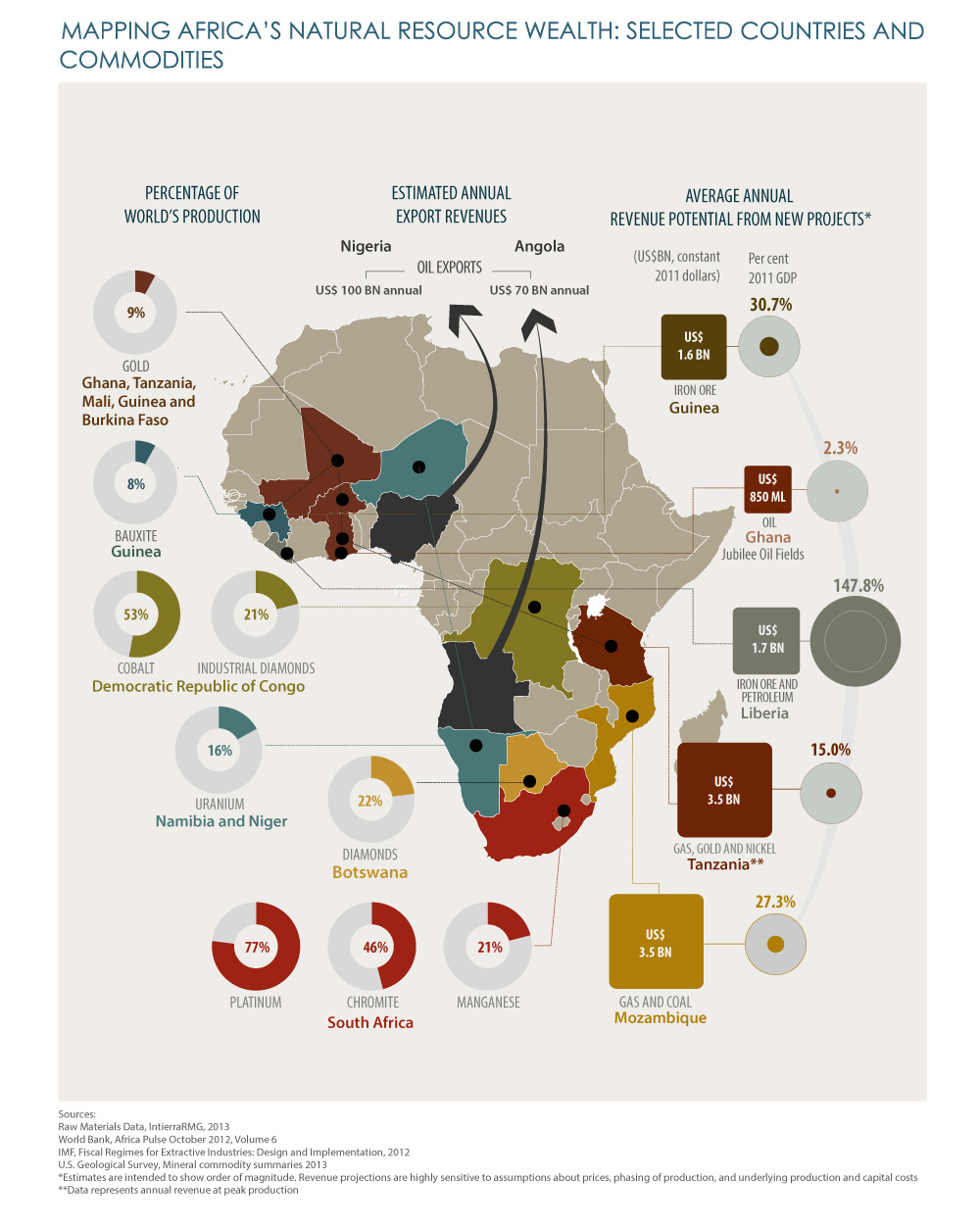
Africa, a continent of immense diversity and vast landscapes, is also a treasure trove of natural resources. Its rich geological formations and diverse ecosystems hold an abundance of minerals, energy sources, and agricultural potential, shaping the continent’s economic landscape and influencing its global role. A comprehensive understanding of Africa’s natural resource distribution, however, requires more than just a superficial glance at a map. It demands a deeper dive into the complex interplay of geology, geography, and socio-economic factors that define the continent’s resource potential.
