Illuminating the World: Understanding Day and Night Maps
Related Articles: Illuminating the World: Understanding Day and Night Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Illuminating the World: Understanding Day and Night Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Illuminating the World: Understanding Day and Night Maps

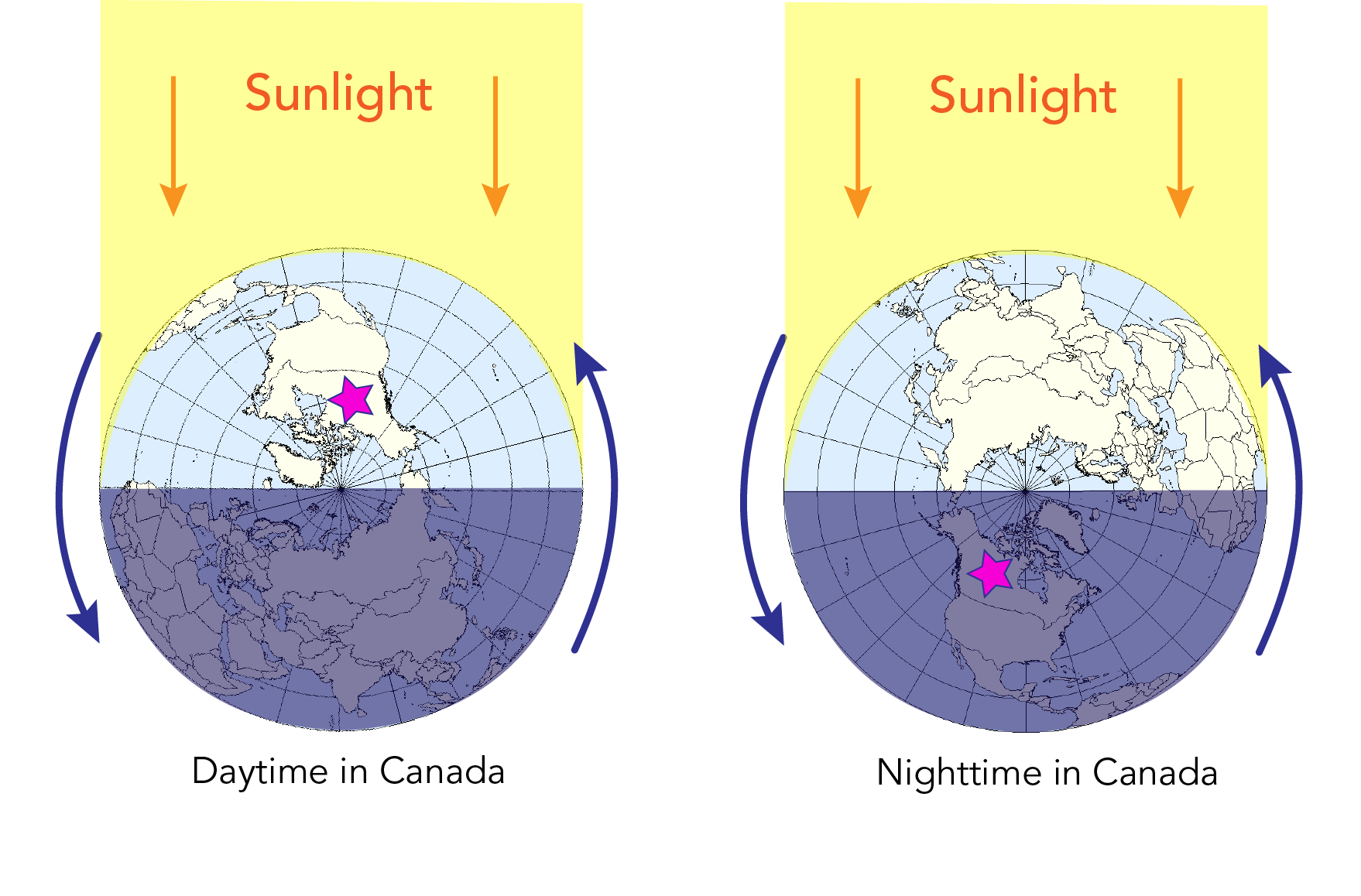
The Earth’s constant rotation on its axis, coupled with its orbit around the sun, creates the cyclical phenomenon of day and night. This fundamental aspect of our planet’s existence is visually represented through day and night maps, powerful tools that depict the distribution of sunlight across the globe at a specific moment in time. These maps offer a unique perspective on our world, highlighting the interplay of light and darkness and revealing the dynamic nature of our planet.
