Navigating the Waters of History and Ecology: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Delaware Bay
Related Articles: Navigating the Waters of History and Ecology: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Delaware Bay
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Waters of History and Ecology: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Delaware Bay. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Waters of History and Ecology: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Delaware Bay
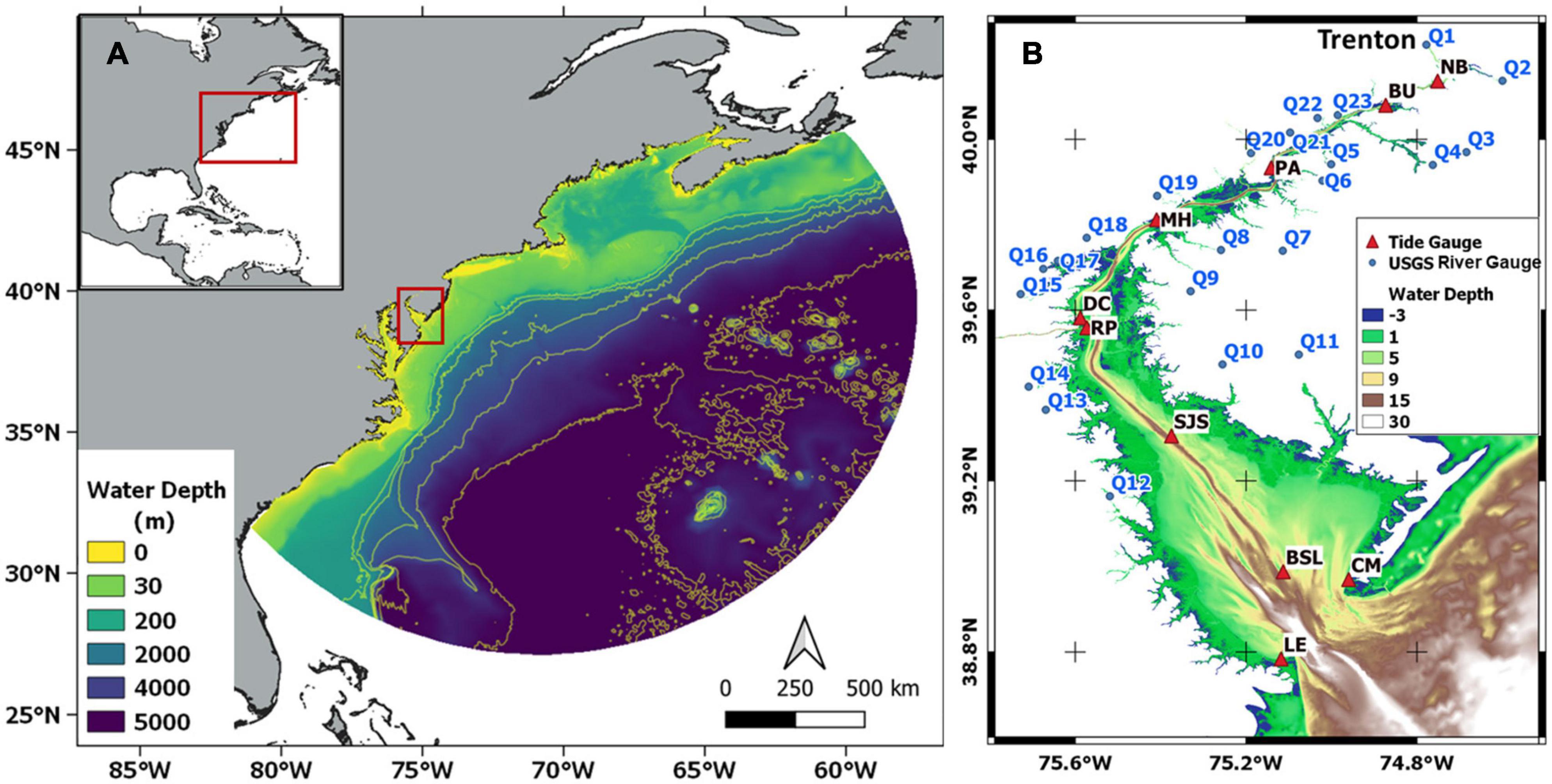
The Delaware Bay, a prominent estuary on the Atlantic Coast of North America, stands as a testament to the intricate interplay of nature and human influence. Its geographic location, encompassing parts of Delaware and New Jersey, has shaped its historical significance, ecological importance, and ongoing challenges. Understanding the Delaware Bay map, with its intricate network of waterways, surrounding landscapes, and human settlements, is crucial for appreciating its multifaceted role in the region.
A Geographic Overview: Delineating the Boundaries
The Delaware Bay’s distinctive shape, reminiscent of a funnel, is a result of its formation. The bay’s headwaters lie at the confluence of the Delaware River and the Schuylkill River, flowing from the Appalachian Mountains. As these rivers converge, they carve a path through the coastal plain, eventually widening into a broad expanse that meets the Atlantic Ocean.
The Delaware Bay map showcases its defining features:
- The Delaware River: This major tributary flows through the heart of the bay, contributing significantly to its freshwater input.
- The Chesapeake and Delaware Canal: This artificial waterway, connecting the Delaware Bay with the Chesapeake Bay, has played a vital role in transportation and trade.
- The Eastern Shore: This peninsula, stretching along the eastern side of the bay, is home to diverse ecosystems and historic settlements.
- The Western Shore: This region, encompassing parts of Delaware and New Jersey, boasts a rich history of agriculture and coastal development.
- The Mouth of the Bay: This area, where the bay meets the Atlantic Ocean, is characterized by strong tidal currents and significant marine life.