A Continent of Contrasts: Mapping the Wealth
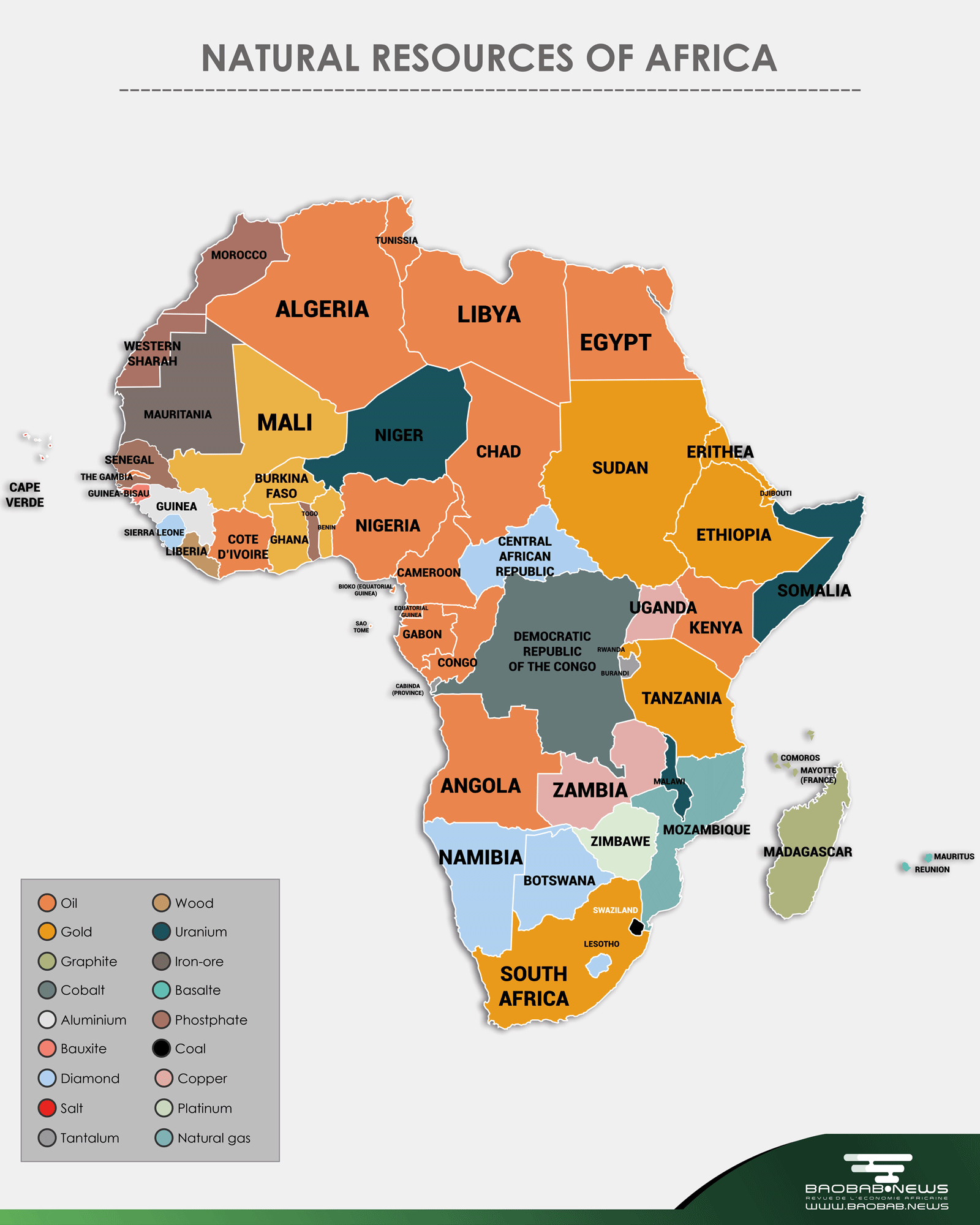
The natural resources map of Africa reveals a striking tapestry of distribution. The continent’s northern and southern edges, with their vast stretches of arid and semi-arid lands, are home to significant deposits of phosphate rock, iron ore, and uranium. The central and eastern regions, characterized by their mountainous terrain and volcanic activity, harbor rich deposits of gold, diamonds, and other precious metals. The coastal areas, with their fertile soils and abundant water resources, are ideal for agriculture and fisheries.
