Delving into the Depths: Understanding Florida’s Aquifer System
Related Articles: Delving into the Depths: Understanding Florida’s Aquifer System
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Depths: Understanding Florida’s Aquifer System. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Delving into the Depths: Understanding Florida’s Aquifer System
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Delving into the Depths: Understanding Florida’s Aquifer System
- 3.1 Mapping the Underground Waterscape: A Glimpse into Florida’s Aquifer System
- 3.2 Unraveling the Importance of Florida’s Aquifers
- 3.3 Understanding the Challenges: Threats to Florida’s Aquifers
- 3.4 Navigating the Future: Strategies for Sustainable Water Management
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions about Florida’s Aquifer System
- 3.6 Tips for Responsible Groundwater Use in Florida
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Call for Action
- 4 Closure
Delving into the Depths: Understanding Florida’s Aquifer System

Florida, known for its sunny beaches and vibrant ecosystems, relies heavily on a hidden treasure: its vast aquifer system. This network of underground water reservoirs, known as aquifers, plays a vital role in sustaining the state’s diverse population, agriculture, and natural environments. Understanding the intricate workings of these aquifers is crucial for ensuring responsible water management and safeguarding Florida’s future.
Mapping the Underground Waterscape: A Glimpse into Florida’s Aquifer System
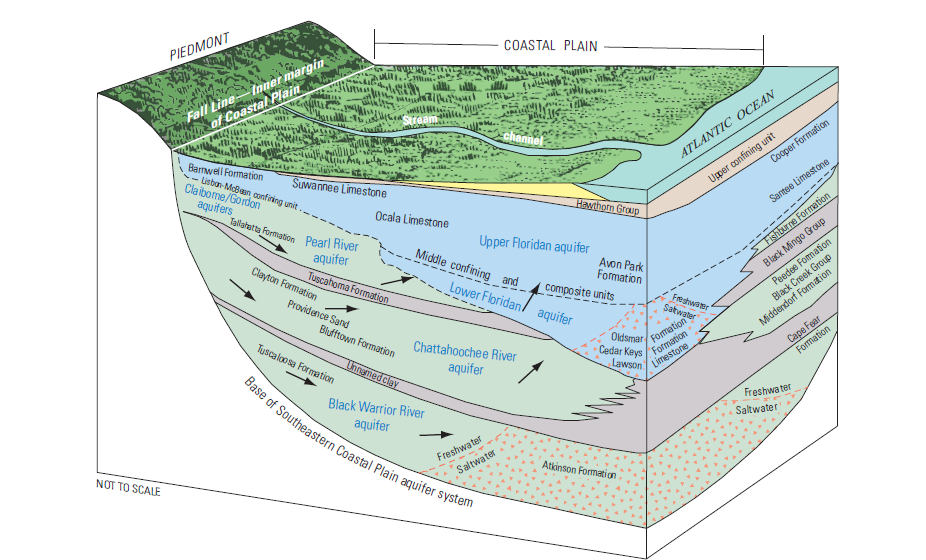
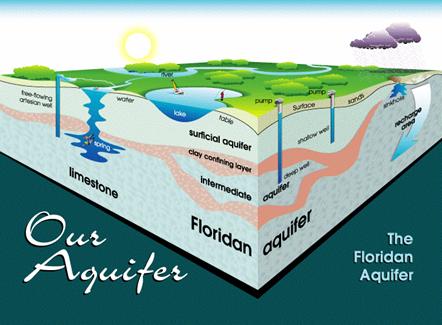
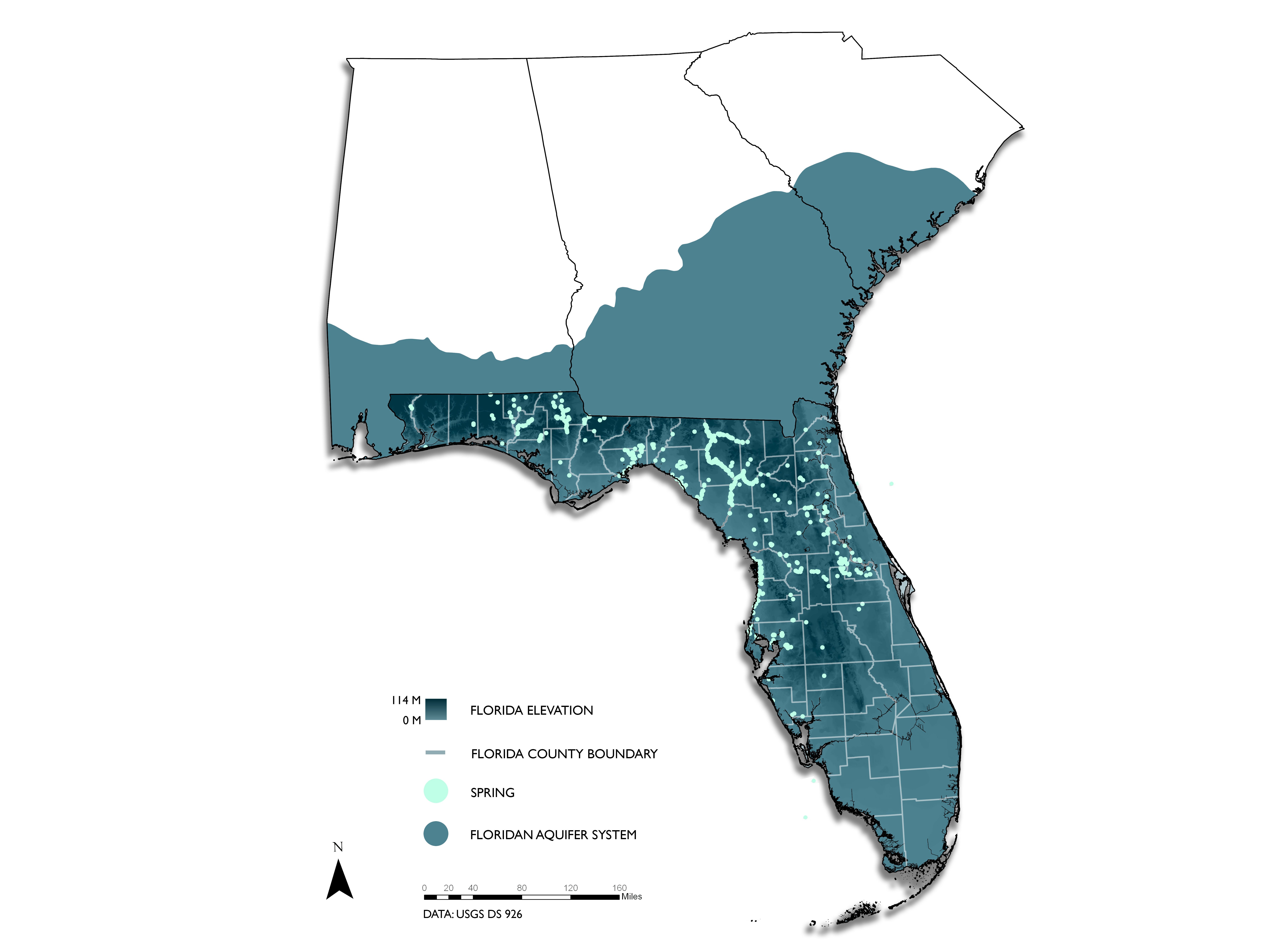
Florida’s aquifer system is composed of several distinct layers, each with unique characteristics and contributions to the state’s water supply. The primary aquifers, from top to bottom, are:
-
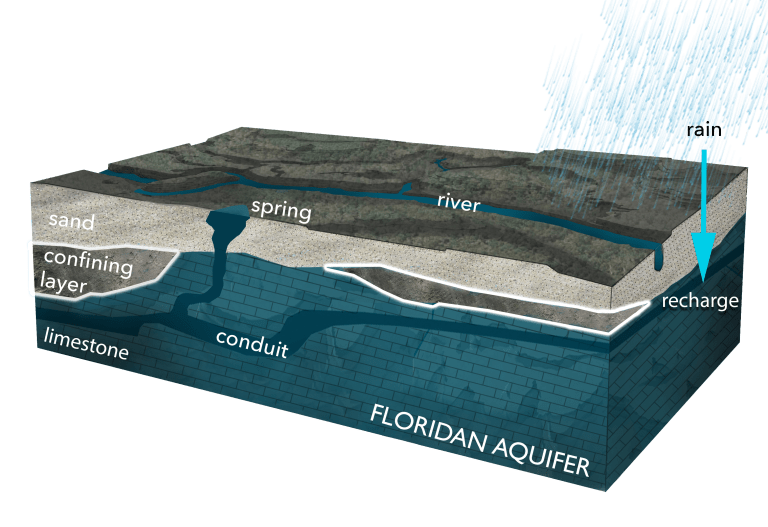
The Floridan Aquifer: This massive, interconnected system, spanning across much of Florida, is the state’s primary source of groundwater. It is composed of limestone and dolomite, highly porous and permeable rocks that readily store and transmit water. The Floridan Aquifer is further subdivided into two units: the Upper Floridan Aquifer, a major source of drinking water, and the Lower Floridan Aquifer, which provides water for irrigation and industrial uses.
-
The Biscayne Aquifer: Primarily found in South Florida, this aquifer is a vital source of drinking water for the region’s densely populated areas. It is composed of porous limestone and sand, making it vulnerable to saltwater intrusion, particularly in coastal areas.
-
The Surficial Aquifers: These shallow aquifers, located near the surface, are composed of sand, clay, and gravel. They are typically used for irrigation and domestic purposes, but their limited capacity makes them more susceptible to pollution and depletion.
