Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding Air Pollution Maps in the United States
Related Articles: Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding Air Pollution Maps in the United States
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding Air Pollution Maps in the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding Air Pollution Maps in the United States

The United States, a nation of sprawling landscapes and bustling cities, faces a complex challenge: air pollution. While often invisible, this pervasive threat impacts public health, the environment, and the economy. Fortunately, tools like air pollution maps provide a crucial lens through which we can understand the scale and distribution of this issue, empowering individuals, communities, and policymakers to take informed action.
Decoding the Data: How Air Pollution Maps Work
Air pollution maps, often displayed online, visually represent the concentration of various pollutants in the atmosphere across a geographic area. These maps rely on data collected from a network of ground-based monitoring stations and satellite imagery, providing a snapshot of air quality at a particular moment.
Key Pollutants and Their Sources
Air pollution maps typically depict the levels of several major pollutants, including:
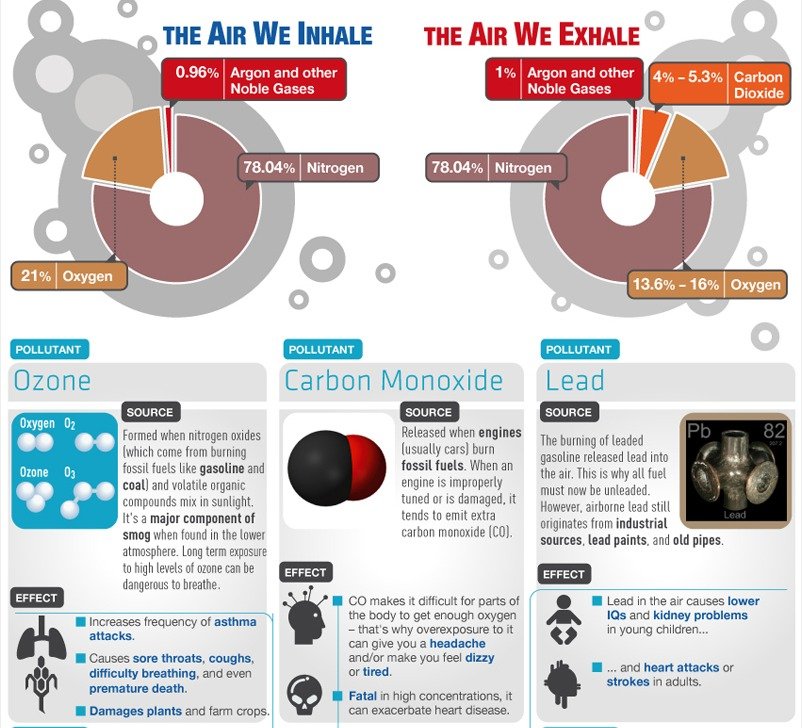
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10): Fine particles, often invisible to the naked eye, that can penetrate deep into the lungs and contribute to respiratory and cardiovascular problems. Sources include vehicle exhaust, industrial emissions, and wildfires.
- Ozone (O3): A gas formed by chemical reactions involving volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the presence of sunlight. Ground-level ozone is a respiratory irritant and can damage lung tissue. Sources include vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and power plants.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas primarily emitted by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels. It can reduce oxygen transport in the blood, leading to health problems. Sources include vehicle exhaust, industrial processes, and wildfires.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): A gas released mainly from the burning of fossil fuels containing sulfur. It contributes to acid rain and respiratory issues. Sources include power plants, industrial processes, and vehicle emissions.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2): A gas produced by the combustion of fossil fuels, particularly in vehicles. It contributes to ozone formation and respiratory problems. Sources include vehicle exhaust, industrial processes, and power plants.
Interpreting the Data: Color-Coded Maps and Air Quality Indices
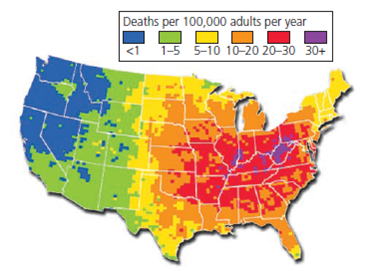
Air pollution maps typically utilize color-coding to represent different levels of pollutant concentrations. Green often signifies good air quality, while red or purple indicates high levels of pollution. This visual representation allows for quick and easy comprehension of air quality trends across different areas.