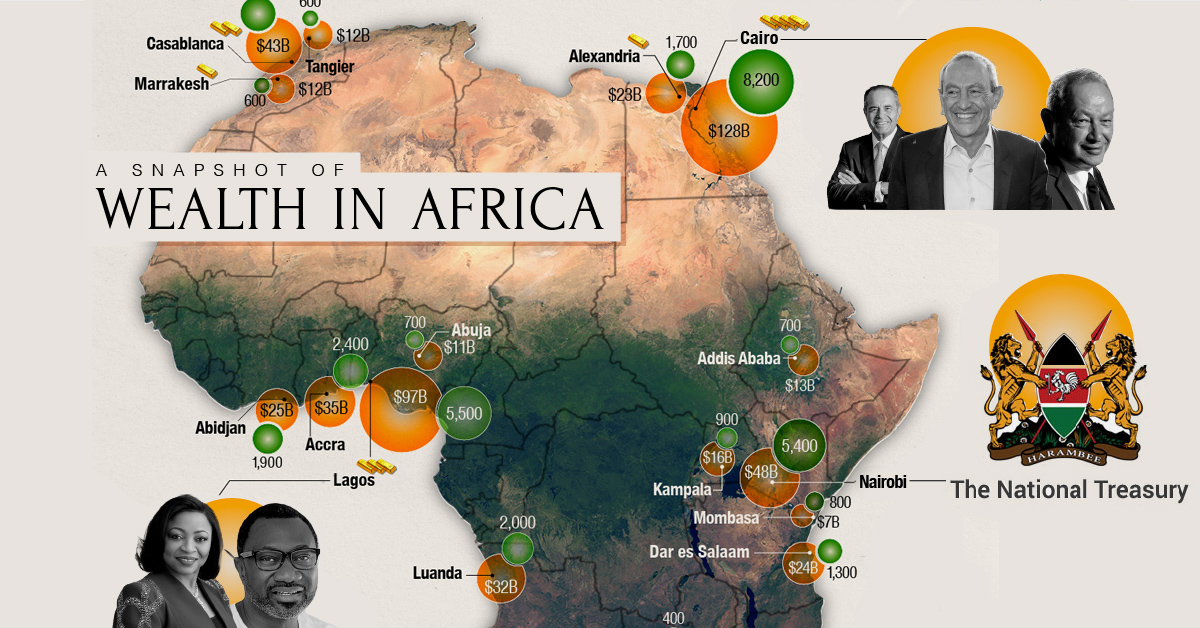
Mineral Riches: The Foundation of Economic Growth
Africa’s mineral wealth is a significant driver of economic growth, contributing substantially to the continent’s GDP and providing employment for millions. South Africa, renowned for its vast reserves of gold, platinum, and diamonds, remains a global leader in mineral production. The Democratic Republic of Congo holds significant reserves of cobalt, a key component in electric vehicle batteries, while Zambia and Zimbabwe are major copper producers. These mineral resources, however, often come with complex challenges, including resource depletion, environmental degradation, and the potential for conflict over resource control.
Energy Potential: Powering the Future
Africa’s vast energy resources offer immense potential for economic development and energy security. The continent holds significant reserves of oil and natural gas, particularly in the Gulf of Guinea region, with Nigeria and Angola leading the way in production. However, the continent also boasts substantial renewable energy potential, particularly in solar, wind, and hydropower. The Sahara Desert, for instance, receives abundant solar radiation, making it an ideal location for large-scale solar power generation. Harnessing this renewable energy potential can contribute to sustainable development, reduce dependence on fossil fuels, and improve energy access for millions of Africans.
