Mapping the Shadows: Understanding the Global History of Slavery Through Visualization
Related Articles: Mapping the Shadows: Understanding the Global History of Slavery Through Visualization
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Shadows: Understanding the Global History of Slavery Through Visualization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Shadows: Understanding the Global History of Slavery Through Visualization

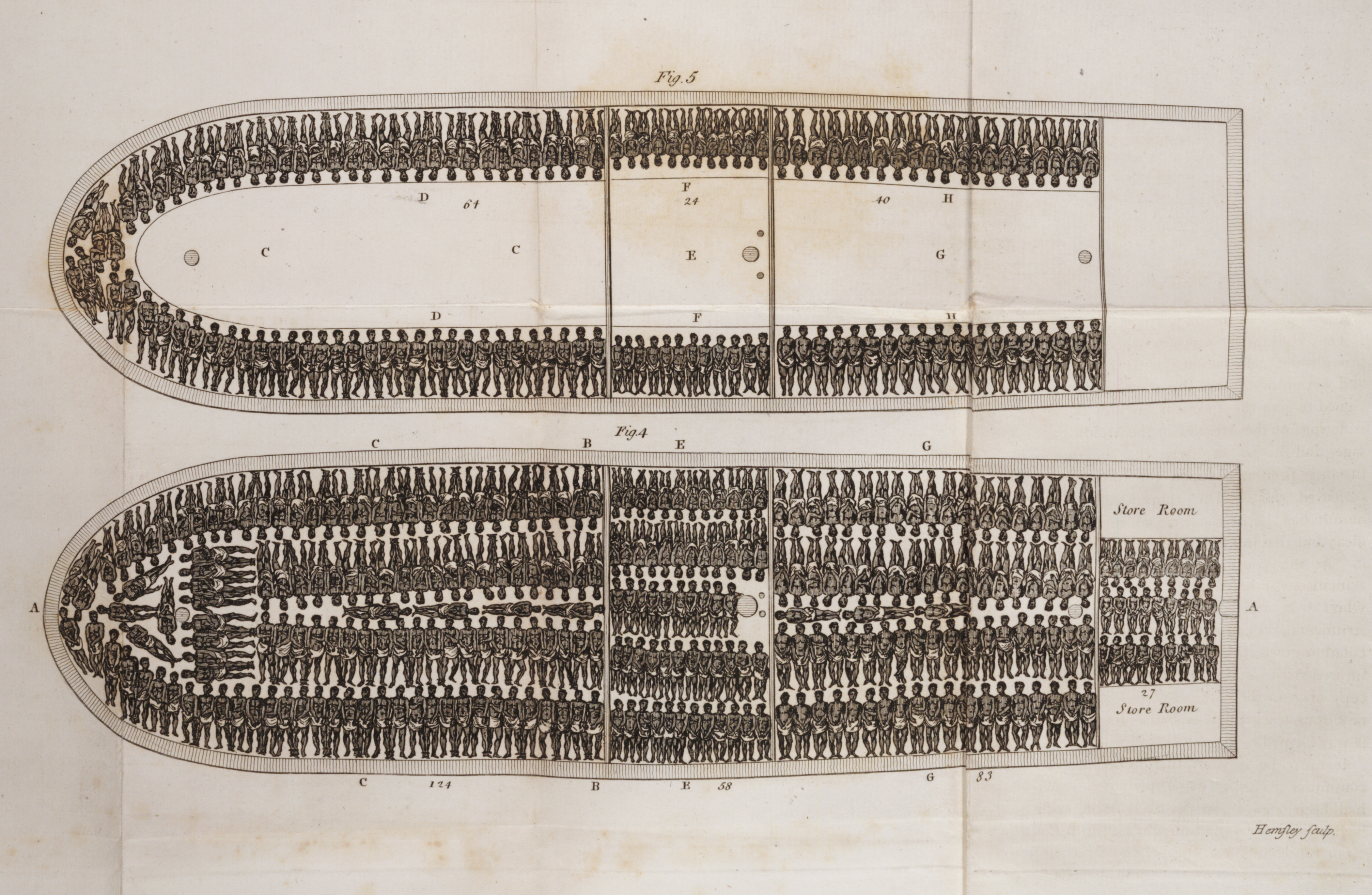
The history of slavery is a complex and often harrowing tapestry woven across continents and centuries. Understanding its vast reach and enduring impact requires a nuanced approach, one that transcends mere narrative and embraces visual representation. Enter the slavery map, a powerful tool for navigating this complex history and illuminating the global network of forced labor that shaped human societies for millennia.
