Charting the Past: The Power of Historical Maps
Related Articles: Charting the Past: The Power of Historical Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Past: The Power of Historical Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Past: The Power of Historical Maps
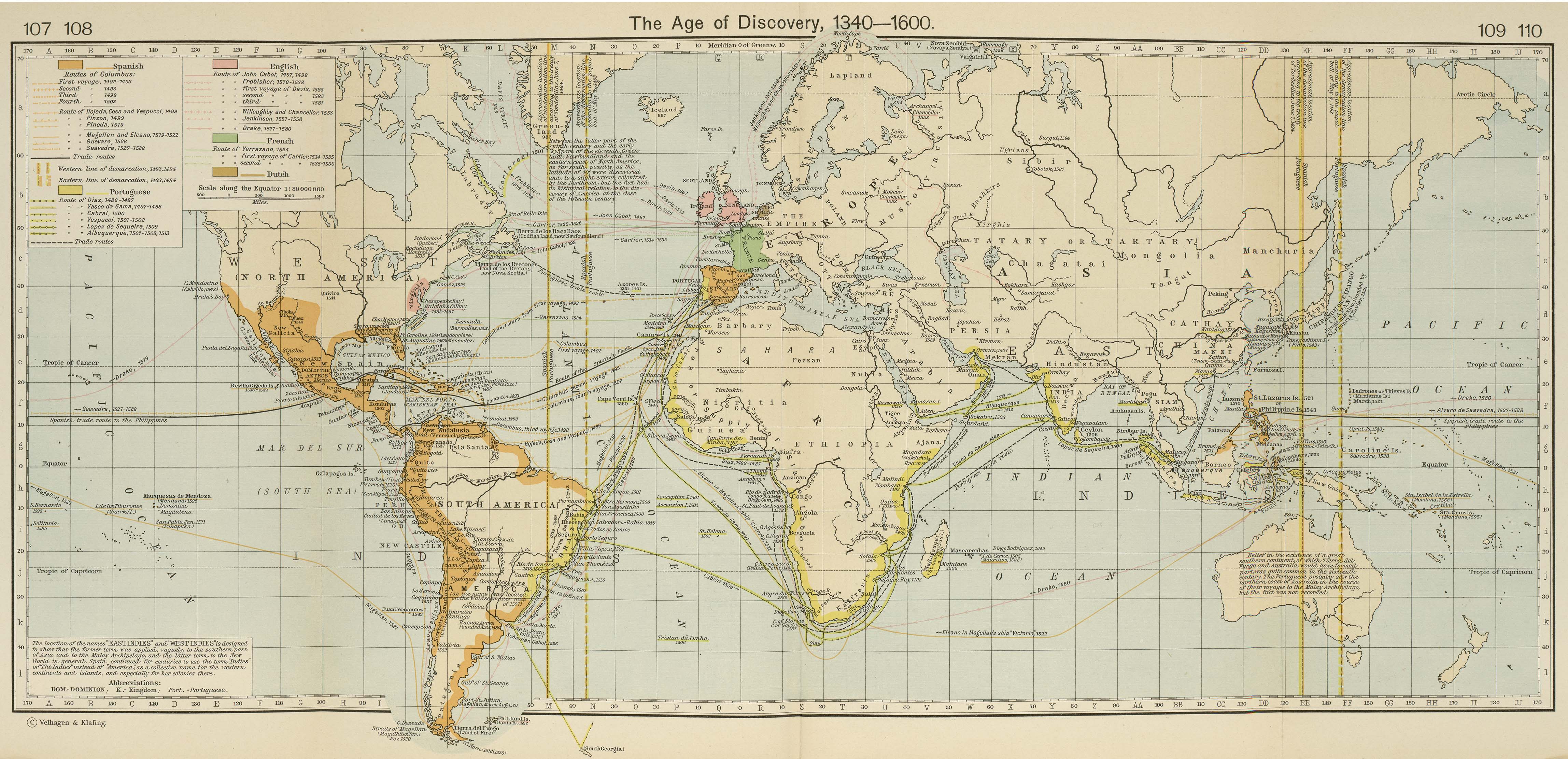
Maps, the silent storytellers of our world, offer a unique lens through which to view the past. Beyond simply depicting geographical features, historical maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding the evolution of human civilization, its triumphs and tragedies, and the complex tapestry of cultural interactions that have shaped our present. They are not mere static representations of the world, but dynamic records of human activity, revealing the ebb and flow of empires, the rise and fall of civilizations, and the intricate dance of power and influence across time.
