Mapping the Scars: Understanding Flood Risks in West Virginia
Related Articles: Mapping the Scars: Understanding Flood Risks in West Virginia
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Scars: Understanding Flood Risks in West Virginia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Scars: Understanding Flood Risks in West Virginia
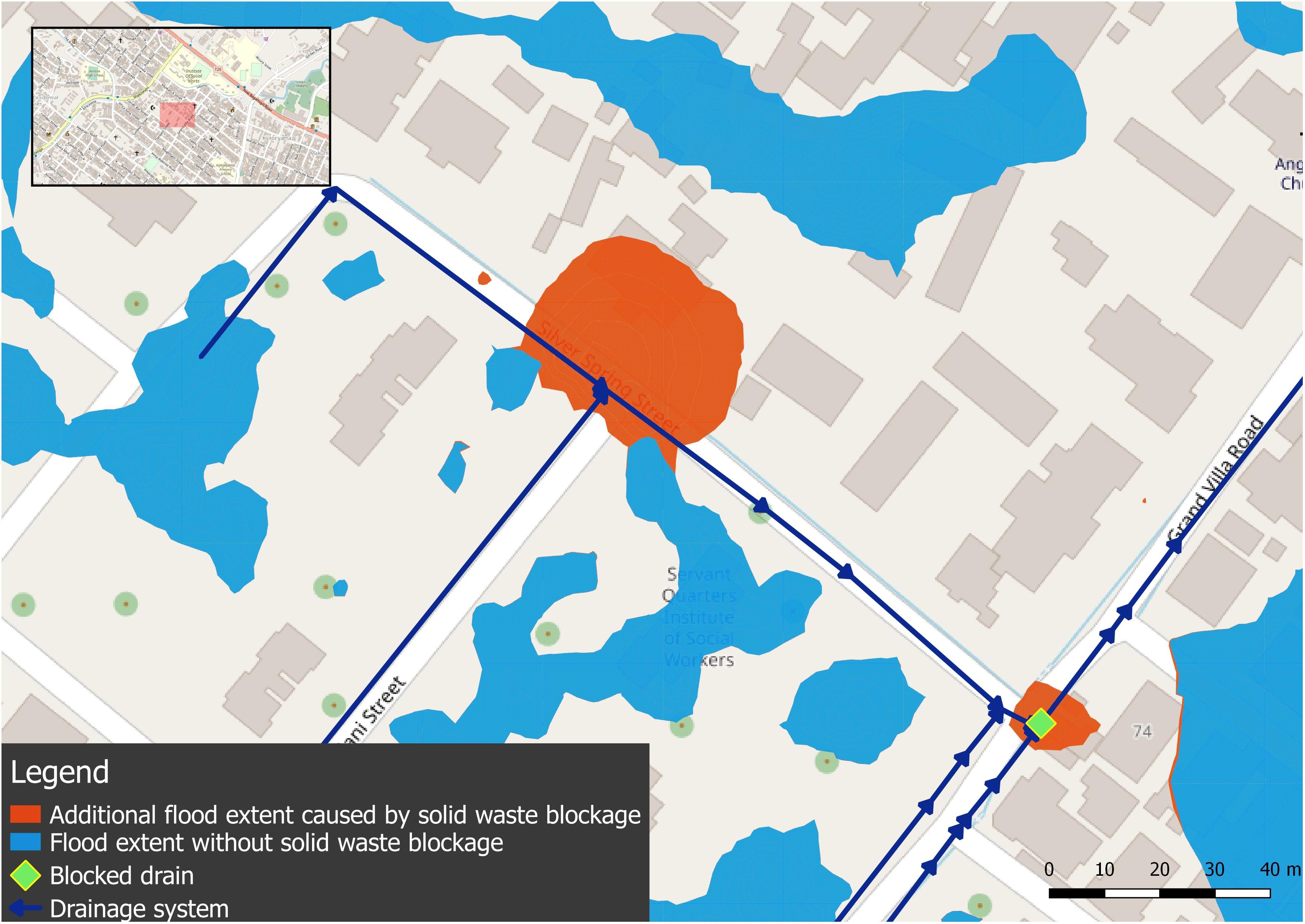
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/KGSNE4NSUFE6DHHJ6LNU72FKTY.png)
West Virginia, a state renowned for its rugged beauty and Appalachian heritage, faces a persistent threat: flooding. The state’s mountainous terrain, dense forests, and often-intense rainfall create a perfect storm for devastating floods, leaving communities vulnerable and infrastructure in ruins. Understanding the geography of flooding in West Virginia is crucial for mitigating its impact, fostering preparedness, and informing future development.
