Navigating the Nile: Understanding Ancient Egypt’s Upper and Lower Divisions
Related Articles: Navigating the Nile: Understanding Ancient Egypt’s Upper and Lower Divisions
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Nile: Understanding Ancient Egypt’s Upper and Lower Divisions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Nile: Understanding Ancient Egypt’s Upper and Lower Divisions
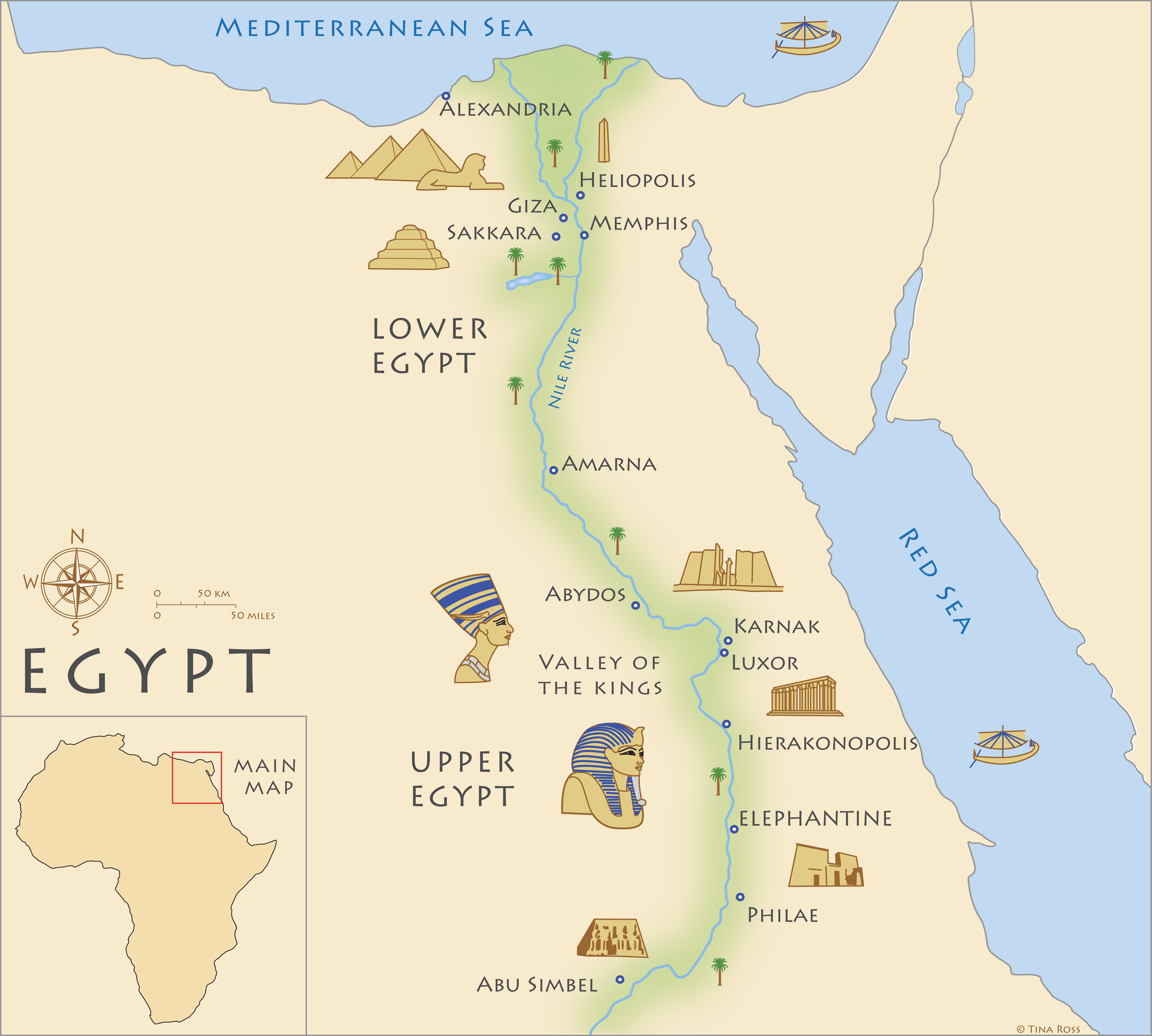
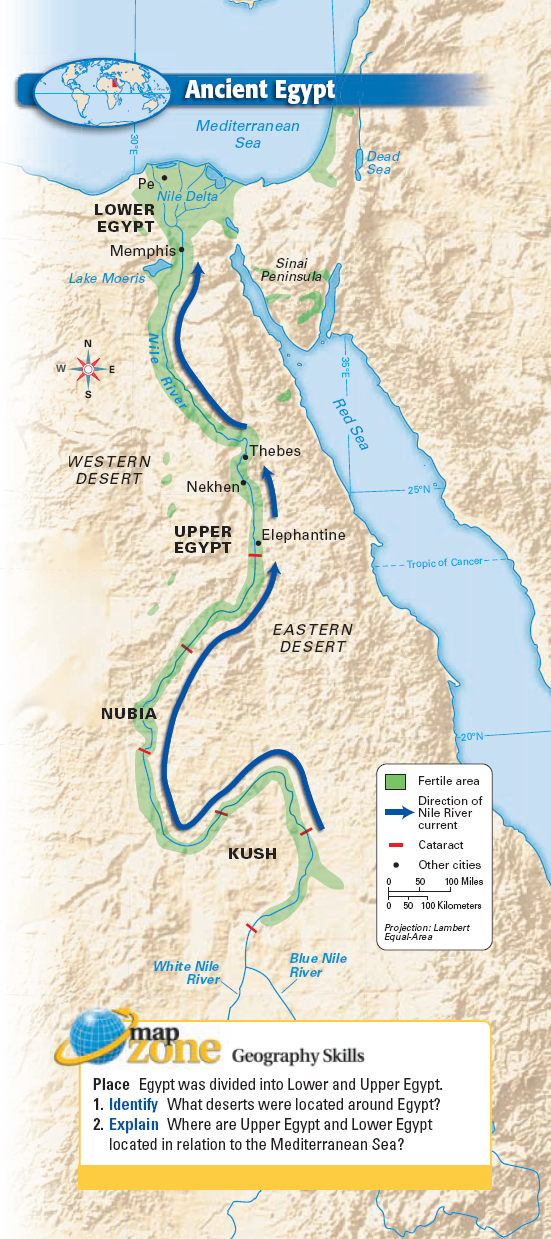
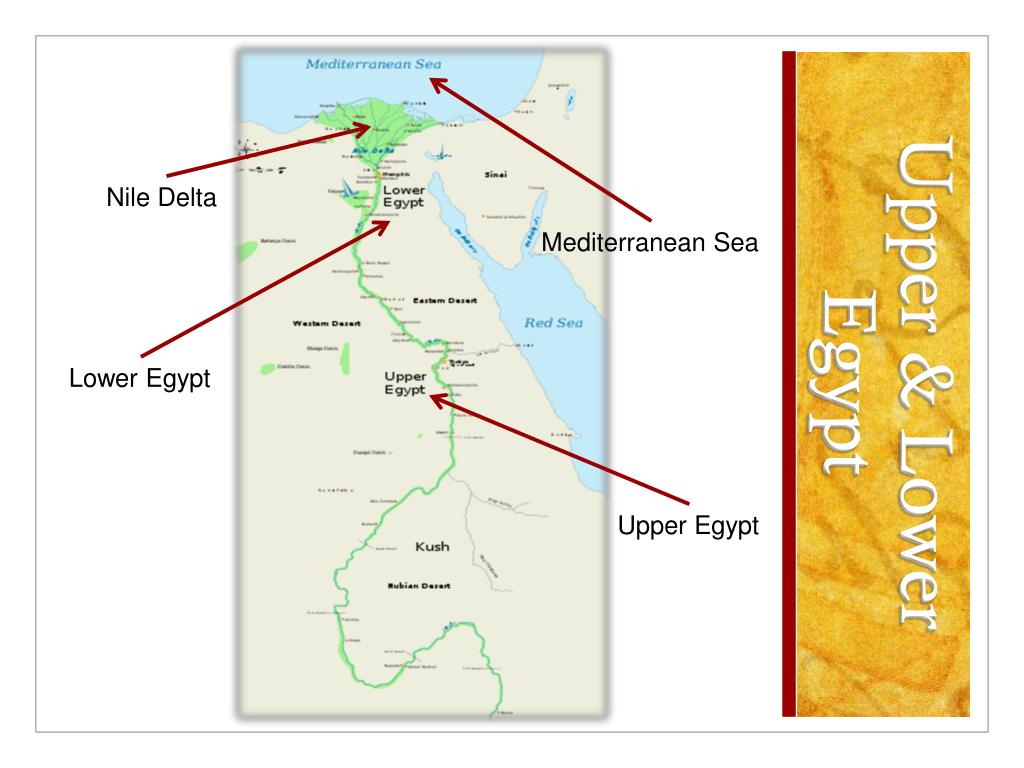
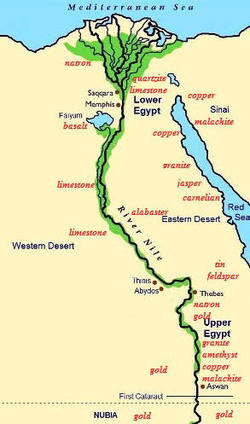
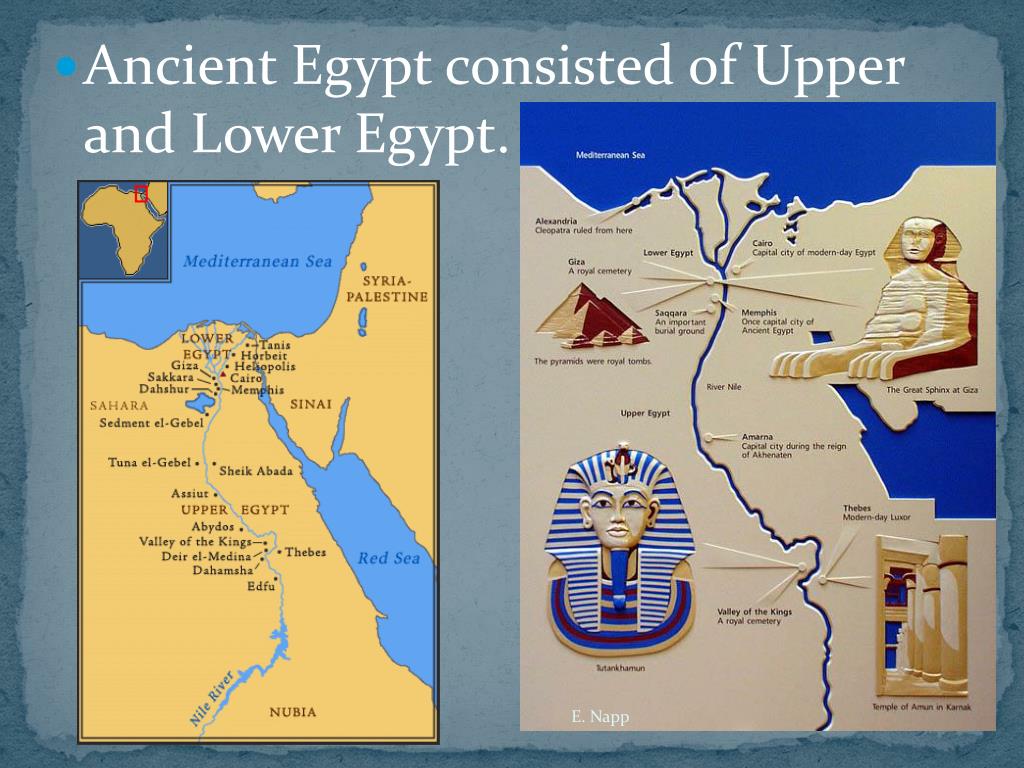
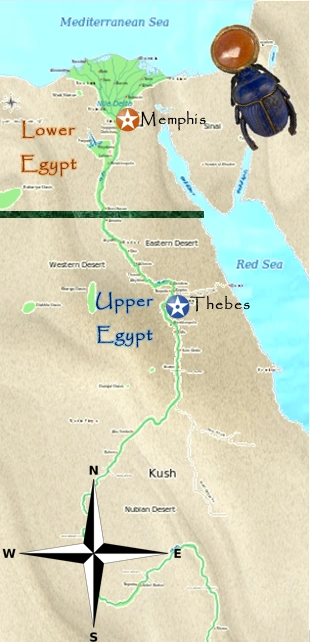
The ancient Egyptians, renowned for their sophisticated civilization, viewed their land through a unique lens: that of the Nile River. This mighty waterway, the lifeblood of their civilization, was not just a source of water and sustenance, but a defining geographical and cultural axis. The ancient Egyptians divided their land into two distinct regions, "Upper Egypt" and "Lower Egypt," based on the Nile’s flow and their relative positions.