Visualizing the Unseen: The Power of Mapping Slavery
A slavery map is not merely a static illustration of geographic locations where slavery occurred. It is a dynamic, interactive tool that allows researchers, educators, and the general public to explore the interconnectedness of slavery across time and space. By visualizing the movement of enslaved people, the trade routes, and the various forms of forced labor, these maps offer a unique perspective on the human cost of this system.
Types of Slavery Maps and Their Significance
The types of slavery maps vary widely, each serving a distinct purpose and offering different insights into the complex history of forced labor:
- Historical Maps: These maps illustrate the geographic scope of slavery in specific periods, showcasing the locations of slave trading centers, plantations, and the routes of slave ships. They provide a visual representation of the physical spaces where slavery was practiced, offering valuable insights into the spatial dimensions of this global phenomenon.
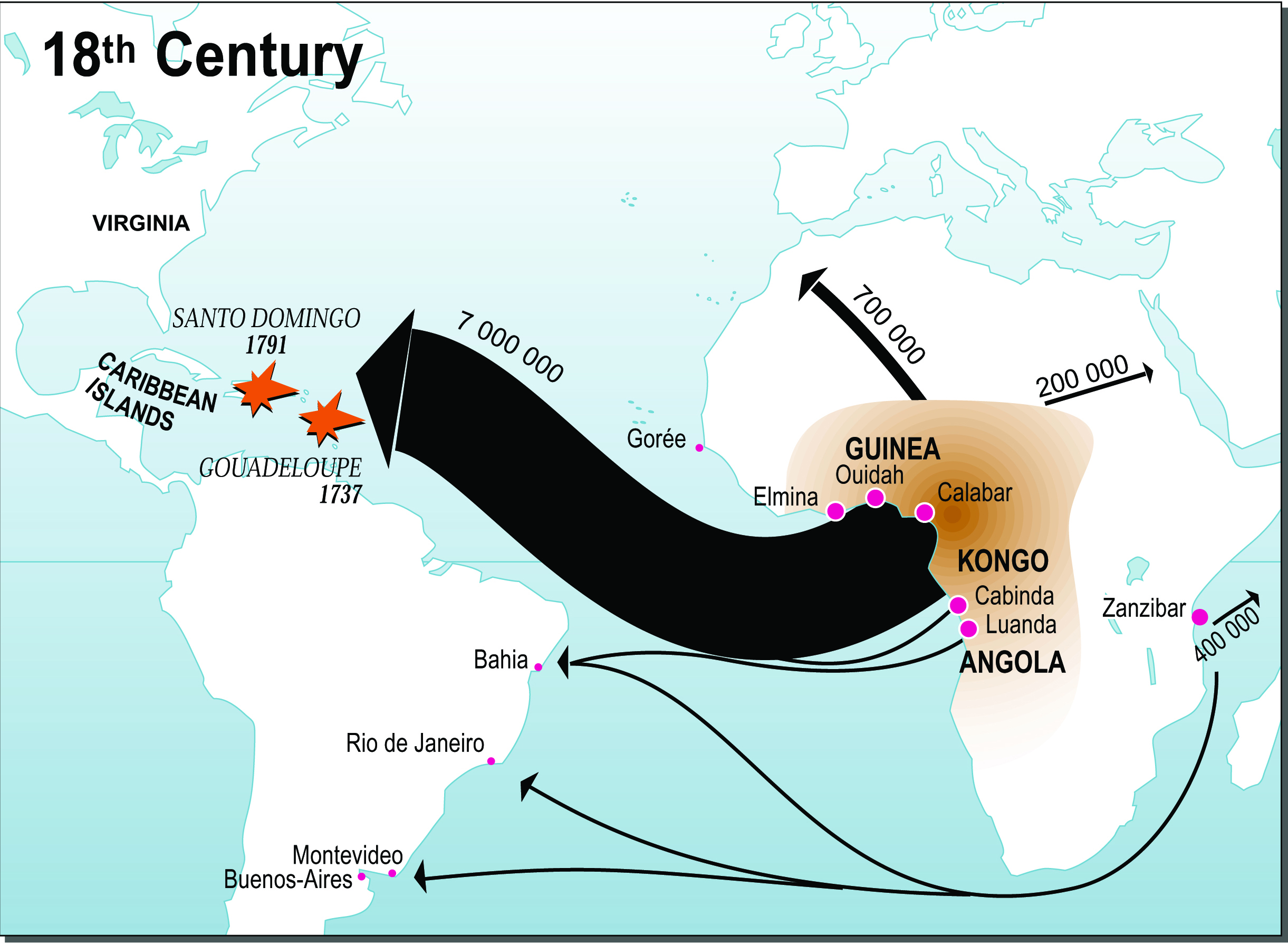
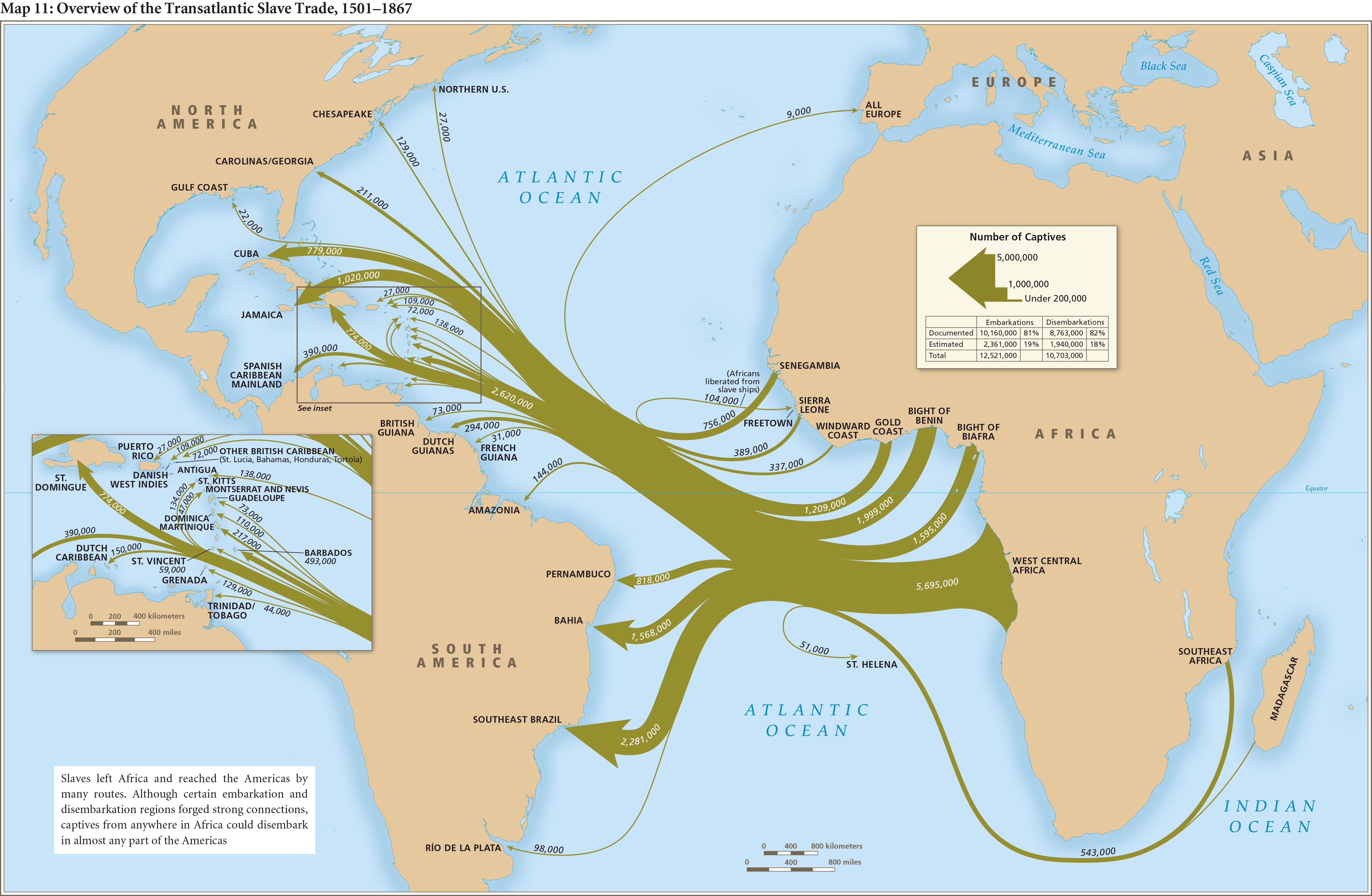
- Demographic Maps: These maps focus on the movement of enslaved people, depicting the origins, destinations, and routes of forced migration. By visualizing the human cost of slavery, they provide a powerful testament to the devastating impact of this system on individuals and communities.
- Thematic Maps: These maps explore specific aspects of slavery, such as the types of labor involved, the legal frameworks governing slavery, or the social and economic factors that shaped the institution. They offer a deeper understanding of the nuances and complexities of slavery in different regions and time periods.