A State Shaped by Water:
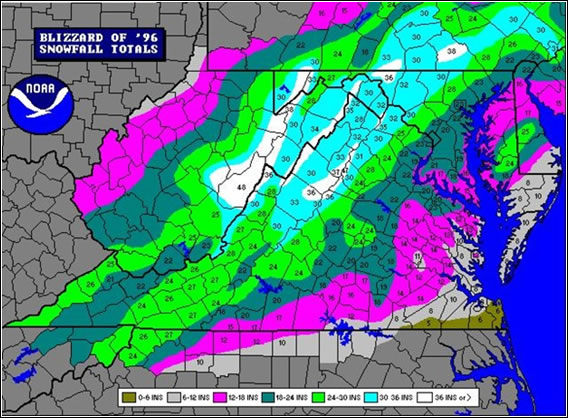
West Virginia’s topography plays a pivotal role in its susceptibility to flooding. Its numerous rivers, streams, and tributaries, carving their way through the Appalachian Mountains, act as natural conduits for water flow. The steep slopes and narrow valleys amplify the speed and volume of water rushing downstream, quickly transforming gentle streams into raging torrents. This rapid flow exacerbates the impact of rainfall, especially during intense storms or periods of snowmelt.
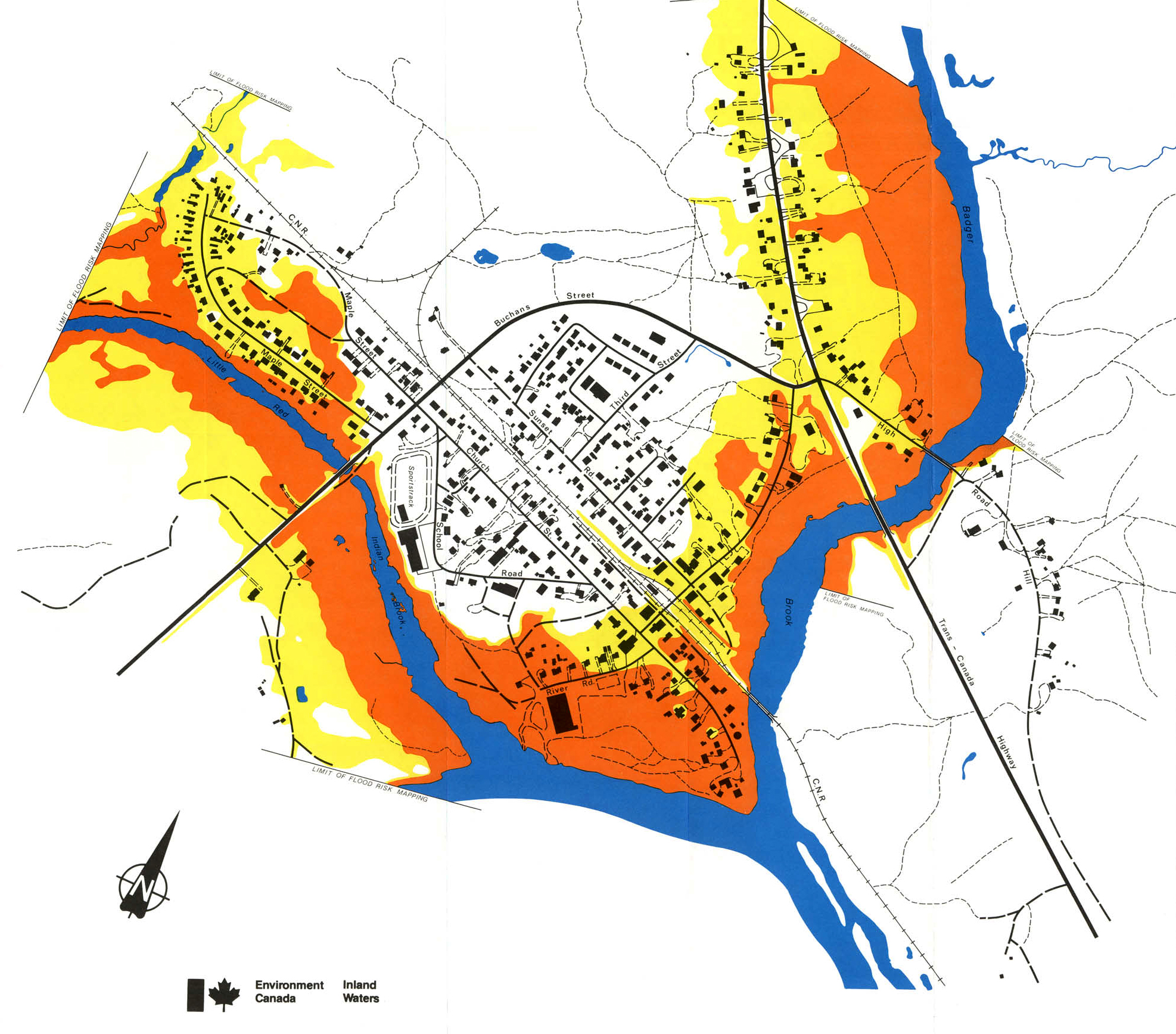
Mapping the Flood Zones:
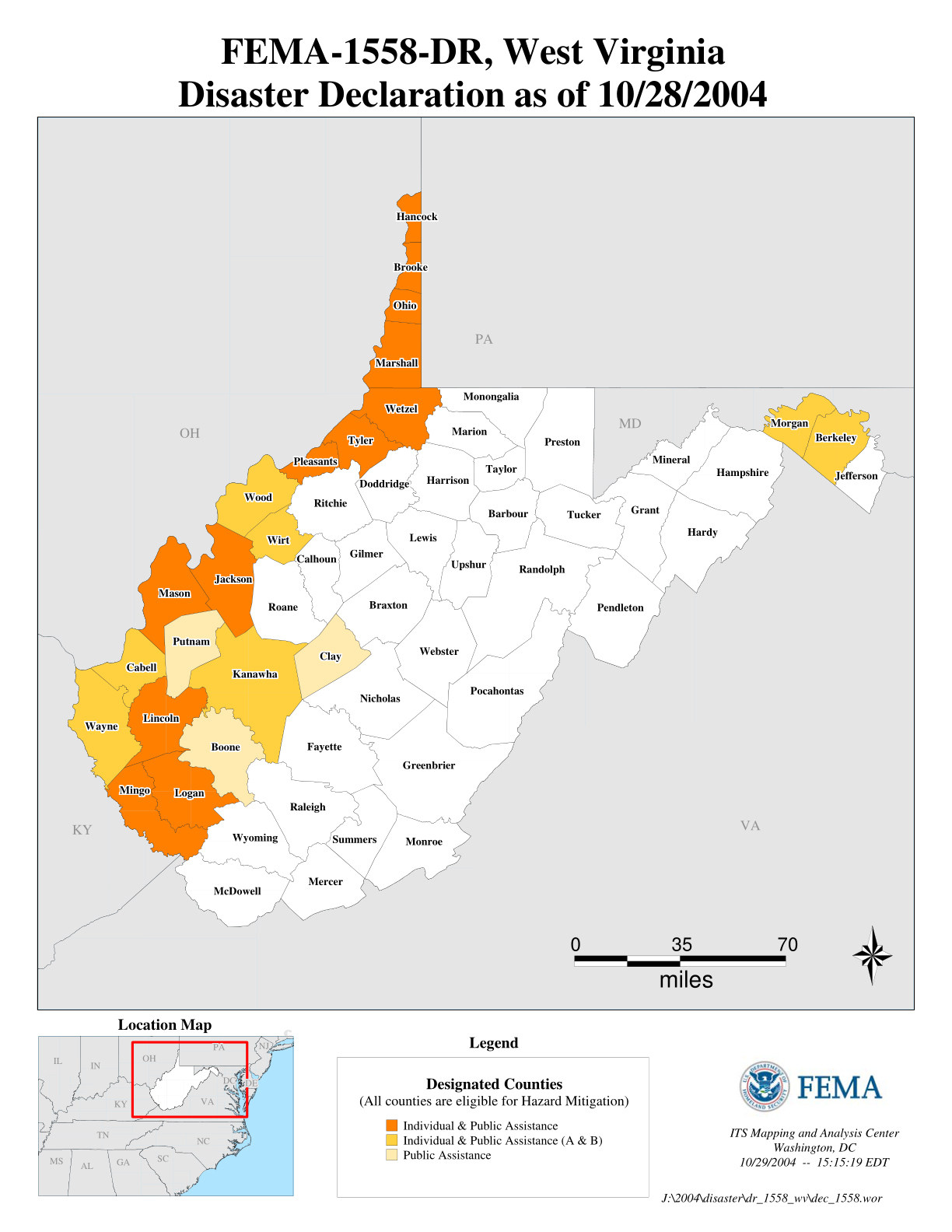
Maps serve as invaluable tools for visualizing flood risk, revealing the areas most vulnerable to inundation. These maps, often created by government agencies like the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), utilize data on historical flood events, elevation, and river flow to identify floodplains and hazard zones.
