Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to California’s Rainfall Map
Related Articles: Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to California’s Rainfall Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to California’s Rainfall Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to California’s Rainfall Map
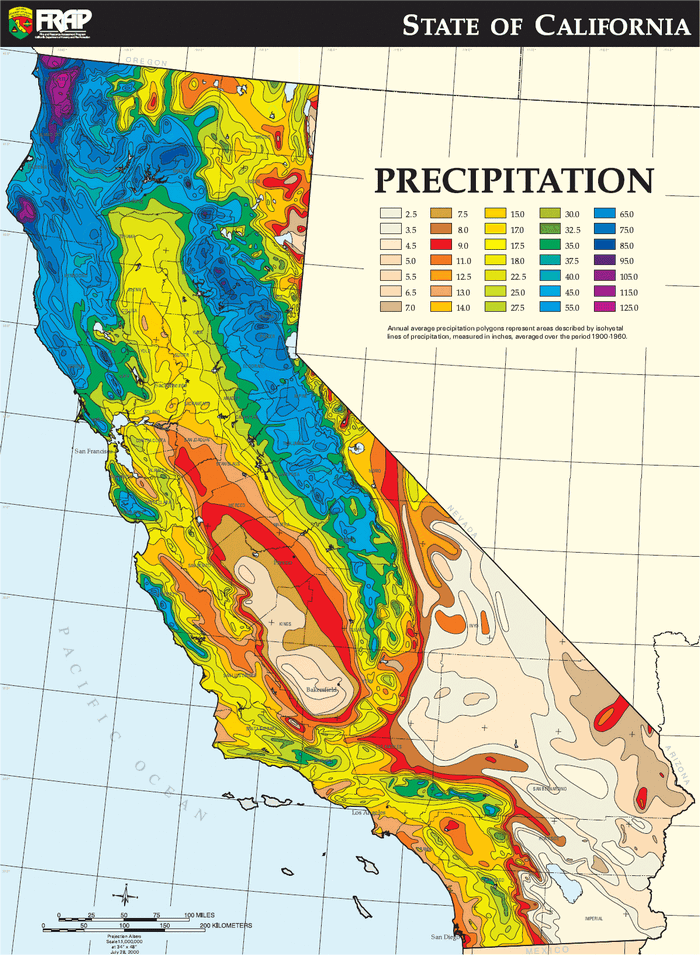
California, a state renowned for its diverse landscapes and vibrant ecosystems, is heavily reliant on precipitation. Understanding the distribution and variability of rainfall across the state is crucial for managing water resources, planning agricultural activities, and mitigating the impacts of drought. This article delves into the intricacies of California’s rainfall map, exploring its significance and providing insights into the factors that influence its patterns.
The Importance of a Rainfall Map
A rainfall map is a visual representation of precipitation levels across a geographic area. In the context of California, these maps serve as vital tools for:
- Water Resource Management: By illustrating regional variations in rainfall, the maps help water managers understand water availability and make informed decisions regarding allocation, storage, and distribution.
- Agricultural Planning: Farmers rely on rainfall data to optimize planting schedules, irrigation strategies, and crop selection, ensuring efficient water use and maximizing yields.
- Drought Monitoring and Response: Rainfall maps provide a clear picture of drought conditions, enabling agencies to assess the severity of the situation, identify vulnerable areas, and implement appropriate mitigation measures.
- Flood Prediction and Prevention: Understanding historical rainfall patterns and identifying areas prone to heavy rainfall allows for better flood prediction and the development of effective flood control strategies.
- Ecosystem Health: Rainfall patterns directly influence the health and resilience of California’s diverse ecosystems, impacting vegetation, wildlife, and overall biodiversity.
Factors Influencing Rainfall Patterns
Several factors contribute to the distinct rainfall patterns observed on California’s rainfall map:
- Orographic Lift: As moist air masses from the Pacific Ocean encounter the Sierra Nevada and Coast Ranges, they are forced upwards, cooling and causing condensation, leading to increased precipitation on the western slopes.
- Latitude: California’s diverse latitude spans from the subtropical south to the temperate north, resulting in variations in rainfall amounts and seasonality. Southern California generally receives less rainfall than the north.
- Ocean Currents: The California Current, a cold current flowing southward along the coast, influences coastal climates, contributing to relatively cool and wet conditions in Northern California.
- El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO): This climate pattern significantly impacts California’s rainfall. During El Niño years, the state typically experiences above-average precipitation, while La Niña years often bring below-average rainfall.
- Climate Change: The changing climate is altering rainfall patterns, leading to more intense storms, longer periods of drought, and shifts in seasonal precipitation.