Agricultural Bounty: Feeding the Continent and Beyond
Africa’s fertile lands and favorable climate conditions offer immense potential for agricultural development. The continent is home to a wide range of crops, including cereals, fruits, vegetables, and cash crops like coffee and cocoa. Its livestock sector also plays a significant role in food production and livelihoods. However, agricultural productivity in Africa is often constrained by factors such as poor infrastructure, limited access to technology, and climate change impacts. Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring food security and achieving sustainable agricultural growth.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Resource Landscape
While Africa’s natural resources offer immense potential for development, they also present a complex set of challenges. These include:
- Resource Depletion: Unsustainable extraction practices can lead to resource depletion, particularly in the mining sector, threatening long-term economic sustainability.
- Environmental Degradation: Mining, oil and gas extraction, and deforestation can have significant environmental impacts, leading to habitat loss, pollution, and climate change.
- Conflict over Resources: Competition for resources, particularly in areas with scarce resources or weak governance, can lead to conflict and instability.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Limited infrastructure, including roads, transportation networks, and energy grids, can hinder the development and efficient utilization of natural resources.
- Governance and Transparency: Weak governance and corruption can lead to resource mismanagement, inequality, and a lack of benefits for local communities.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-pronged approach that focuses on:
- Sustainable Resource Management: Implementing sustainable extraction practices, promoting resource conservation, and adopting circular economy principles.
- Environmental Protection: Implementing environmental regulations, promoting biodiversity conservation, and mitigating climate change impacts.
- Conflict Resolution: Promoting peaceful resource sharing, addressing grievances, and fostering inclusive governance.
- Infrastructure Development: Investing in infrastructure to improve access to resources, facilitate trade, and enhance economic competitiveness.
- Good Governance and Transparency: Strengthening governance institutions, promoting transparency in resource management, and ensuring equitable distribution of benefits.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. What are the most important natural resources in Africa?
Africa’s most important natural resources include minerals (gold, diamonds, platinum, cobalt, copper), oil and gas, agricultural products (coffee, cocoa, cereals, fruits, vegetables), and renewable energy sources (solar, wind, hydropower).
2. How are natural resources impacting Africa’s economic development?
Natural resources contribute significantly to Africa’s GDP, provide employment, and fuel economic growth. However, their impact is often uneven, with some countries benefiting more than others, and challenges like resource depletion and environmental degradation can hinder long-term development.
3. What are the major challenges associated with Africa’s natural resources?
Challenges include resource depletion, environmental degradation, conflict over resources, lack of infrastructure, and weak governance and transparency.
4. What are the key strategies for managing Africa’s natural resources sustainably?
Sustainable resource management strategies include implementing sustainable extraction practices, promoting resource conservation, investing in infrastructure, strengthening governance, and ensuring equitable benefit sharing.
5. How can Africa leverage its natural resources to achieve sustainable development?
Africa can achieve sustainable development by focusing on responsible resource management, promoting inclusive growth, investing in human capital, and fostering technological innovation.
Tips for Navigating Africa’s Resource Landscape
- Embrace Sustainable Practices: Implement sustainable extraction practices, promote resource conservation, and adopt circular economy principles.
- Invest in Infrastructure: Develop infrastructure to facilitate resource development, transportation, and access to markets.
- Strengthen Governance: Promote good governance, transparency, and accountability in resource management.
- Promote Regional Cooperation: Collaborate with neighboring countries to manage shared resources and address transboundary issues.
- Invest in Human Capital: Build capacity in resource management, technology, and innovation.
Conclusion: A Continent of Opportunity
Africa’s natural resources represent a vast reservoir of potential for economic development and social progress. By embracing sustainable practices, investing in infrastructure, strengthening governance, and fostering regional cooperation, Africa can harness its natural wealth to create a more prosperous and equitable future for its people. The continent’s resource map, while revealing challenges, ultimately highlights the immense opportunity for sustainable growth and development, positioning Africa as a key player in the global economy.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Wealth: Unraveling Africa’s Natural Resources. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!