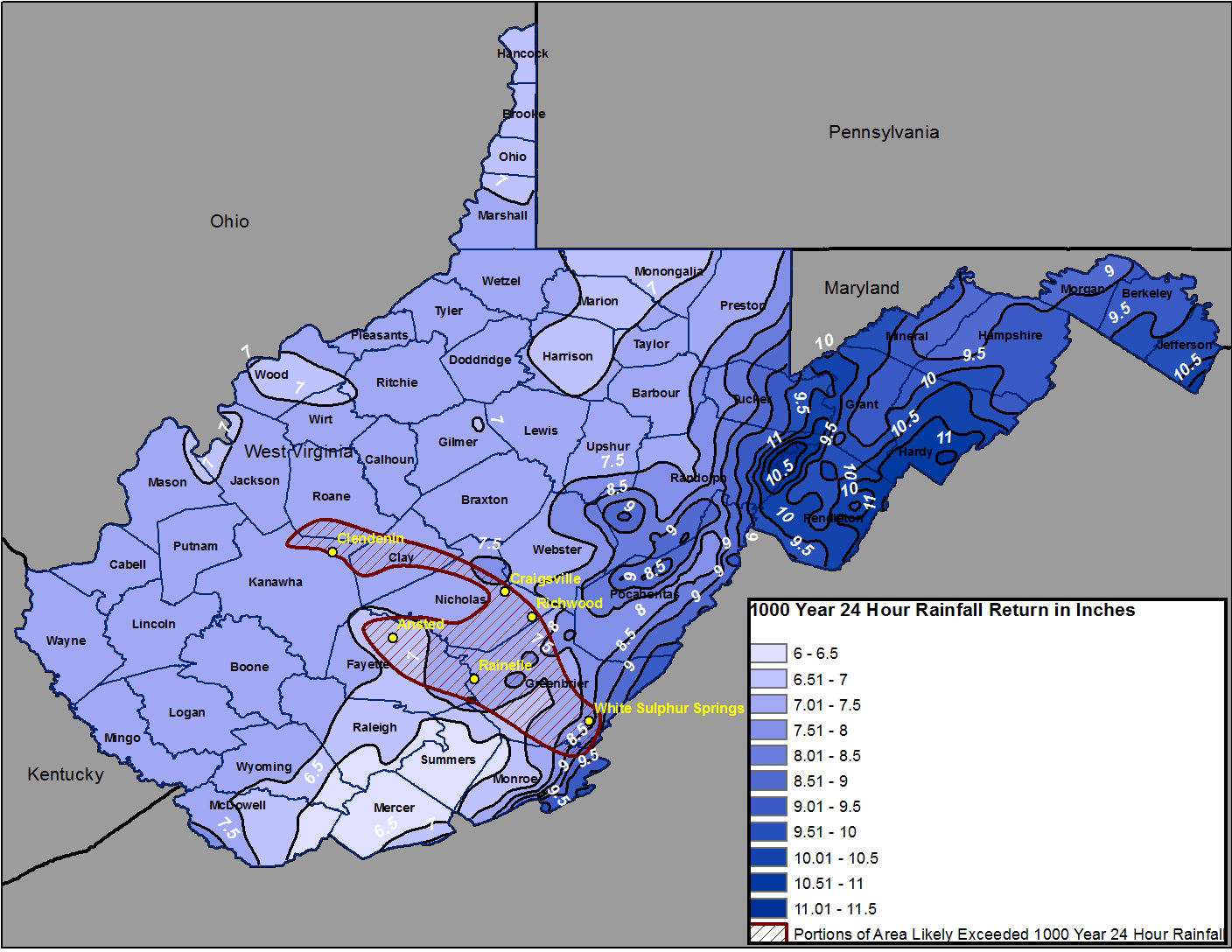
Understanding the Color Codes:
Flood hazard maps typically use color coding to delineate different levels of flood risk. For instance, areas shaded in blue may represent a 100-year floodplain, signifying a 1% chance of flooding in any given year. Areas in darker shades, like red or purple, indicate higher flood risks, suggesting a greater probability of inundation.