Interpreting California’s Rainfall Map
The rainfall map of California typically displays precipitation data as:
- Isohyets: Lines connecting points of equal rainfall, providing a visual representation of rainfall gradients.
- Color-Coded Regions: Different colors represent distinct rainfall ranges, allowing for quick identification of areas with high, moderate, or low precipitation.
- Average Annual Rainfall: The map often includes average annual rainfall data for specific locations or regions, providing a historical context for understanding long-term rainfall trends.
Understanding Regional Variations
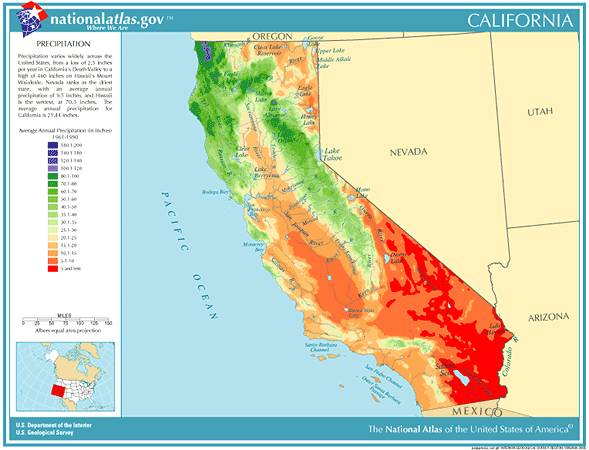
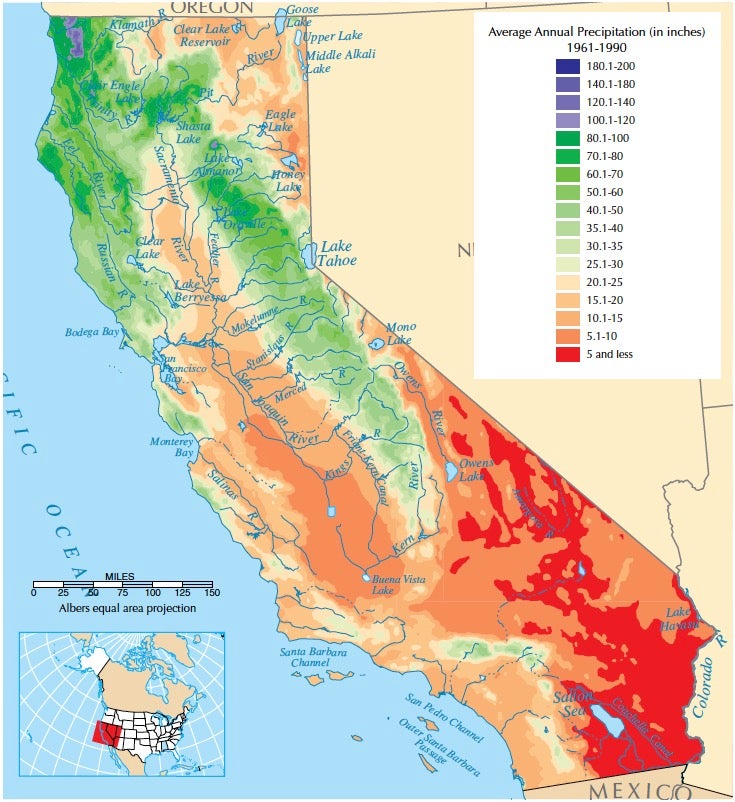
California’s rainfall map reveals significant regional variations in precipitation:
- North Coast: The north coast region receives the highest rainfall in the state, benefiting from the influence of the Pacific Ocean and the orographic lift caused by the Coast Ranges.
- Sierra Nevada: The western slopes of the Sierra Nevada experience substantial rainfall, particularly at higher elevations, due to orographic lift.
- Central Valley: The Central Valley, located between the Coast Ranges and the Sierra Nevada, receives relatively low rainfall, making it susceptible to drought.
- Southern California: Southern California generally receives the lowest rainfall in the state, with arid conditions prevalent in the desert regions.
The Importance of Data Accuracy
Accurate rainfall data is crucial for effective decision-making. Rainfall maps rely on data collected from various sources, including:
- Rain Gauges: Ground-based instruments that measure rainfall directly.
- Weather Stations: Stations equipped with rain gauges and other weather sensors that provide real-time data.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites equipped with sensors can detect rainfall from space, providing a broader view of precipitation patterns.
- Climate Models: Complex computer models that simulate atmospheric processes to predict future rainfall patterns.
FAQs about California’s Rainfall Map
Q: What is the average annual rainfall in California?
A: The average annual rainfall in California varies significantly across the state. The north coast receives the highest average rainfall, with over 60 inches per year, while Southern California averages around 10 inches.
