Navigating the Labyrinth: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nervous System Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Labyrinth: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nervous System Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Labyrinth: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nervous System Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Labyrinth: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nervous System Map

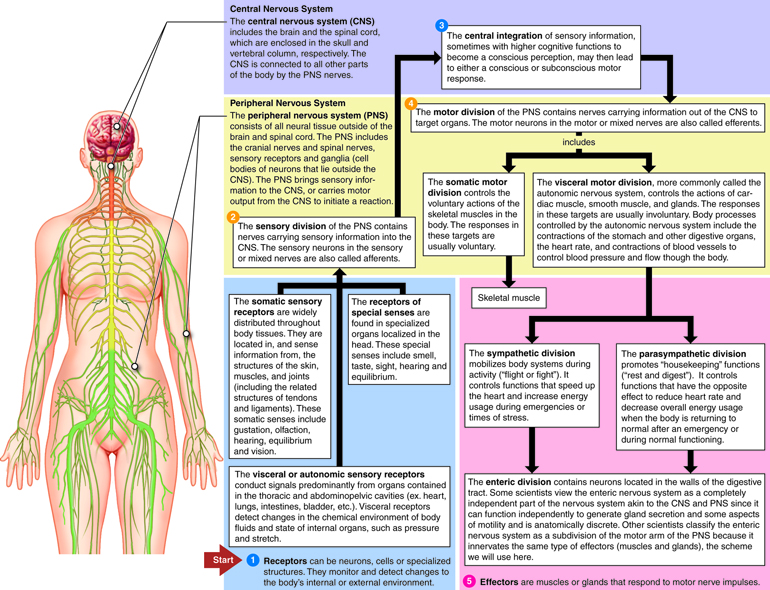
The human nervous system, a complex and intricate network of specialized cells, is the body’s command center. It orchestrates everything from basic reflexes to higher-level cognitive functions, allowing us to perceive the world, interact with our environment, and experience a vast array of emotions. Understanding this intricate system requires a clear and organized approach, which is where the concept of a "nervous system map" comes into play.
A nervous system map is a visual representation of the anatomical structure and functional organization of the nervous system. It serves as a guide, helping us navigate the intricate pathways of nerves, understand the interconnectedness of different brain regions, and appreciate the diverse functions they perform. This map, while not a physical entity, is a powerful tool for research, education, and clinical practice.
Delving into the Central Nervous System:
The nervous system map begins with the central nervous system (CNS), the body’s control center, comprising the brain and spinal cord. The brain, housed within the protective skull, is responsible for higher-level functions like thought, memory, language, and consciousness. It can be visualized as a complex network of interconnected regions, each specialized for particular tasks.
- Cerebrum: The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum is responsible for voluntary movement, sensory perception, language, learning, and memory. It is divided into two hemispheres, each controlling the opposite side of the body.
- Cerebellum: Located at the back of the brain, the cerebellum coordinates movement, balance, and posture. It receives information from the cerebrum and sensory organs, fine-tuning motor commands to ensure smooth and coordinated actions.
- Brainstem: Connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord, the brainstem controls vital functions like breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. It also acts as a relay center for sensory and motor information.
- Spinal Cord: Extending from the brainstem down the back, the spinal cord serves as a communication pathway between the brain and the rest of the body. It carries sensory information from the body to the brain and motor commands from the brain to muscles and glands.
Extending Beyond the Central Core: The Peripheral Nervous System
While the CNS acts as the command center, the peripheral nervous system (PNS) serves as the communication network, extending outward from the CNS to reach every part of the body. It is responsible for transmitting sensory information to the CNS and relaying motor commands from the CNS to muscles and glands.
The PNS can be further divided into two main branches:
- Somatic Nervous System: This branch controls voluntary movements, allowing us to consciously interact with our environment. It consists of nerves that connect the CNS to skeletal muscles, enabling us to walk, talk, write, and perform countless other actions.
- Autonomic Nervous System: This branch regulates involuntary functions, such as heart rate, breathing, digestion, and body temperature. It operates largely without conscious control, maintaining homeostasis and adapting to changing conditions.