The Evolution of Historical Maps:
The history of mapmaking itself is a captivating journey, reflecting the growing understanding of the world and the development of advanced cartographic techniques. Early maps, often etched onto clay tablets or papyrus scrolls, were rudimentary, focusing on immediate surroundings and practical needs such as navigation and trade routes. The ancient Egyptians, renowned for their precise surveying skills, produced detailed maps of their kingdom, while the Greeks, fueled by their thirst for knowledge, developed sophisticated methods for projecting the spherical Earth onto a flat surface.
The Renaissance, with its renewed interest in classical learning, witnessed a resurgence in mapmaking. The invention of the printing press facilitated the mass production and dissemination of maps, leading to a wider understanding of global geography. Explorers like Christopher Columbus and Ferdinand Magellan, driven by the desire to find new trade routes and expand European influence, produced maps that helped shape our understanding of the world.
The age of exploration also saw the development of more accurate and detailed maps, aided by advances in navigation instruments like the compass and astrolabe. The invention of the telescope further refined the process of celestial navigation, leading to more precise measurements of latitude and longitude.
Historical Maps as Windows to the Past:
Historical maps offer a wealth of information that transcends the mere depiction of geographical features. They provide insights into:
1. Political Boundaries and Power Dynamics:
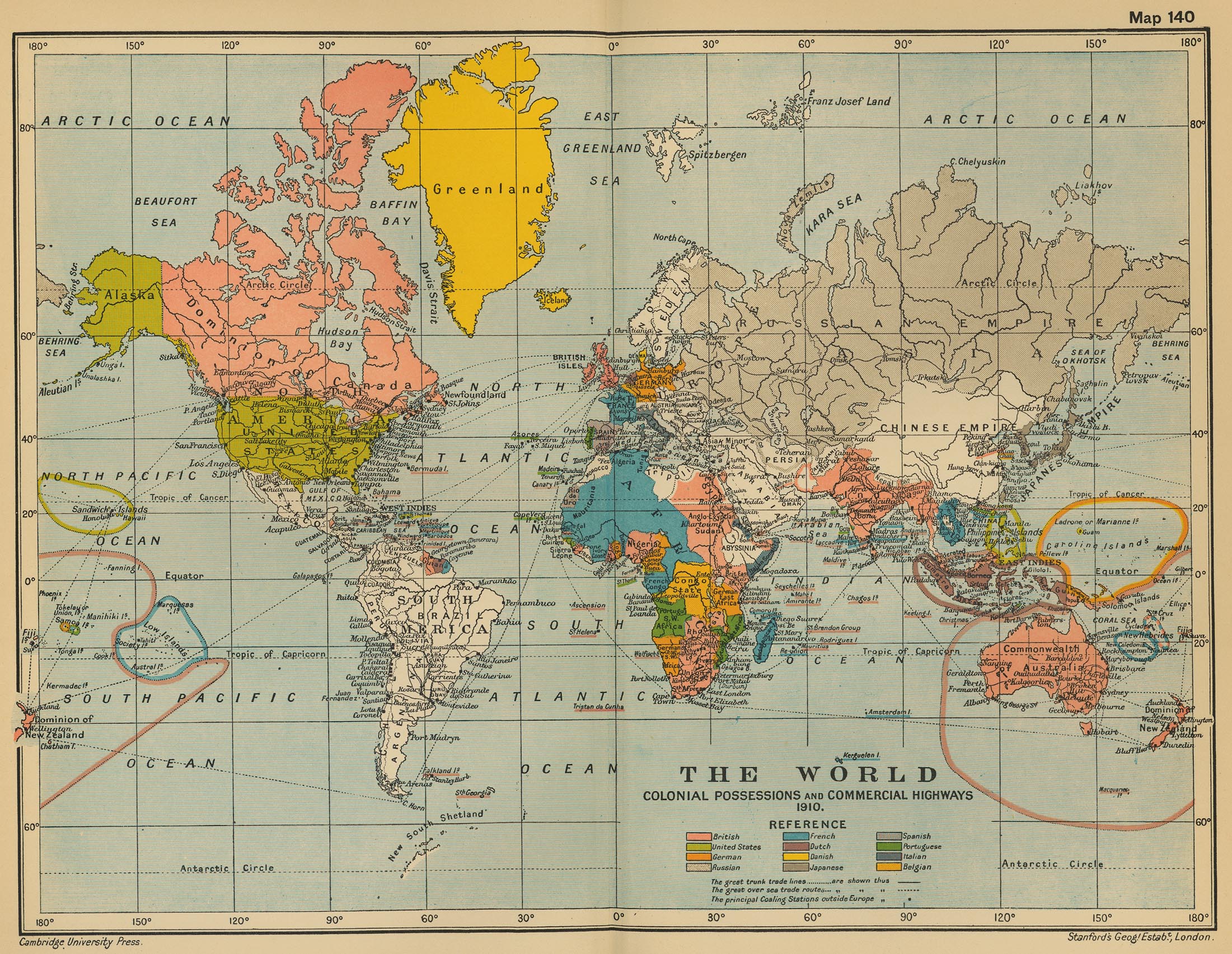
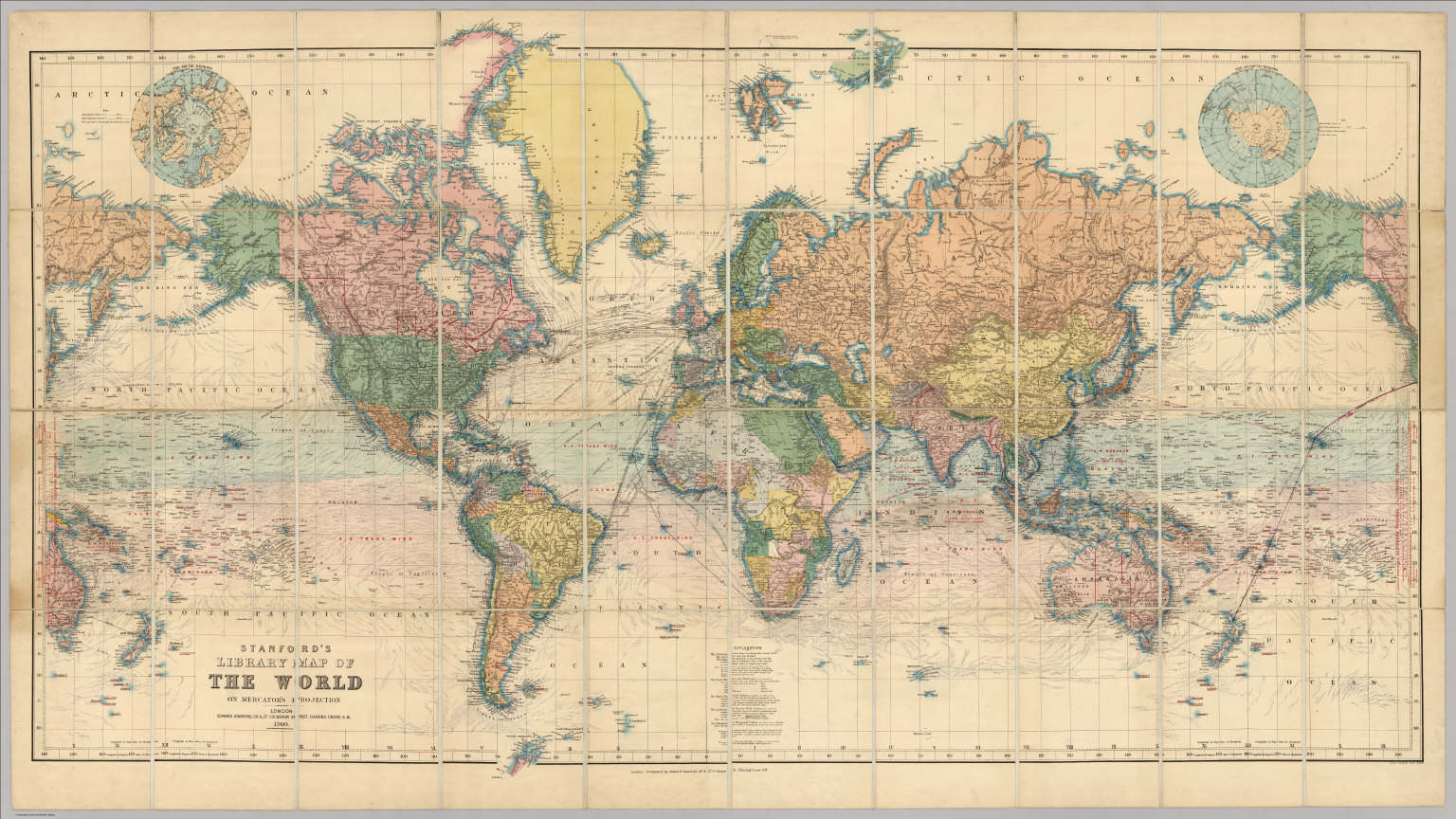
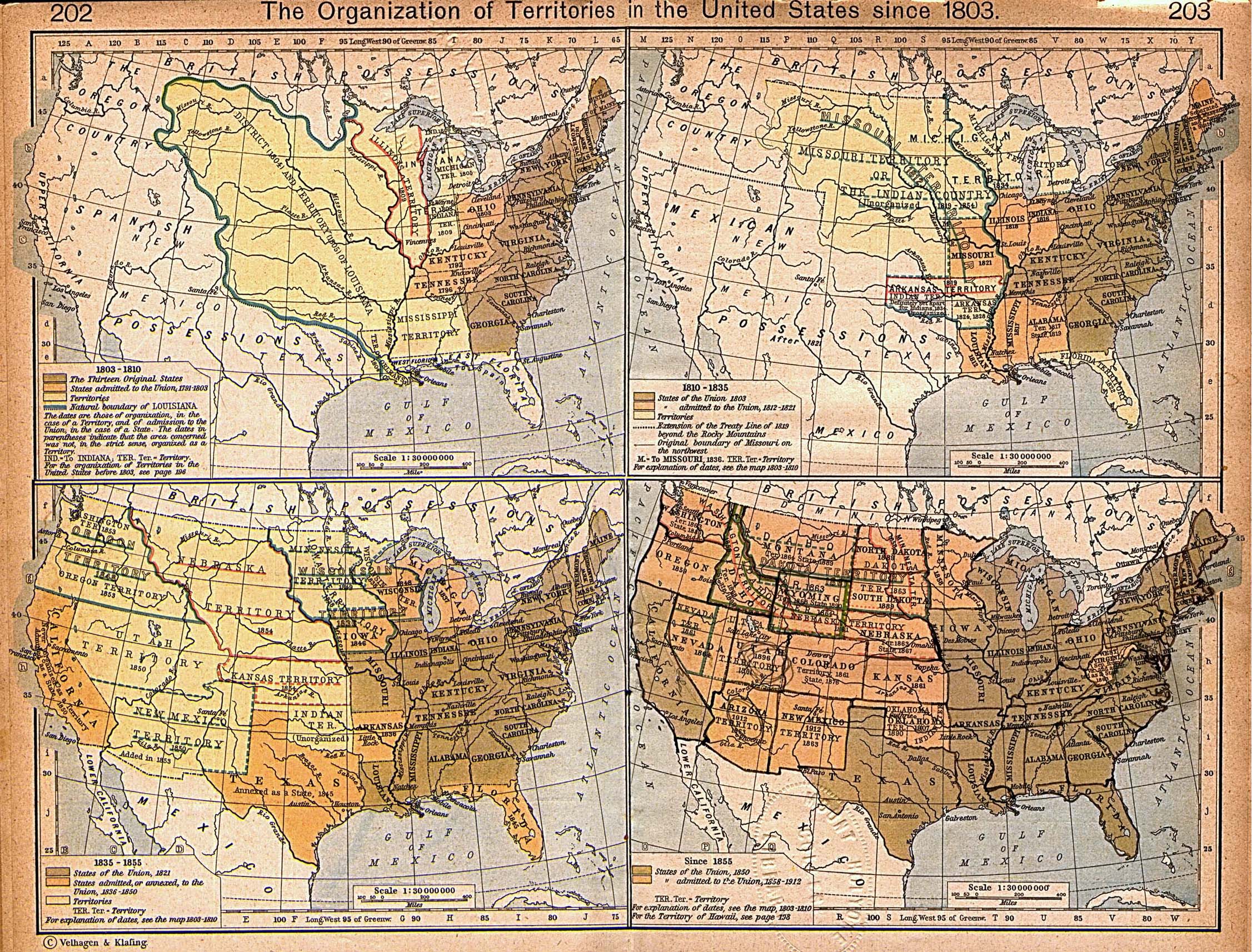
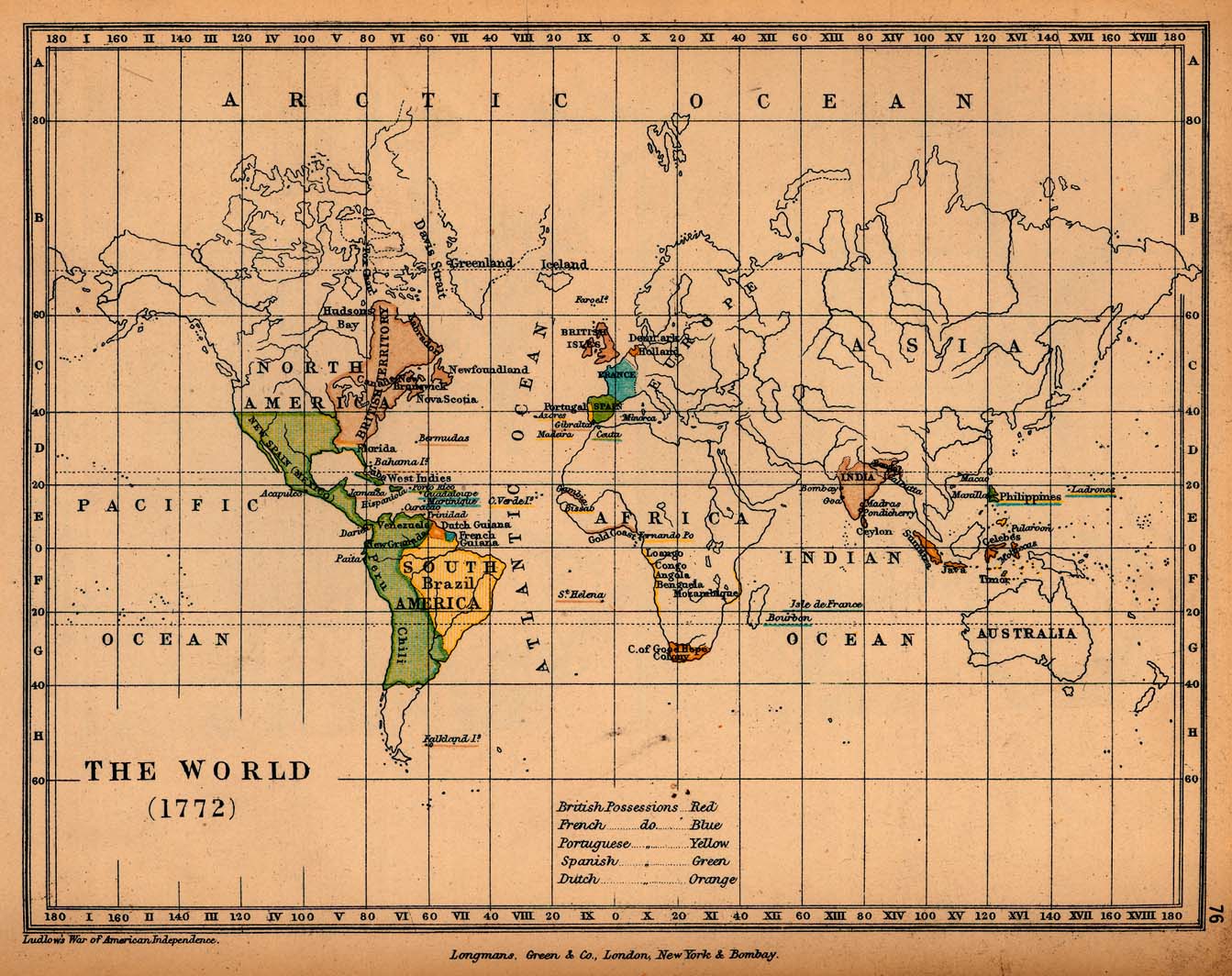
Maps reveal the ever-shifting political landscape, showcasing the rise and fall of empires, the formation of new nations, and the impact of wars and treaties on territorial boundaries. The fragmentation and consolidation of empires, the expansion of colonial powers, and the creation of modern nation-states are all vividly captured within the lines and colors of historical maps.