Upper Egypt: The Source of Life
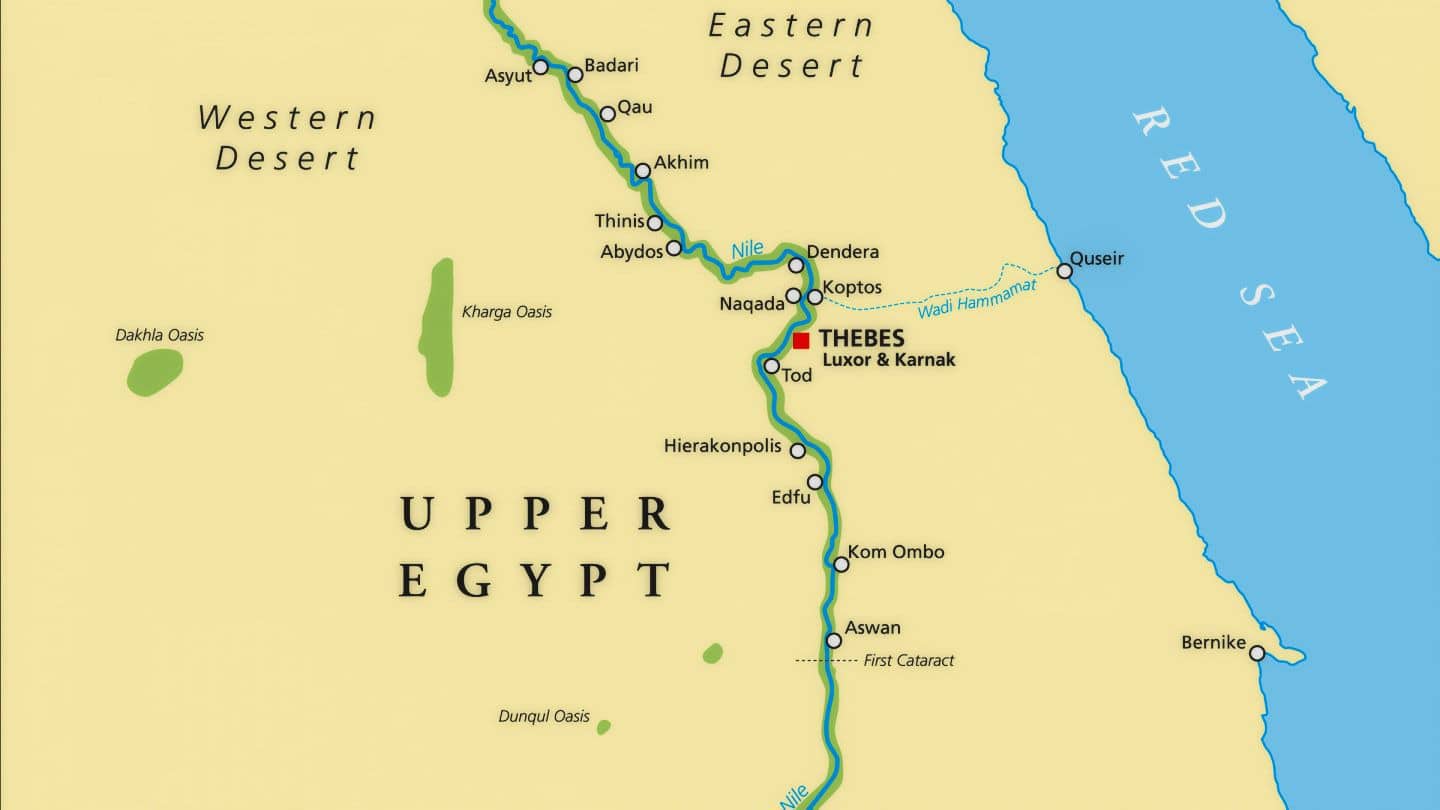
Upper Egypt, situated in the south, encompassed the area where the Nile River originated in the highlands of Ethiopia. This region was characterized by its arid, desert landscape, punctuated by fertile oases and the verdant Nile Valley. The mountainous terrain and rugged landscape of Upper Egypt made it a natural barrier, fostering a sense of isolation and independence.
The Importance of Upper Egypt:
- Land of the Pharaohs: Upper Egypt served as the cradle of Egyptian civilization. The first pharaohs emerged from the fertile lands of Upper Egypt, establishing their capital at Thebes (modern Luxor), a city rich in history and religious significance.
- Agricultural Hub: The Nile’s annual flooding, a vital source of irrigation, allowed for the cultivation of crops like wheat, barley, and papyrus. This agricultural bounty supported a growing population and fueled the development of a complex society.
- Religious Center: Upper Egypt was home to numerous temples and religious sites, including the iconic Karnak Temple complex and the Valley of the Kings, where pharaohs were entombed. These sites were not only places of worship but also centers of learning and artistic expression.
