Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical Overview with Capitals
Related Articles: Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical Overview with Capitals
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical Overview with Capitals. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical Overview with Capitals

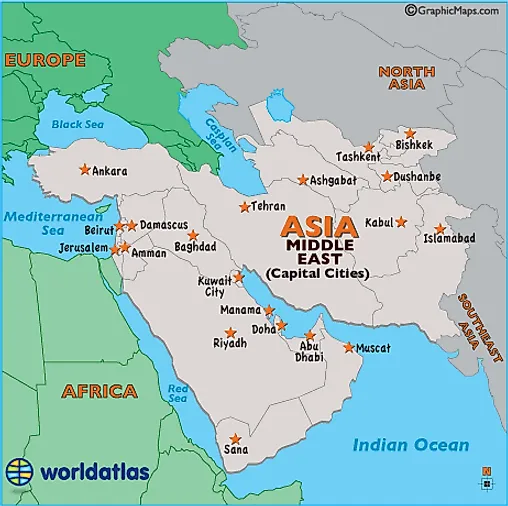
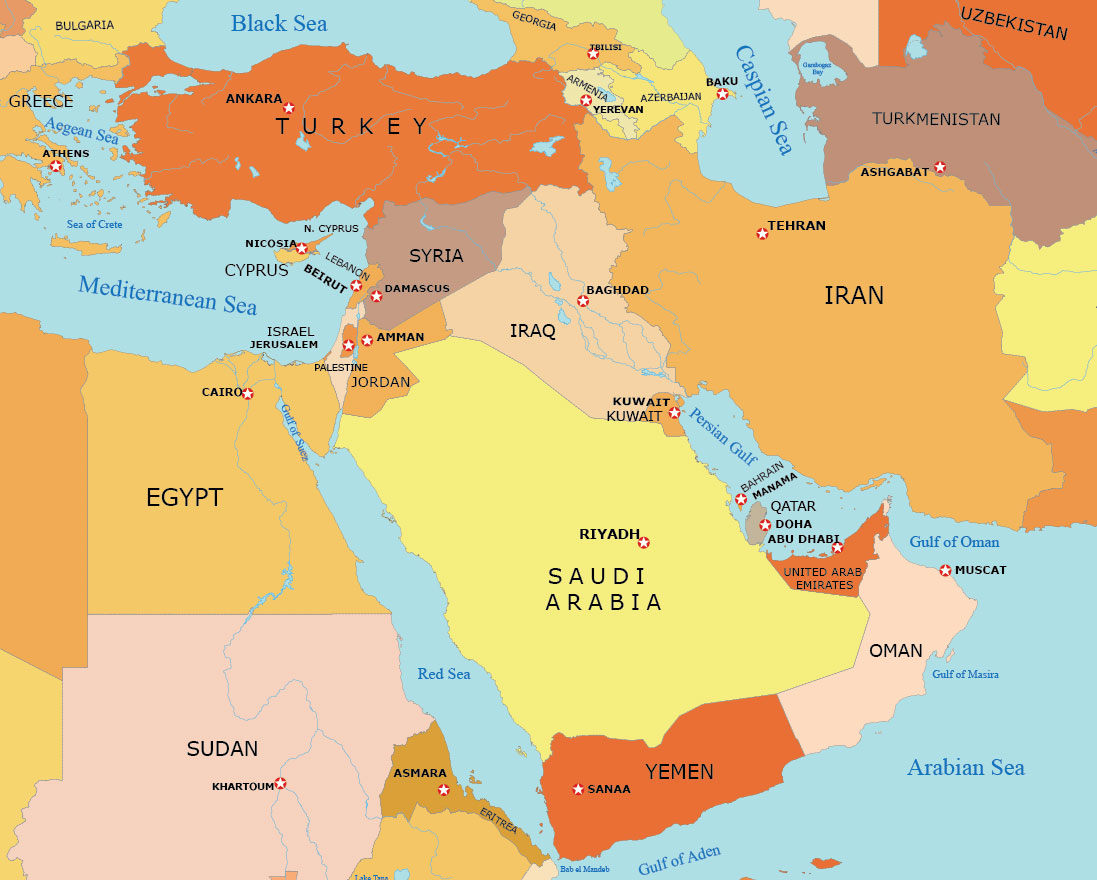
The Middle East, a region encompassing a diverse tapestry of cultures, languages, and landscapes, holds a pivotal position on the global stage. Its strategic location at the crossroads of Africa, Asia, and Europe has made it a hub for trade, cultural exchange, and, unfortunately, conflict for millennia. Understanding the geography of this region, including its capital cities, is crucial for comprehending its history, complexities, and ongoing challenges.
A Geographical Snapshot
The Middle East, also known as the Near East, is a vast and varied region. Its boundaries are not universally agreed upon, but generally include countries like:
- Arabian Peninsula: Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Bahrain, and Kuwait.
- Levant: Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, and Palestine.
- Mesopotamia: Iraq.
- North Africa: Egypt.
- Caucasus: Turkey, Azerbaijan, Armenia, and Georgia.
This geographic diversity is reflected in the region’s landscapes, ranging from the vast deserts of the Arabian Peninsula to the fertile plains of Mesopotamia, the snow-capped mountains of the Caucasus, and the Mediterranean coastline.
