Latvia on the World Map: A Baltic Jewel with a Rich History and Vibrant Present
Related Articles: Latvia on the World Map: A Baltic Jewel with a Rich History and Vibrant Present
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Latvia on the World Map: A Baltic Jewel with a Rich History and Vibrant Present. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Latvia on the World Map: A Baltic Jewel with a Rich History and Vibrant Present

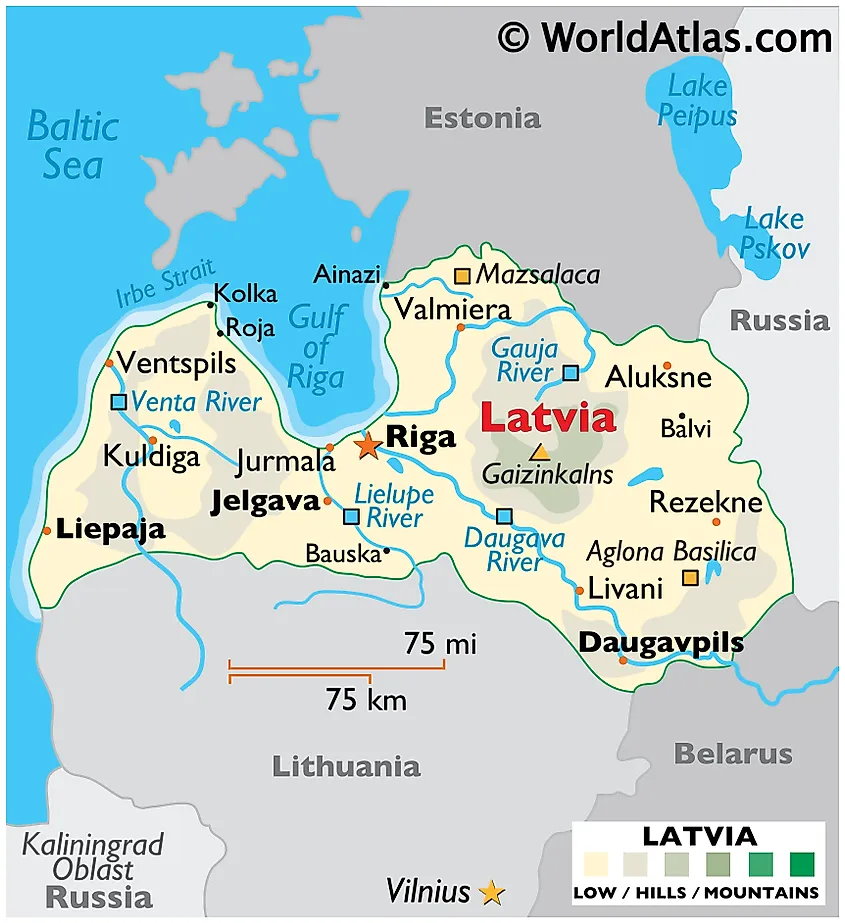
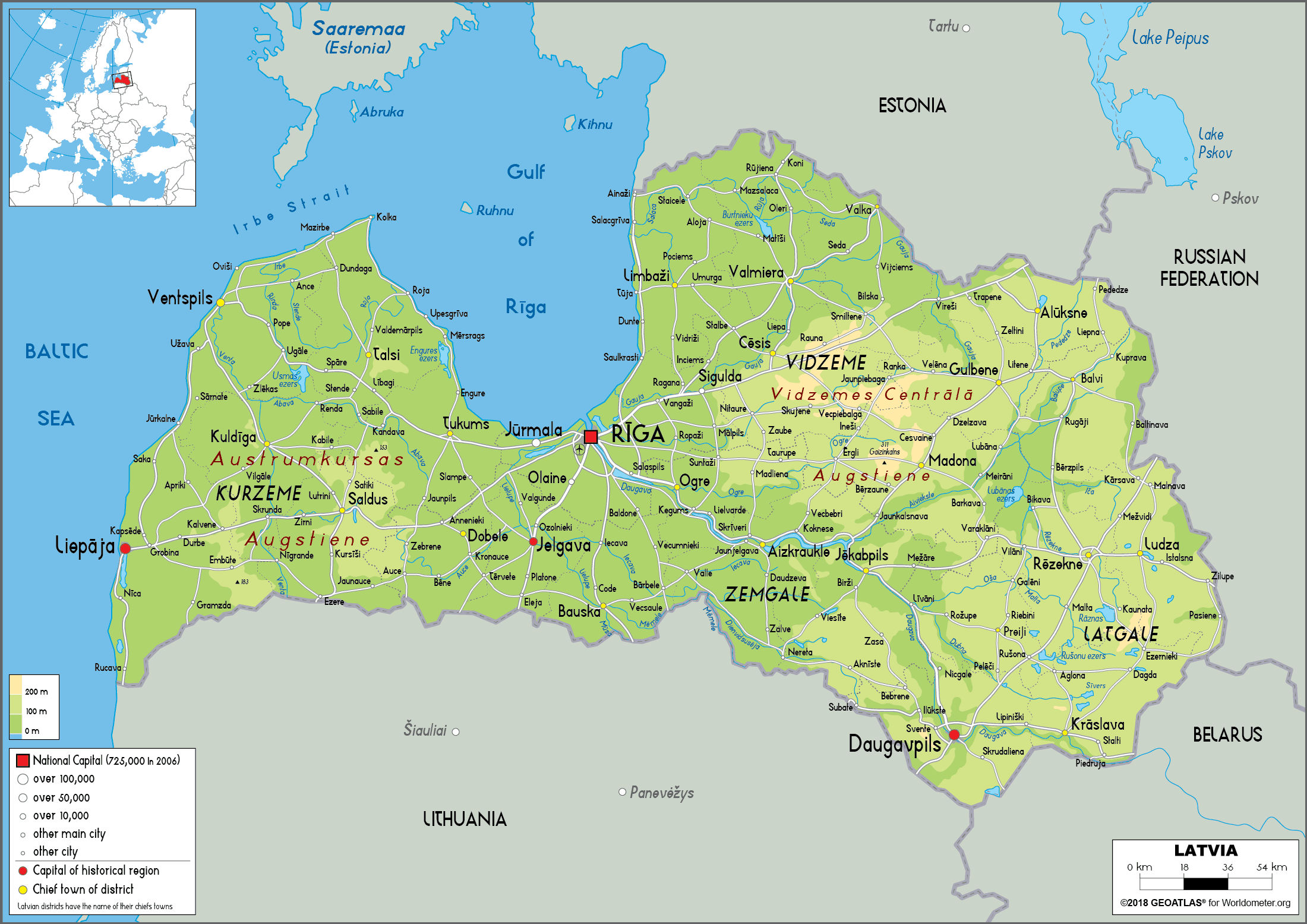
Latvia, a small yet captivating nation nestled in the heart of the Baltic region, holds a unique position on the world map. Its strategic location, bordering both the Baltic Sea and its neighbors Estonia and Lithuania, has shaped its history and continues to influence its present. Understanding Latvia’s place on the world map requires delving into its geographical characteristics, historical significance, cultural richness, and economic potential.
Geographical Significance:
Latvia occupies a relatively small area of 64,589 square kilometers, making it one of the smaller countries in Europe. Despite its size, Latvia possesses a diverse landscape, ranging from the rolling hills of Vidzeme to the sandy shores of the Baltic Sea. The Daugava River, the longest river in Latvia, flows through the country, providing a vital waterway and contributing to the nation’s agricultural output.
Latvia’s location on the eastern edge of the Baltic Sea has played a crucial role in its history. The sea provided access to trade routes, fostering cultural exchange and economic prosperity. The coastline also offers stunning natural beauty, attracting tourists and contributing to the country’s tourism industry.
Historical Context:
Latvia’s history is intertwined with the broader narrative of the Baltic region. The country has witnessed periods of independence, foreign rule, and ultimately, the re-establishment of its sovereignty.
- Early History: The territory of Latvia was inhabited by various Baltic tribes, including the Latgallians, Semigallians, and Couronians. These tribes engaged in agriculture and fishing, developing a distinct cultural identity.
- Foreign Rule: From the 13th century onwards, Latvia was subjected to foreign rule, first by the Livonian Order and later by Sweden, Poland, and Russia. This period saw the introduction of Christianity and the development of urban centers.
- Independence: Latvia declared its independence in 1918, after the collapse of the Russian Empire. This period marked a golden age for Latvian culture and economy, with significant progress in education, infrastructure, and arts.
- Soviet Era: In 1940, Latvia was annexed by the Soviet Union, marking the beginning of a period of suppression and political oppression.