2. Trade Routes and Economic Networks:
Maps document the flow of goods and resources across continents, highlighting the intricate web of trade connections that sustained civilizations. They reveal the importance of maritime trade routes, the silk road, and other historical trade networks that facilitated the exchange of ideas, goods, and cultural influences.
3. Cultural Landscapes and Settlement Patterns:
Historical maps provide valuable insights into the distribution of settlements, the development of urban centers, and the evolution of cultural landscapes. They reveal the impact of environmental factors on human settlements, the growth of cities as centers of trade and power, and the cultural diversity that characterized different regions.
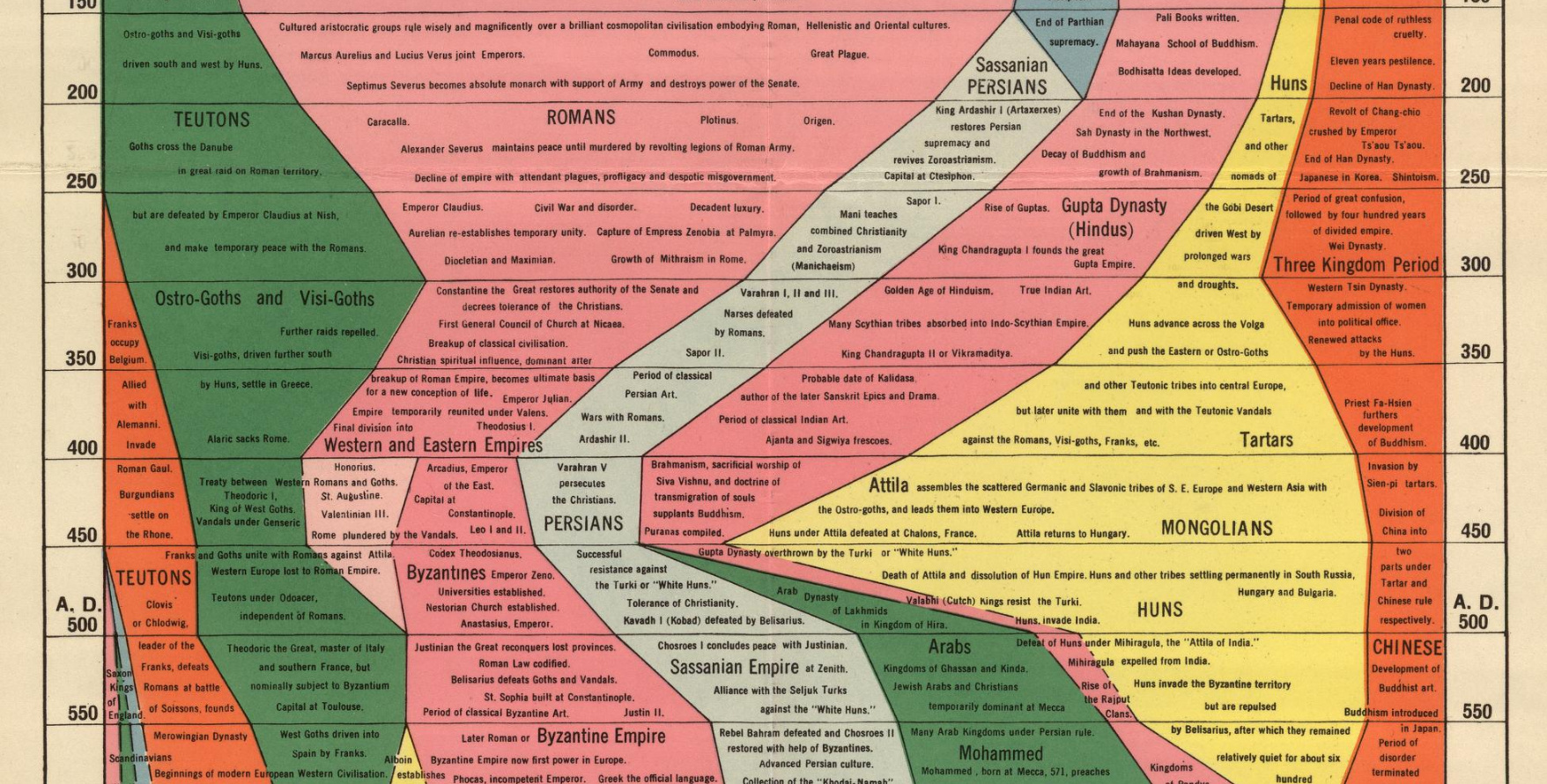
4. Historical Events and Military Campaigns:
Maps serve as invaluable records of historical events, depicting the locations of battles, the movements of armies, and the strategies employed during military campaigns. They offer a visual representation of the impact of war on the landscape, the significance of key battlefields, and the strategies used to conquer and defend territory.
5. Social and Demographic Trends:
Historical maps can also provide insights into population density, migration patterns, and the distribution of different ethnic groups. They reveal the impact of urbanization, the displacement of populations, and the changing demographics of various regions.
FAQs:
1. What makes a historical map valuable?
The value of a historical map depends on its age, accuracy, rarity, and the information it provides. Maps created by prominent cartographers, those depicting significant historical events, or those showcasing unique perspectives on the world are particularly valuable.
2. How can I find historical maps?
Historical maps can be found in libraries, archives, museums, and online repositories. Many institutions offer digitized collections of historical maps, making them accessible to a wider audience.
3. What are the different types of historical maps?
Historical maps encompass a wide range of categories, including:
- Political maps: Depicting national boundaries, territories, and administrative divisions.