Delving into the Depiction of Light and Shadow
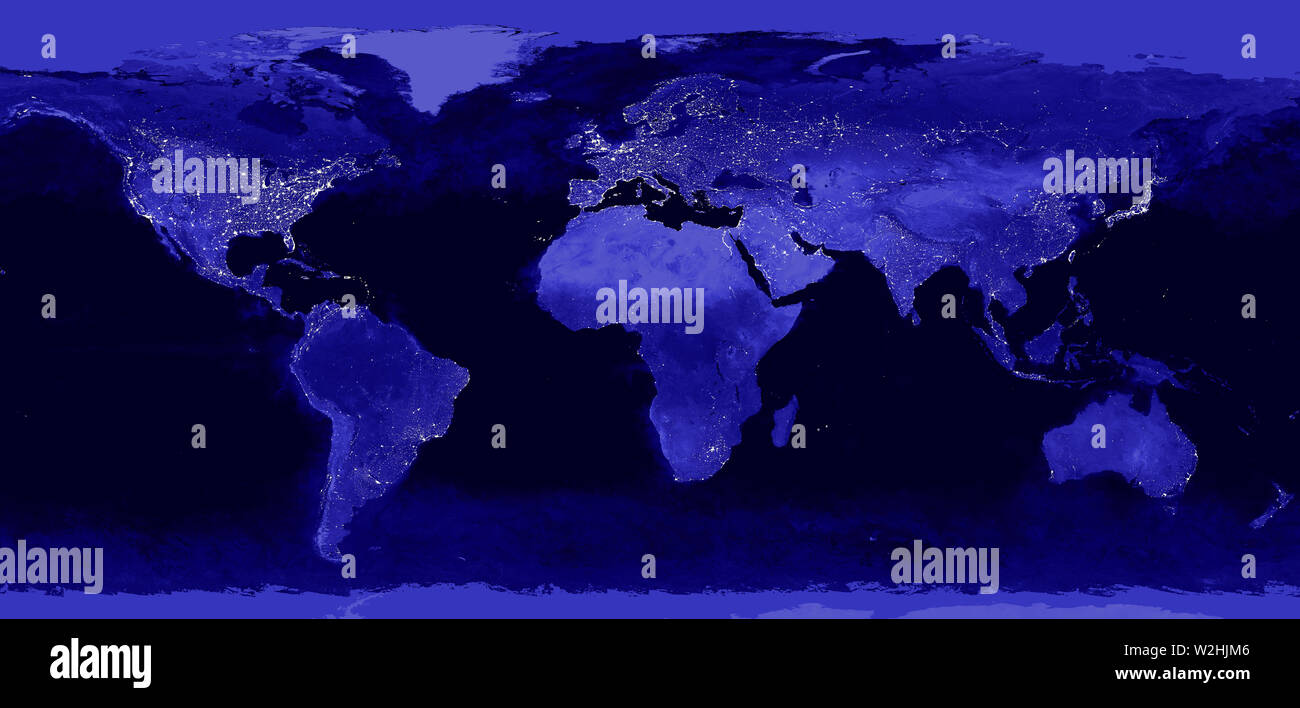
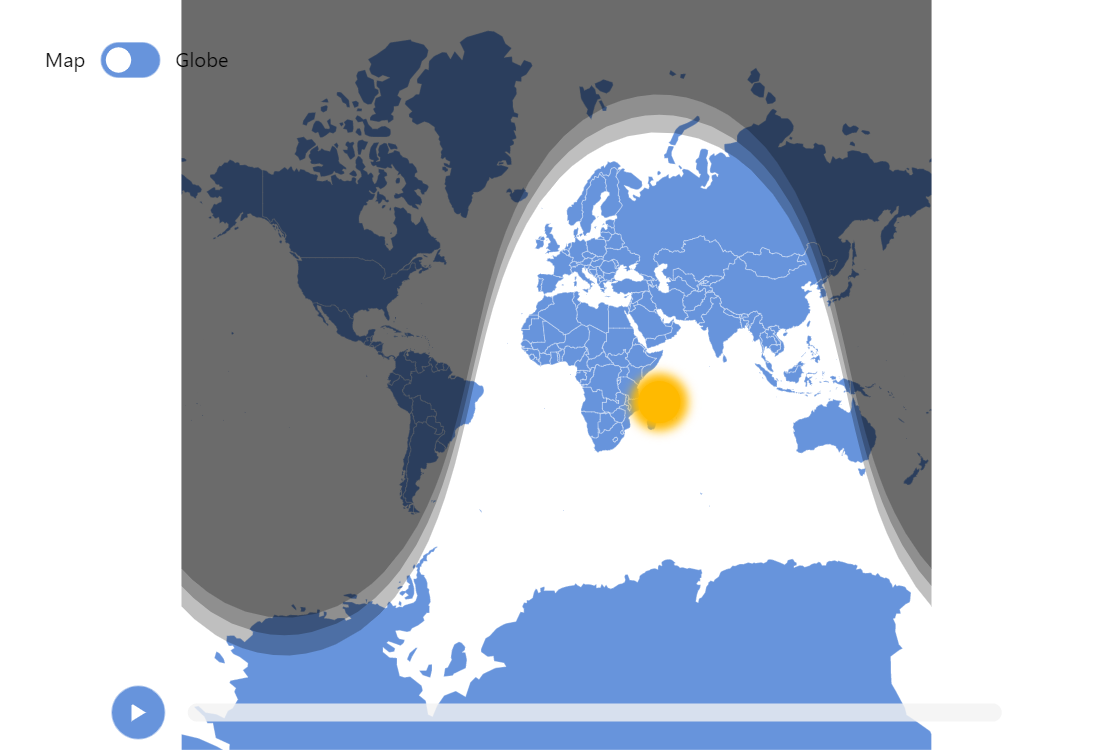
Day and night maps, often referred to as terminator maps, are visual representations of the line separating day and night, known as the terminator. This line, a great circle on the Earth’s surface, divides the illuminated hemisphere (daytime) from the shadowed hemisphere (nighttime). The terminator’s position continuously shifts as the Earth rotates, creating a dynamic boundary between light and darkness.