Unraveling the Importance of Florida’s Aquifers
The Florida aquifer system is not just a reservoir of water; it is the lifeblood of the state. Its importance can be summarized in several key areas:
-
Drinking Water Supply: Aquifers are the primary source of drinking water for millions of Floridians. They provide a safe and reliable supply, particularly in areas where surface water sources are limited or impacted by pollution.
-
Agricultural Irrigation: Florida’s agricultural industry relies heavily on groundwater from aquifers for irrigation. This is crucial for producing a wide range of crops, from citrus fruits to vegetables, contributing significantly to the state’s economy.
-
Environmental Sustainability: Aquifers play a crucial role in maintaining Florida’s diverse ecosystems. They sustain wetlands, springs, and rivers, providing habitat for a vast array of flora and fauna.
-
Economic Growth: The availability of reliable water resources from aquifers is a key factor in attracting businesses and industries to Florida. This contributes to the state’s economic growth and development.
Understanding the Challenges: Threats to Florida’s Aquifers
Despite their importance, Florida’s aquifers face several challenges:
-
Overpumping: Excessive withdrawal of groundwater can lead to aquifer depletion, lowering water levels and potentially causing land subsidence. This can negatively impact water supply, agriculture, and natural ecosystems.
-
Pollution: Contamination from various sources, including agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and sewage leaks, can degrade the quality of groundwater, making it unfit for drinking or other uses.
-
Saltwater Intrusion: In coastal areas, overpumping can draw saltwater from the ocean into freshwater aquifers, rendering them unusable for drinking or irrigation.
-
Climate Change: Sea level rise and changes in rainfall patterns can exacerbate existing challenges, increasing the risk of saltwater intrusion and aquifer depletion.
Navigating the Future: Strategies for Sustainable Water Management
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach to water management, emphasizing sustainability and conservation:
-
Water Conservation: Implementing water-saving measures in homes, businesses, and agricultural practices can significantly reduce the demand on aquifers.
-
Water Reuse: Utilizing treated wastewater for irrigation and other purposes can alleviate the pressure on groundwater resources.
-
Aquifer Recharge: Replenishing aquifers through artificial recharge projects, such as injecting treated wastewater or surface water, can help maintain water levels and mitigate depletion.
-
Monitoring and Regulation: Establishing rigorous monitoring programs to track aquifer levels and water quality, along with appropriate regulations to control groundwater extraction and pollution, are crucial for protecting this vital resource.
Frequently Asked Questions about Florida’s Aquifer System
1. How does the Floridan Aquifer differ from the Biscayne Aquifer?
The Floridan Aquifer is a vast, interconnected system spanning across much of Florida, while the Biscayne Aquifer is primarily found in South Florida. The Floridan Aquifer is composed of limestone and dolomite, while the Biscayne Aquifer is composed of porous limestone and sand. The Floridan Aquifer is generally deeper than the Biscayne Aquifer and is less susceptible to saltwater intrusion.
2. What are the main sources of pollution affecting Florida’s aquifers?
Pollution sources can be categorized as point sources, such as industrial discharges or sewage leaks, and non-point sources, such as agricultural runoff or urban stormwater. Agricultural runoff containing fertilizers and pesticides is a significant contributor to aquifer contamination.
3. How can I conserve water and help protect Florida’s aquifers?
Simple water-saving measures at home can make a difference. These include using low-flow showerheads and toilets, watering lawns efficiently, and fixing leaks promptly. Supporting policies that promote water conservation and sustainable water management practices can also contribute to aquifer protection.
4. What is the role of the Florida Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) in aquifer management?
The DEP plays a crucial role in regulating groundwater use and protecting water quality. They set standards for water quality, monitor aquifer levels and pollution, and issue permits for groundwater withdrawals.
5. What are the long-term implications of overpumping aquifers?
Overpumping can lead to aquifer depletion, lowering water levels and potentially causing land subsidence. This can negatively impact water supply, agriculture, and natural ecosystems. In coastal areas, overpumping can also lead to saltwater intrusion, rendering aquifers unusable.
Tips for Responsible Groundwater Use in Florida
- Conserve water: Implement water-saving measures in your home and garden, such as using low-flow appliances and watering lawns efficiently.
- Support water conservation policies: Advocate for policies that promote water conservation and sustainable water management practices.
- Be aware of potential sources of pollution: Avoid using harmful chemicals in your yard and dispose of hazardous materials responsibly.
- Report any suspected pollution or water quality issues: Contact your local water management district or the Florida Department of Environmental Protection.
Conclusion: A Call for Action
Florida’s aquifer system is a precious resource that must be carefully managed for the benefit of present and future generations. Understanding the complexities of this underground water network, recognizing the threats it faces, and implementing sustainable water management strategies are crucial for ensuring the long-term health and prosperity of the state. By embracing responsible water use and supporting policies that protect aquifers, we can ensure that this vital resource continues to sustain Florida’s vibrant ecosystems, thriving economy, and diverse population for years to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Depths: Understanding Florida’s Aquifer System. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!