Lower Egypt: The Land of the Delta
Lower Egypt, located in the north, encompassed the Nile Delta region, where the river branched out into numerous tributaries, creating a fertile delta plain. This region was characterized by its flat, fertile land, abundant waterways, and a dense population.
The Importance of Lower Egypt:
- Economic Powerhouse: The Nile Delta, with its rich agricultural resources, became the economic heartland of ancient Egypt. It was a major producer of grain, flax, and papyrus, vital commodities for trade and commerce.
- Trade Hub: Lower Egypt’s strategic location at the mouth of the Nile, connecting the interior to the Mediterranean Sea, made it a hub for international trade. The Egyptians established trading posts along the Mediterranean coast, facilitating the exchange of goods with neighboring civilizations.
- Political Center: The capital of Lower Egypt, Memphis, served as a powerful political center, rivaling Thebes in Upper Egypt. The unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the pharaoh Menes marked a pivotal moment in Egyptian history, signifying the rise of a unified kingdom.
The Symbiotic Relationship:
Upper and Lower Egypt, despite their geographical and cultural differences, were inextricably linked by the Nile River. This vital waterway facilitated trade, communication, and the exchange of ideas between the two regions, fostering a sense of unity and shared identity. The annual flooding of the Nile, a natural phenomenon that brought life to the land, symbolized the interconnectedness of Upper and Lower Egypt, reminding them of their shared destiny.
The Legacy of Upper and Lower Egypt:
The ancient Egyptians’ division of their land into Upper and Lower Egypt reflects a deep understanding of their environment and its influence on their civilization. This division played a crucial role in shaping their political, economic, and cultural development, leaving an enduring legacy that continues to fascinate and inspire us today.
FAQs about Upper and Lower Egypt:
1. How did the ancient Egyptians distinguish between Upper and Lower Egypt?
The ancient Egyptians used the direction of the Nile River’s flow to determine the distinction between Upper and Lower Egypt. The Nile flows from south to north, hence the source of the river in the south was considered "Upper" while the delta region in the north was considered "Lower."
2. What were the main differences between Upper and Lower Egypt?
Upper Egypt was characterized by its arid, mountainous terrain, while Lower Egypt was known for its flat, fertile delta plain. Upper Egypt was the birthplace of the pharaohs and a center of religious activity, while Lower Egypt served as the economic heartland and a hub for trade and commerce.
3. How did the Nile River connect Upper and Lower Egypt?
The Nile River served as a vital lifeline for both Upper and Lower Egypt, facilitating trade, communication, and the exchange of ideas between the two regions. The annual flooding of the Nile, a natural phenomenon that brought life to the land, symbolized the interconnectedness of the two regions.
4. What are some of the most important historical sites in Upper and Lower Egypt?
In Upper Egypt, some of the most significant historical sites include the Karnak Temple complex, the Valley of the Kings, and the temple at Luxor. In Lower Egypt, notable sites include the Great Pyramid of Giza, the Sphinx, and the ancient city of Memphis.
5. How did the division of Egypt into Upper and Lower Egypt influence its development?
The division of Egypt into Upper and Lower Egypt fostered a sense of regional identity and autonomy while simultaneously promoting unity and cooperation through the shared resource of the Nile River. This division played a crucial role in shaping the political, economic, and cultural development of ancient Egypt.
Tips for Exploring Upper and Lower Egypt:
- Plan your trip: Egypt offers a wealth of historical sites, so it’s essential to plan your itinerary in advance, focusing on the regions that interest you most.
- Embrace the Nile: The Nile River is the heart of Egypt. Consider taking a cruise along the Nile to experience the beauty of the landscape and visit ancient sites along its banks.
- Learn about the history: Before your trip, familiarize yourself with the history of ancient Egypt, its pharaohs, and its mythology. This will enhance your appreciation of the sites you visit.
- Respect the culture: Egypt is a country rich in culture and traditions. Be respectful of local customs and dress appropriately when visiting religious sites.
- Bargain for souvenirs: Haggling is a common practice in Egypt. Don’t be afraid to bargain for souvenirs and handicrafts, but be fair and respectful.
Conclusion:
The ancient Egyptians’ division of their land into Upper and Lower Egypt, while a simple geographical distinction, reveals a profound understanding of their environment and its influence on their civilization. This division shaped their political, economic, and cultural development, leaving an enduring legacy that continues to fascinate and inspire us today. By understanding the unique characteristics and contributions of each region, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and richness of ancient Egyptian civilization.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Nile: Understanding Ancient Egypt’s Upper and Lower Divisions. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!