These maps typically employ a color scheme where the illuminated portion of the globe is depicted in shades of white, yellow, or orange, symbolizing sunlight. Conversely, the shadowed region is represented in shades of blue or purple, signifying the absence of direct sunlight. The terminator itself is often illustrated as a distinct line, marking the transition between the two hemispheres.
The Science Behind the Visualization
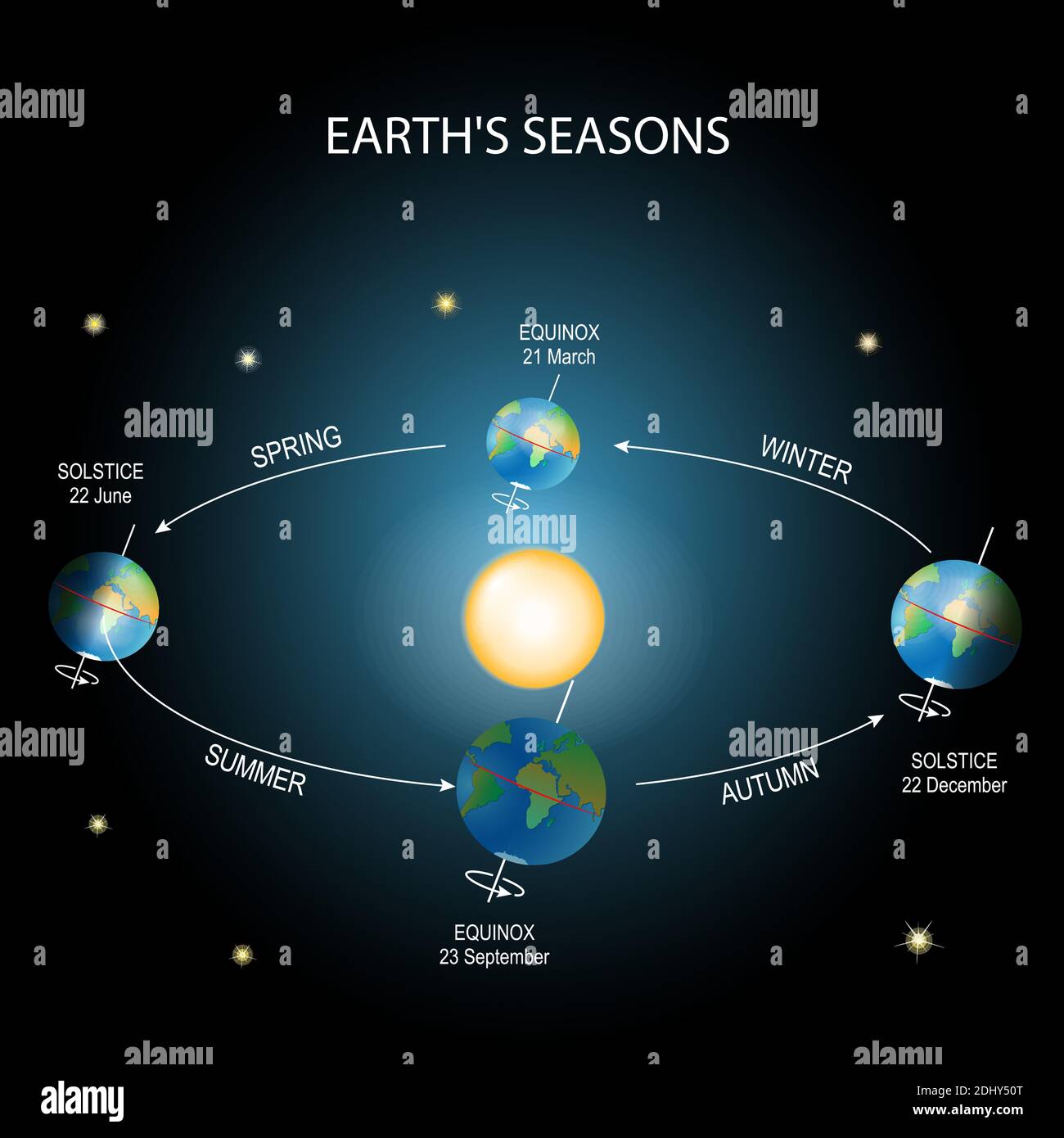
The creation of day and night maps relies on fundamental astronomical principles. The Earth’s rotation on its axis, completing one full rotation approximately every 24 hours, is the primary driver of the day-night cycle. The Earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of approximately 23.5 degrees relative to its orbital plane, leading to the varying lengths of day and night throughout the year. This tilt is responsible for the seasons, with different hemispheres experiencing longer days during their respective summers and shorter days during their winters.