Understanding the Capitals
Each nation within the Middle East is represented by its capital city, serving as the center of government, administration, and often cultural life. These capitals offer valuable insights into the region’s political, economic, and social dynamics.
Here is a concise overview of the capitals and their significance:
- Saudi Arabia: Riyadh, a modern metropolis, is the country’s political and economic hub, home to major government institutions, financial centers, and cultural landmarks.
- Yemen: Sana’a, a historic city nestled amidst mountains, is a testament to Yemen’s rich cultural heritage.
- Oman: Muscat, a coastal city with a blend of traditional and modern architecture, is a key port and commercial center.
- United Arab Emirates: Abu Dhabi, a modern city with a rapidly growing economy, is the capital and the country’s largest emirate.
- Qatar: Doha, a vibrant city known for its modern skyline and hosting of major events like the FIFA World Cup, is a major financial and cultural center.
- Bahrain: Manama, a coastal city with a long history of pearl diving, is a commercial hub and a center for finance and tourism.
- Kuwait: Kuwait City, a modern metropolis located on the Persian Gulf, is a major oil exporter and a regional financial center.
- Syria: Damascus, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, is a historical and cultural hub, though currently impacted by conflict.
- Lebanon: Beirut, known as the "Paris of the Middle East," is a cosmopolitan city with a vibrant cultural scene and a major financial center.
- Jordan: Amman, a modern city with a mix of ancient and modern architecture, is a major tourist destination and a regional hub for trade and transportation.
- Israel: Jerusalem, a holy city for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, is a contested territory with significant historical and religious importance.
- Palestine: East Jerusalem (claimed by Palestine) and Ramallah (de facto capital), both cities are central to the Palestinian identity and struggle for self-determination.
- Iraq: Baghdad, a historic city on the Tigris River, is a major cultural center and a key player in Iraqi politics.
- Egypt: Cairo, a sprawling metropolis on the Nile River, is the largest city in the Arab world and a center for culture, education, and commerce.
- Turkey: Ankara, a modern city built in the early 20th century, is the country’s political and administrative center.
- Azerbaijan: Baku, a coastal city on the Caspian Sea, is a major oil and gas hub and a center for culture and tourism.
- Armenia: Yerevan, a historic city known for its architecture and cultural heritage, is the country’s political and economic center.
- Georgia: Tbilisi, a historic city with a blend of modern and traditional architecture, is a major cultural and economic center.
The Importance of Understanding Capital Cities
Understanding the capitals of the Middle East is crucial for several reasons:
- Political Dynamics: These cities are the seats of power, where political decisions are made and national policies are formulated. Studying their political landscapes provides insights into the region’s governance, stability, and challenges.
- Economic Growth: Many capitals are major economic hubs, attracting investment and driving regional development. Analyzing their economic activities sheds light on the region’s economic potential and challenges.
- Cultural Exchange: Capitals are often centers of cultural expression, home to museums, theaters, universities, and other institutions that shape the region’s cultural landscape. Understanding these centers provides valuable insights into the region’s rich history, diverse traditions, and evolving identity.
- Global Connections: As centers of power and influence, capitals serve as gateways to the Middle East for international organizations, businesses, and individuals. Understanding their role in global affairs is essential for fostering collaboration and understanding.
FAQs
Q: What is the largest city in the Middle East?
A: Cairo, the capital of Egypt, is the largest city in the Middle East, with a population exceeding 20 million.
Q: Which capital city is considered the "Paris of the Middle East"?
A: Beirut, the capital of Lebanon, is often referred to as the "Paris of the Middle East" due to its cosmopolitan atmosphere, vibrant cultural scene, and architectural beauty.
Q: Which capital city is located on the Tigris River?
A: Baghdad, the capital of Iraq, is located on the Tigris River, one of the two major rivers that define Mesopotamia.
Q: Which capital city is home to the oldest continuously inhabited city in the world?
A: Damascus, the capital of Syria, is considered one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, with a history dating back over 11,000 years.
Q: Which capital city is a major oil and gas hub?
A: Baku, the capital of Azerbaijan, is a major oil and gas hub, playing a significant role in the region’s energy sector.
Tips for Exploring the Middle East
- Research Thoroughly: Before traveling, delve into the history, culture, and current events of each country you plan to visit.
- Respect Local Customs: Be mindful of local customs and traditions, especially regarding dress, behavior, and religious practices.
- Learn Basic Phrases: Learning a few basic phrases in the local language can enhance your interactions with locals and make your journey more enriching.
- Embrace Diversity: The Middle East is a region of immense diversity, so be open to experiencing different cultures, religions, and ways of life.
- Stay Informed: Stay updated on current events and travel advisories, and be aware of any potential security concerns.
Conclusion
The Middle East is a region of immense complexity and dynamism. Understanding its geography, including its capital cities, is essential for navigating its political, economic, and cultural landscapes. By appreciating the unique character of each capital, we gain a deeper understanding of the region’s rich history, diverse cultures, and ongoing challenges. This knowledge is crucial for fostering dialogue, promoting understanding, and contributing to a more peaceful and prosperous future for the Middle East and the world.

![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical Overview with Capitals. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!