- Thematic maps: Focusing on specific themes like population density, climate, or resource distribution.
- Military maps: Depicting battlefields, troop movements, and fortifications.
- Nautical maps: Charting coastlines, sea routes, and important navigational features.
- Atlases: Collections of maps bound together in a single volume.
4. How can I interpret historical maps?
Interpreting historical maps requires an understanding of the context in which they were created. It is important to consider:
- The mapmaker’s perspective: Their biases, beliefs, and motivations can influence the map’s content.
- The intended audience: Maps were often created for specific purposes, and their interpretation should reflect this.
- The available technology: The accuracy of historical maps was limited by the tools and techniques available at the time.
Tips for Using Historical Maps:
- Compare and contrast different maps: Examining multiple maps from different periods can reveal changes in political boundaries, trade routes, and cultural landscapes.
- Consider the map’s scale: The scale of a map determines its level of detail and the information it can convey.
- Pay attention to the map’s legend: The legend provides information about the symbols, colors, and other features used on the map.
- Research the map’s creator: Understanding the mapmaker’s background, purpose, and biases can enhance your interpretation of the map.
Conclusion:
Historical maps serve as powerful tools for understanding the past, providing a unique perspective on the evolution of human civilization, the interplay of cultures, and the complex tapestry of events that have shaped our world. They are not mere static representations of the world, but dynamic records of human activity, revealing the triumphs and tragedies, the successes and failures, and the intricate dance of power and influence that have marked the course of human history. By delving into the world of historical maps, we gain a deeper understanding of the past, its complexities, and its enduring legacy on the present.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Past: The Power of Historical Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!