The terminator’s position is directly influenced by the Earth’s rotation and the angle of the sun’s rays. During the equinoxes, when the sun’s rays fall directly on the equator, the terminator passes through both poles, dividing the Earth into two equal halves. As the Earth moves through its annual orbit, the terminator shifts, leading to longer days in one hemisphere and shorter days in the other.
Beyond the Visual: Understanding the Implications
Day and night maps serve as more than just visual representations of the Earth’s rotation. They offer a deeper understanding of various interconnected phenomena, including:
- Time Zones: The terminator’s movement across the globe directly influences the establishment of time zones. As the Earth rotates, different regions enter and exit daylight hours, necessitating the implementation of standardized time zones to ensure efficient communication and coordination.
- Solar Energy Potential: Day and night maps play a crucial role in assessing the potential for solar energy generation. By highlighting the duration of sunlight in different regions, these maps enable the determination of optimal locations for solar power plants.
- Satellite Operations: Day and night maps are essential for planning satellite missions. Understanding the timing of daylight and darkness is crucial for optimizing satellite orbits and ensuring proper functioning of instruments.
- Weather Patterns: The terminator’s movement can influence weather patterns. The transition between day and night affects atmospheric temperatures and wind currents, contributing to the formation of weather phenomena.
- Animal Behavior: Many animals exhibit diurnal or nocturnal behavior, adapting their activities to the presence or absence of sunlight. Day and night maps provide insights into the timing of these behaviors and their ecological significance.
Unveiling the Power of Visualization
Day and night maps offer a powerful tool for visualizing the complex interplay of celestial mechanics and Earth’s rotation. They provide a tangible representation of the dynamic nature of our planet, highlighting the constant movement and change that shape our world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What causes the day-night cycle?
A: The Earth’s rotation on its axis, taking approximately 24 hours to complete one full rotation, is the primary cause of the day-night cycle. As the Earth rotates, different regions face the sun, experiencing daylight, while other regions face away from the sun, experiencing night.
Q: Why is the terminator not always a straight line?
A: The terminator is not always a straight line due to the Earth’s tilt on its axis. This tilt causes the sun’s rays to fall at different angles on different parts of the Earth throughout the year, resulting in a curved terminator.
Q: How do day and night maps help in understanding time zones?
A: Day and night maps illustrate the movement of the terminator across the globe, which directly influences the establishment of time zones. As different regions enter and exit daylight hours, standardized time zones are implemented to ensure efficient communication and coordination.
Q: Can day and night maps be used to predict solar energy potential?
A: Yes, day and night maps are crucial for assessing the potential for solar energy generation. By highlighting the duration of sunlight in different regions, these maps enable the determination of optimal locations for solar power plants.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing Day and Night Maps
- Pay attention to the date and time: Day and night maps depict the distribution of sunlight at a specific moment in time. Ensure you are referencing the correct date and time for accurate interpretation.
- Consider the Earth’s tilt: The Earth’s tilt on its axis significantly impacts the terminator’s position and the length of day and night. Be mindful of the tilt’s influence when analyzing day and night maps.
- Explore interactive maps: Interactive day and night maps allow for dynamic exploration, enabling you to adjust the date and time to observe the terminator’s movement.
- Relate to real-world phenomena: Utilize day and night maps to understand real-world phenomena like time zones, satellite operations, and animal behavior.
Conclusion
Day and night maps provide a visual representation of the Earth’s rotation and the distribution of sunlight across the globe. These maps serve as powerful tools for understanding various interconnected phenomena, including time zones, solar energy potential, and animal behavior. By visualizing the dynamic interplay of light and darkness, day and night maps offer a deeper appreciation for the complexity and interconnectedness of our planet. They serve as a reminder of the continuous movement and change that shape our world, illuminating the intricacies of our existence.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Illuminating the World: Understanding Day and Night Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!