In addition to color-coding, air pollution maps often incorporate the Air Quality Index (AQI). The AQI is a numerical scale that translates pollutant concentrations into a single number, making it easier to understand the overall air quality in a specific location.
Benefits of Air Pollution Maps: Empowering Action and Understanding
Air pollution maps serve as valuable tools for:
- Public Awareness: Raising awareness about air quality issues in local communities, prompting individuals to take preventative measures like reducing their exposure to polluted air.
- Health Monitoring: Helping individuals with pre-existing health conditions, particularly respiratory and cardiovascular problems, to make informed decisions about outdoor activities based on air quality levels.
- Environmental Management: Providing valuable data for environmental agencies to monitor pollution trends, identify pollution hotspots, and implement targeted mitigation strategies.
- Policy Development: Informing policymakers about the effectiveness of pollution control measures, enabling them to develop effective strategies for improving air quality and protecting public health.
Navigating the Data: Key Considerations and Limitations
While air pollution maps offer valuable insights, it’s essential to consider the following:
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of air pollution maps depends on the density and reliability of the monitoring network and the quality of satellite imagery.
- Spatial Resolution: Maps often display data at a certain spatial resolution, meaning that they may not capture localized variations in pollution levels.
- Temporal Resolution: Air pollution levels fluctuate throughout the day and across seasons, so maps represent a snapshot in time.
- Data Interpretation: Understanding the context of the data, such as the location of pollution sources and meteorological conditions, is crucial for accurate interpretation.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What are the health effects of air pollution?
A: Air pollution can have a wide range of health effects, including respiratory problems like asthma, bronchitis, and lung cancer; cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes; and neurological disorders. Long-term exposure to air pollution can also lead to premature death.
Q: How can I protect myself from air pollution?
A: To minimize exposure to air pollution, consider:
- Checking air quality forecasts: Monitor air pollution maps and forecasts to avoid outdoor activities during periods of high pollution.
- Staying indoors during high pollution episodes: Limit outdoor activities, especially during periods of high pollution, and keep windows and doors closed.
- Using air purifiers: Consider using air purifiers in your home, especially during periods of high pollution.
- Avoiding strenuous activities: Reduce outdoor activities, particularly those involving physical exertion, during high pollution episodes.
Q: What can I do to reduce air pollution?
A: Individuals can contribute to reducing air pollution by:
- Using public transportation, walking, or cycling: Reducing reliance on personal vehicles can significantly decrease emissions.
- Conserving energy: Reducing energy consumption at home and in the workplace can reduce emissions from power plants.
- Supporting clean energy policies: Advocate for policies that promote renewable energy sources and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Choosing environmentally friendly products: Opt for products that minimize emissions and pollution throughout their lifecycle.
Tips for Using Air Pollution Maps Effectively
- Choose a reputable source: Select air pollution maps from reliable sources like government agencies, environmental organizations, and academic institutions.
- Understand the data: Familiarize yourself with the pollutants displayed on the map, their sources, and their health effects.
- Consider local factors: Take into account local factors such as weather patterns, topography, and industrial activity that can influence air quality.
- Use the data for informed decisions: Use the information provided by air pollution maps to make informed decisions about outdoor activities, health management, and advocacy.
Conclusion: A Collective Responsibility
Air pollution maps are powerful tools that illuminate the invisible threat of air pollution, empowering individuals, communities, and policymakers to take action. By understanding the data, interpreting the trends, and engaging in responsible practices, we can collectively contribute to improving air quality and safeguarding the health of our communities and the environment.
![Air Quality in the contiguous United States [3500×2198] : r/MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/i3CuXwkonbxMyAjDJsBEqSJ_qMdv3_Dzwv1WtAlQF_w.gif?format=png8u0026s=d17f253bf79a8adb5fc36cb25cb8b5eede7bf531)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding Air Pollution Maps in the United States. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!