- Re-Independence: Latvia regained its independence in 1991, following the collapse of the Soviet Union. This period saw a rapid transition to a democratic society and market economy.
Cultural Identity:
Latvia boasts a vibrant cultural heritage, deeply rooted in its history and traditions. The country’s folk music, dance, and crafts are renowned for their unique character and beauty. Latvian literature, particularly the works of authors like Rainis and Aspazija, has contributed significantly to the nation’s cultural identity.
The country’s language, Latvian, belongs to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is spoken by over 1.2 million people worldwide, primarily in Latvia and its diaspora.
Economic Development:
Since regaining independence, Latvia has made significant progress in developing its economy. The country has transitioned to a market economy, with a focus on export-oriented industries, technology, and tourism.
Latvia’s strategic location, skilled workforce, and membership in the European Union and NATO have attracted foreign investment and contributed to economic growth. The country’s economy is primarily driven by the following sectors:
- Agriculture: Latvia’s fertile land supports a robust agricultural sector, producing a variety of crops, livestock, and dairy products.
- Manufacturing: The country has a strong manufacturing sector, producing a range of goods, including machinery, electronics, and textiles.
- Technology: Latvia has emerged as a hub for technology and innovation, with a growing IT sector and a strong focus on developing digital solutions.
- Tourism: Latvia’s natural beauty, historical landmarks, and vibrant culture attract tourists from around the world, contributing significantly to the economy.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its progress, Latvia faces several challenges, including:
- Demographic decline: Latvia has a declining population, which poses challenges for the economy and social services.
- Regional disparities: The country’s economic development is uneven, with a significant gap between the capital city, Riga, and other regions.
- Corruption: Corruption remains a challenge, hindering investment and economic growth.
However, Latvia also possesses significant opportunities for growth and development:
- EU membership: Latvia’s membership in the EU provides access to a large market and financial support.
- Technological advancements: The country’s focus on technology and innovation can drive economic growth and create new opportunities.
- Tourism potential: Latvia’s natural beauty and cultural heritage offer significant potential for attracting tourists.
Latvia on the World Stage:
Latvia actively participates in international organizations and initiatives, promoting its interests and contributing to global efforts. The country is a member of the European Union, NATO, the United Nations, and the World Trade Organization. Latvia’s active role in these organizations demonstrates its commitment to international cooperation and its desire to contribute to global peace and prosperity.
FAQs about Latvia:
Q1: What is the capital of Latvia?
A: The capital of Latvia is Riga, located on the banks of the Daugava River.
Q2: What is the official language of Latvia?
A: The official language of Latvia is Latvian, a Baltic language.
Q3: What is the currency of Latvia?
A: The official currency of Latvia is the euro (EUR), adopted in 2014.
Q4: What is the main religion in Latvia?
A: While Latvia has no official state religion, the majority of the population identifies as Christian, with Lutheranism being the dominant denomination.
Q5: What are some popular tourist attractions in Latvia?
A: Popular tourist attractions in Latvia include:
- Riga’s Old Town: A UNESCO World Heritage Site, showcasing medieval architecture, cobblestone streets, and charming cafes.
- Jurmala: A popular seaside resort town known for its sandy beaches and spa facilities.
- Gauja National Park: A scenic national park with stunning forests, waterfalls, and castles.
- Sigulda: A historic town known for its medieval castle ruins and scenic hiking trails.
Tips for Visiting Latvia:
- Learn a few Latvian phrases: Even a few basic phrases can go a long way in enhancing your experience.
- Explore Riga’s Old Town: Take a stroll through the charming streets, visit the Riga Cathedral, and enjoy the vibrant nightlife.
- Visit Jurmala: Relax on the sandy beaches, enjoy the spa facilities, and experience the seaside atmosphere.
- Explore the countryside: Discover the beauty of Latvia’s national parks, forests, and lakes.
- Sample local cuisine: Indulge in traditional Latvian dishes like grey pea soup, rye bread, and smoked meats.
Conclusion:
Latvia, a small nation with a rich history and vibrant culture, holds a prominent position on the world map. Its strategic location, diverse landscape, and resilient people have shaped its unique identity. From its historical struggles to its economic growth, Latvia’s journey is a testament to its adaptability and determination. As the country continues to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, its place on the world map will remain firmly secured, a beacon of Baltic resilience and cultural richness.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Latvia on the World Map: A Baltic Jewel with a Rich History and Vibrant Present. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!