The Importance of Flood Maps:
Flood maps serve several critical functions:
- Risk Assessment: Maps provide a visual representation of flood risk, allowing individuals, communities, and policymakers to understand the potential dangers and prioritize mitigation efforts.
- Development Planning: By identifying flood-prone areas, maps guide responsible land use planning, preventing the construction of critical infrastructure or residential developments in high-risk zones.
- Insurance and Financing: Flood maps inform insurance premiums and loan eligibility, enabling individuals and businesses to assess their financial exposure to flooding.
- Emergency Response: Maps assist emergency responders in identifying vulnerable areas, optimizing evacuation routes, and allocating resources during flood events.
Beyond the Maps: A Multifaceted Approach to Flood Mitigation:
While maps provide valuable insights, they are just one tool in a multifaceted approach to flood mitigation. Effective flood management requires a collaborative effort involving:
- Engineering Solutions: Implementing flood control structures like dams, levees, and channels can reduce the impact of flooding by managing water flow and diverting excess water.
- Land Use Planning: Restricting development in floodplains and promoting natural floodplains can minimize flood damage and enhance the natural resilience of ecosystems.
- Early Warning Systems: Advanced weather forecasting and early warning systems allow communities to prepare for impending floods, enabling timely evacuations and reducing loss of life.
- Community Education and Preparedness: Educating residents about flood risks, promoting flood insurance, and fostering community-based preparedness plans are crucial for minimizing the impact of flooding.
FAQs About Flood Maps in West Virginia:
Q: How can I find flood maps for my area in West Virginia?
A: You can access flood maps through the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) website, the West Virginia Department of Homeland Security, and local county and municipal government websites.
Q: What does a 100-year floodplain mean?
A: A 100-year floodplain signifies a 1% chance of flooding in any given year. It does not mean that flooding will occur only once every 100 years, but rather that there is a 1% probability of flooding in any given year.
Q: Are flood maps updated regularly?
A: Flood maps are periodically updated based on new data, including historical flood events, climate change projections, and changes in land use. It is essential to consult the most recent versions of the maps for accurate information.
Q: What are the consequences of building in a floodplain?
A: Building in a floodplain poses significant risks, including potential property damage, financial losses, and even loss of life. It is crucial to consider the potential impact of flooding before making any development decisions.
Tips for Using Flood Maps in West Virginia:
- Understand your risk: Identify your property’s location relative to floodplains and hazard zones.
- Consult with local officials: Seek guidance from local government agencies regarding flood risks and regulations.
- Consider flood insurance: Obtain flood insurance if your property is located in a flood-prone area.
- Prepare for emergencies: Develop a family emergency plan, including evacuation routes and communication protocols.
- Stay informed about weather forecasts: Monitor weather reports and heed warnings about potential flooding.
Conclusion:
Flood maps are essential tools for understanding and mitigating flood risks in West Virginia. By visualizing flood-prone areas, these maps empower individuals, communities, and policymakers to make informed decisions, prioritize development, and protect lives and property. While maps are critical for assessing flood risk, they are just one component of a multifaceted approach to flood management. By integrating engineering solutions, land use planning, early warning systems, and community preparedness, West Virginia can work towards a future where flooding is not a devastating force but a manageable risk.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Scars: Understanding Flood Risks in West Virginia. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!