Understanding the Nervous System’s Functional Organization
The nervous system map not only illustrates the anatomical structure but also highlights the functional organization of the nervous system. This organization allows for efficient communication and coordination of activities throughout the body.
- Sensory Pathways: These pathways carry sensory information from the body to the CNS. They include pathways for touch, temperature, pain, pressure, taste, smell, sight, and hearing.
- Motor Pathways: These pathways carry motor commands from the CNS to muscles and glands. They control voluntary movements, as well as involuntary functions like heart rate and digestion.
- Reflex Pathways: These specialized pathways allow for rapid, involuntary responses to stimuli. They bypass the brain, enabling quick reactions to potentially dangerous situations.
The Importance of the Nervous System Map
The nervous system map is not merely a static diagram; it is a dynamic tool that aids in understanding the complex interplay of structures and functions within the nervous system. Its applications are diverse and far-reaching:
- Research: Researchers use the map to identify specific brain regions involved in different cognitive functions, helping to understand the neural basis of behavior and cognition.
- Education: Medical students, neurologists, and other healthcare professionals rely on the map to learn the anatomy and physiology of the nervous system, laying the foundation for effective diagnosis and treatment.
- Clinical Practice: Clinicians use the map to interpret diagnostic tests, localize brain lesions, and plan surgical interventions. For example, understanding the pathways involved in speech production can guide surgeons during brain tumor removal.
- Neuromarketing: The map aids in understanding consumer behavior and responses to marketing stimuli. By studying brain activity related to specific products or advertisements, marketers can tailor their campaigns for greater effectiveness.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Nervous System Map
1. Is the nervous system map a fixed entity or a dynamic model?
The nervous system map is a dynamic model that evolves as scientific understanding of the nervous system advances. New discoveries and research findings constantly refine our understanding of the complex connections and functions within the nervous system, leading to updates and modifications of the map.
2. How is the nervous system map used in clinical diagnosis?
Clinicians use the map to interpret diagnostic tests like MRI and CT scans, which provide detailed images of the brain and spinal cord. By comparing the images to the map, clinicians can identify abnormalities, such as tumors, strokes, or developmental anomalies, and pinpoint their location within the nervous system.
3. Can the nervous system map be used to predict individual differences in brain function?
While the map provides a general framework for understanding the nervous system, it cannot predict individual differences in brain function. Factors like genetics, environment, and life experiences contribute to unique brain wiring and individual variations in cognitive abilities and personality traits.
4. Can the nervous system map be used to understand mental illnesses?
The nervous system map is a valuable tool for understanding the neural basis of mental illnesses. Research using the map has identified specific brain regions and pathways associated with various disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. This knowledge helps develop more targeted and effective treatments.
5. How does the nervous system map relate to artificial intelligence?
The nervous system map provides inspiration for the development of artificial intelligence (AI). By studying the intricate connections and information processing capabilities of the brain, researchers aim to create AI systems that can mimic human intelligence and solve complex problems.
Tips for Navigating the Complexities of the Nervous System Map
- Visualize the Map: Use diagrams, 3D models, and interactive software to create a mental picture of the nervous system’s structure and connections.
- Focus on Function: Don’t just memorize names and locations; understand the functions of different brain regions and pathways.
- Break it Down: Start by understanding the basic components of the nervous system and gradually build your knowledge by exploring specific regions and pathways.
- Seek Connections: Recognize the interconnectedness of different parts of the nervous system. Understand how sensory information is processed, motor commands are generated, and reflexes are triggered.
- Engage in Active Learning: Use flashcards, quizzes, and practice questions to reinforce your understanding of the nervous system map.
Conclusion: A Journey of Discovery
The nervous system map is a powerful tool that guides us through the intricate labyrinth of the human nervous system. It provides a framework for understanding the anatomical structure and functional organization of this vital system, paving the way for advancements in research, education, and clinical practice. By embracing the map as a tool for exploration and discovery, we can unravel the mysteries of the nervous system, gaining a deeper appreciation for its complexity and marveling at its remarkable ability to orchestrate the symphony of life.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Labyrinth: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nervous System Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!