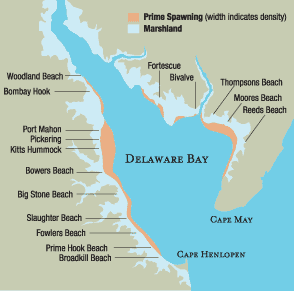
A Tapestry of Ecosystems: Unveiling the Rich Biodiversity
The Delaware Bay map reveals a diverse range of ecosystems, each contributing to the region’s ecological richness:
- Saltmarshes: These coastal wetlands, teeming with plant and animal life, play a vital role in filtering pollutants, providing habitat for migratory birds, and buffering coastal areas from storm surges.
- Tidal Flats: These mudflats, exposed at low tide, serve as feeding grounds for numerous shorebirds and shellfish.
- Submerged Aquatic Vegetation: These underwater meadows, providing habitat for fish and other marine life, contribute to the bay’s overall health.
- Estuarine Forests: These woodlands, adapted to the brackish water environment, offer shelter and breeding grounds for a variety of species.
- Open Waters: The open areas of the bay support a rich diversity of fish, invertebrates, and marine mammals.
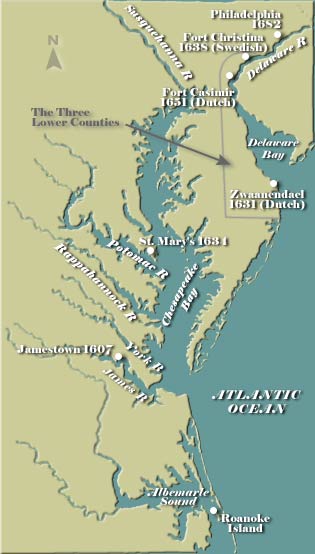
A Historical Journey: Tracing the Tides of Time
The Delaware Bay map reflects a rich history, marked by human settlement, economic development, and cultural influence:
- Native American Presence: The Lenape people, indigenous to the region, inhabited the Delaware Bay area for centuries, relying on its resources for sustenance and trade.
- European Colonization: European settlers arrived in the 17th century, establishing settlements along the bay’s shores and utilizing its waterways for transportation and trade.
- Industrial Revolution: The bay witnessed significant industrial growth in the 19th and 20th centuries, with shipyards, factories, and refineries lining its shores.
- Modern Development: The bay continues to be a hub of economic activity, supporting fishing, tourism, and transportation industries.
Challenges and Conservation: Navigating a Sustainable Future
The Delaware Bay map also reveals ongoing challenges, highlighting the need for sustainable management practices:
- Pollution: Industrial activities, agricultural runoff, and urban development contribute to water pollution, impacting the bay’s water quality and ecosystem health.
- Habitat Loss: Coastal development, dredging, and other human activities have resulted in the loss of critical habitats for wildlife.
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels, increased storm frequency, and changing water temperatures pose significant threats to the bay’s ecosystems and communities.
Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing these challenges, numerous conservation initiatives are underway:
- Water Quality Monitoring: Regular monitoring programs assess water quality, identifying pollution sources and promoting mitigation efforts.
- Habitat Restoration: Projects focus on restoring degraded habitats, such as saltmarshes and tidal flats, to enhance biodiversity and resilience.
- Sustainable Practices: Efforts promote sustainable fishing practices, responsible development, and pollution reduction strategies to protect the bay’s resources.
The Delaware Bay: A Vital Resource for the Future
The Delaware Bay map, encompassing its geography, ecosystems, history, and challenges, underscores its vital role in the region’s economy, environment, and culture. Its unique characteristics, from its diverse habitats to its rich history, make it a valuable resource that requires careful stewardship. By understanding the interconnectedness of the bay’s components and embracing sustainable practices, we can ensure its continued health and prosperity for generations to come.
FAQs about the Delaware Bay Map:
Q: What is the significance of the Delaware Bay?
A: The Delaware Bay is a crucial estuary, providing essential habitat for a diverse range of wildlife, supporting commercial fishing and recreation, and playing a vital role in the regional economy.
Q: Why is the Delaware Bay important for migratory birds?
A: The bay’s extensive saltmarshes and tidal flats provide critical stopover points for millions of migratory birds, offering food and rest during their long journeys.
Q: How does the Delaware Bay contribute to the economy?
A: The bay supports a thriving fishing industry, attracts tourism, and facilitates transportation through its waterways, contributing significantly to the regional economy.
Q: What are the major threats facing the Delaware Bay?
A: Pollution, habitat loss, and climate change pose significant threats to the bay’s ecosystem and the communities that rely on it.
Q: What are some ways to protect the Delaware Bay?
A: Supporting conservation initiatives, promoting sustainable practices, and advocating for responsible development are crucial steps in protecting the bay’s resources.
Tips for Navigating the Delaware Bay Map:
- Utilize online mapping tools: Explore interactive maps that provide detailed information on the bay’s geography, ecosystems, and points of interest.
- Engage with local organizations: Connect with conservation groups and research institutions to learn about their efforts and contribute to their initiatives.
- Support sustainable practices: Choose eco-friendly products, reduce your carbon footprint, and advocate for policies that protect the bay’s environment.
- Explore the bay’s diverse landscapes: Visit the bay’s shores, observe its wildlife, and appreciate its natural beauty.
Conclusion:
The Delaware Bay map serves as a roadmap to a complex and dynamic ecosystem. It highlights the bay’s historical significance, ecological importance, and ongoing challenges. By understanding the intricate web of relationships within the bay, we can appreciate its value and contribute to its sustainable management. Through collective efforts, we can ensure that the Delaware Bay continues to thrive as a vital resource for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Waters of History and Ecology: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Delaware Bay. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!