- Interactive Maps: These digital maps offer a dynamic and engaging experience, allowing users to explore data, zoom in on specific locations, and interact with various layers of information. They provide a more accessible and user-friendly way to engage with the history of slavery, making it more relevant and impactful for a wider audience.
Benefits of Utilizing Slavery Maps
The use of slavery maps offers numerous benefits for understanding and engaging with this complex and often uncomfortable history:
- Visualizing the Scope: Maps provide a powerful visual representation of the global reach of slavery, illustrating its presence across continents and its impact on diverse societies. This visual understanding helps to contextualize the history of slavery and its enduring legacy.
- Understanding the Interconnections: Maps reveal the interconnectedness of slavery, highlighting the complex network of trade routes, political alliances, and economic forces that fueled the system. This understanding helps to dispel the misconception that slavery was a localized phenomenon.
- Humanizing the Victims: By visualizing the movement of enslaved people and the conditions they endured, maps help to humanize the victims of slavery, reminding us that they were individuals with families, hopes, and dreams. This humanization is crucial for fostering empathy and understanding.
- Promoting Dialogue and Education: Maps can serve as a powerful tool for education and public engagement, sparking dialogue and raising awareness about the history of slavery and its ongoing impact. They can be used in classrooms, museums, and online platforms to engage diverse audiences.
- Facilitating Research: Maps can be invaluable resources for researchers studying slavery. They provide a visual framework for analyzing data, identifying patterns, and exploring the complex relationships between different aspects of the system.
Challenges and Considerations
While slavery maps offer a valuable tool for understanding history, it is essential to acknowledge their limitations and potential biases:
- Data Gaps and Inaccuracies: Data on slavery can be incomplete or inaccurate, especially for pre-colonial periods. This lack of information can lead to gaps in mapping and potentially misrepresent the true extent of slavery.
- Generalization and Simplification: Maps can sometimes oversimplify complex historical processes, leading to generalizations that may not capture the full range of experiences associated with slavery.
- Focus on Geographic Space: While maps are effective in visualizing geographic locations, they may not adequately capture the social, economic, and political dimensions of slavery.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of slavery maps raises ethical considerations, particularly in relation to the sensitivity surrounding the topic and the potential for exploitation or misrepresentation of historical narratives.
FAQs on Slavery Maps
Q: What is the most comprehensive slavery map available?
A: There is no single "most comprehensive" slavery map. The best map for your needs will depend on the specific historical period, geographic region, and aspects of slavery you wish to explore. Various organizations and institutions offer valuable maps, including the Transatlantic Slave Trade Database, the National Museum of African American History and Culture, and the University of California, Berkeley’s "Mapping the African Diaspora" project.
Q: How accurate are slavery maps?
A: The accuracy of slavery maps depends on the availability and quality of historical data. While significant progress has been made in documenting the history of slavery, data gaps and inaccuracies still exist. It is important to consult multiple sources and critically evaluate the information presented on any map.
Q: What are the limitations of slavery maps?
A: As mentioned earlier, maps can oversimplify complex historical processes, focus primarily on geographic space, and be susceptible to data gaps and inaccuracies. It is crucial to remember that maps are just one tool for understanding the history of slavery and should be used in conjunction with other sources of information.
Q: Can slavery maps be used in educational settings?
A: Yes, slavery maps can be valuable educational tools. They can help to engage students, spark dialogue, and provide a visual framework for understanding the history of slavery. However, it is essential to use them responsibly and critically, addressing the limitations and potential biases inherent in any map.
Tips for Using Slavery Maps Effectively
- Consult multiple sources: Don’t rely on a single map. Compare different maps and sources to get a more comprehensive understanding of the history of slavery.
- Consider the context: Pay attention to the historical period, geographic region, and specific aspects of slavery that a map is focusing on.
- Look for data sources: Understand the data used to create the map and its limitations.
- Engage in critical thinking: Don’t take maps at face value. Question the information presented and consider alternative perspectives.
- Use maps in conjunction with other resources: Combine maps with written accounts, historical documents, and other sources to gain a more nuanced understanding of the history of slavery.
Conclusion
Slavery maps are powerful tools for visualizing the global history of forced labor. They offer a unique perspective on the interconnectedness of slavery, the human cost of this system, and its enduring impact on societies around the world. While maps have limitations and require careful interpretation, they can serve as valuable resources for research, education, and public engagement. By embracing these tools, we can gain a deeper understanding of this complex and often uncomfortable history and work towards a future where such injustices are never repeated.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Shadows: Understanding the Global History of Slavery Through Visualization. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!