Q: How does El Niño impact California’s rainfall?
A: During El Niño events, warmer waters in the central Pacific Ocean lead to increased atmospheric moisture and a shift in the jet stream, resulting in above-average rainfall in California.
Q: How does climate change affect rainfall patterns in California?
A: Climate change is causing shifts in rainfall patterns, leading to more intense storms, longer periods of drought, and changes in the timing and distribution of precipitation.
Q: What are some strategies for managing water resources in California?
A: Water resource management strategies include:
- Water Conservation: Implementing measures to reduce water use in homes, businesses, and agriculture.
- Water Storage: Building reservoirs and expanding groundwater storage capacity.
- Water Recycling: Treating and reusing wastewater for irrigation and other purposes.
- Water Transfer: Moving water from areas of surplus to areas of deficit.
Tips for Using a Rainfall Map
- Consider the time scale: Rainfall maps can depict average annual rainfall, seasonal rainfall, or rainfall for a specific period.
- Understand the data source: The accuracy of a rainfall map depends on the quality of the data used.
- Compare data with historical trends: Analyzing historical rainfall data can provide insights into long-term patterns and potential changes.
- Use rainfall maps in conjunction with other data sources: Combining rainfall maps with information on soil types, vegetation, and water use patterns can provide a more comprehensive understanding of water resources.
Conclusion
California’s rainfall map is a valuable tool for understanding the state’s precipitation patterns and their implications for water resources, agriculture, and ecosystem health. By analyzing the map, we can gain insights into the factors that influence rainfall, identify areas of high and low precipitation, and make informed decisions regarding water management and drought mitigation. As climate change continues to alter rainfall patterns, it becomes increasingly important to utilize rainfall maps effectively to ensure the sustainability of California’s water resources and ecosystems.





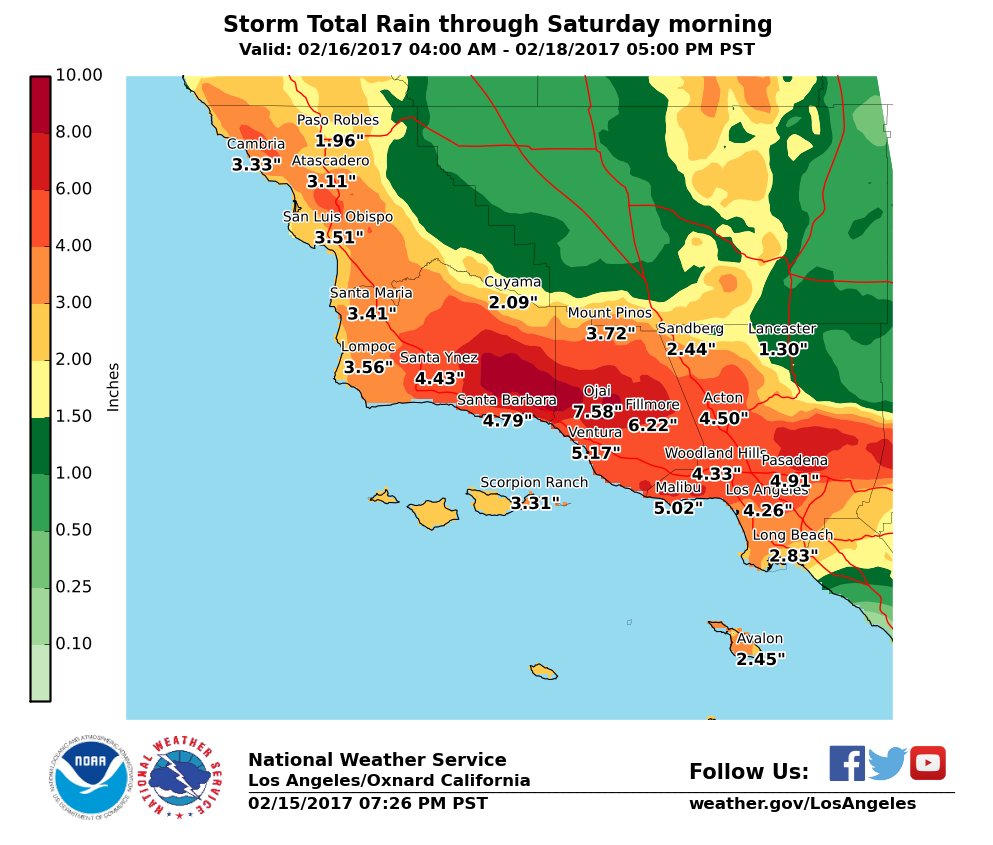
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to California’s Rainfall Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!