South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator
Related Articles: South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator
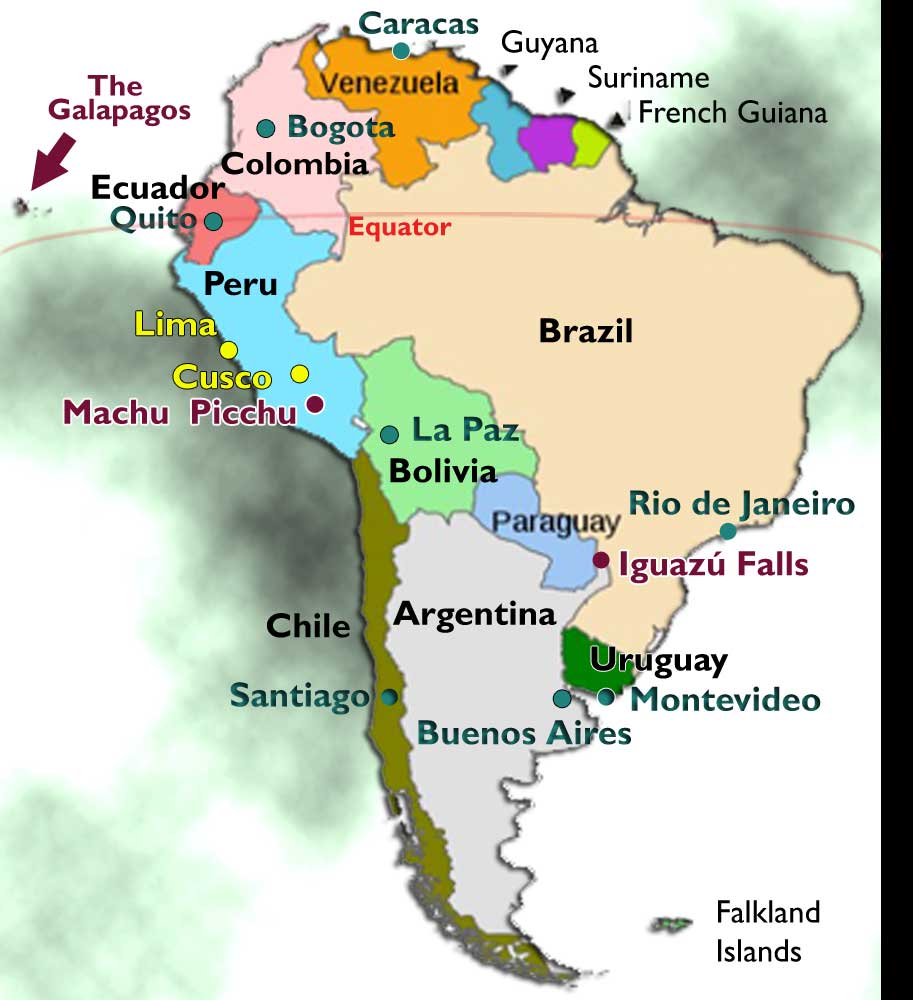
South America, the fourth largest continent by landmass, is a fascinating tapestry of diverse landscapes, cultures, and ecosystems. One of its most defining geographical features is its unique relationship with the equator. This imaginary line, which circles the globe at zero degrees latitude, bisects South America, creating a distinct division between the northern and southern hemispheres.
A Geographical Divide: The Equator’s Impact
The equator’s passage through South America has a profound influence on the continent’s climate, biodiversity, and human settlements.
Climate and Vegetation:
- Tropical Climates: The equatorial region of South America, encompassing countries like Ecuador, Colombia, and northern Peru, experiences a predominantly tropical climate characterized by high temperatures, high humidity, and abundant rainfall. This environment fosters lush rainforests teeming with biodiversity, such as the Amazon rainforest, the world’s largest tropical rainforest.
- Seasonal Variations: Moving further south and north of the equator, the climate becomes more seasonal, with distinct wet and dry seasons. This change is reflected in the vegetation, transitioning from dense rainforests to savannas, grasslands, and even deserts in the Atacama Desert of Chile, the driest non-polar desert in the world.
Biodiversity:
- Rich Ecosystems: The equatorial region of South America is a global biodiversity hotspot, home to an astonishing array of plant and animal species. The Amazon rainforest alone is estimated to hold 10% of the world’s known species.
- Endemic Species: The unique environmental conditions of the equatorial region have led to the evolution of many endemic species, found nowhere else on Earth. This includes iconic animals like the jaguar, the macaw, and the anaconda.
Human Settlements:
- Ancient Civilizations: The equator has played a significant role in the development of South American civilizations. The Inca Empire, for instance, flourished in the Andean highlands, a region straddling the equator.
- Modern Population Centers: Today, major cities like Quito, Ecuador, and Guayaquil, Ecuador, are situated along the equator, highlighting its importance as a transportation hub and center of trade.
Beyond the Equator: A Diverse Continent
While the equator holds a significant place in South America’s geography, the continent is much more than just a tropical paradise.
- Andean Mountains: The towering Andes mountain range, stretching along the western edge of South America, creates diverse microclimates and ecosystems, from snow-capped peaks to arid valleys.
- Patagonia: In the south, the Patagonian region encompasses vast steppes, glaciers, and fjords, offering a stark contrast to the equatorial rainforests.
- Cultural Diversity: South America is home to a rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and traditions, reflecting the continent’s complex history and diverse population.
South America’s Equator: A Source of Inspiration and Wonder
The equator’s passage through South America is a testament to the continent’s geographical diversity and its unique position on the globe. It serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of our planet and the importance of preserving its rich ecosystems and cultural heritage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about South America’s Equator:
1. What is the significance of the equator?
The equator is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at zero degrees latitude, dividing the globe into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It is important because it influences climate, biodiversity, and human settlements.
2. Which countries in South America are crossed by the equator?
The equator passes through six countries in South America: Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, Peru, Guyana, and Suriname.
3. What are the main characteristics of the equatorial climate in South America?
The equatorial climate in South America is characterized by high temperatures, high humidity, and abundant rainfall throughout the year. It is associated with lush rainforests and a high level of biodiversity.
4. What are some of the unique features of the Amazon rainforest?
The Amazon rainforest is the largest tropical rainforest in the world, encompassing over 5.5 million square kilometers. It is home to an estimated 10% of the world’s known species, including countless plants, animals, and insects.
5. How has the equator influenced the development of South American civilizations?
The equator has played a significant role in the development of South American civilizations. The Inca Empire, for instance, flourished in the Andean highlands, a region straddling the equator. The availability of resources and fertile land along the equator has been crucial for human settlements and agricultural development.
6. What are some of the challenges associated with the equatorial region of South America?
The equatorial region of South America faces challenges such as deforestation, climate change, and biodiversity loss. The Amazon rainforest, for example, is threatened by deforestation due to agricultural expansion and illegal logging.
Tips for Exploring South America’s Equator:
- Visit Ecuador: Ecuador, as its name suggests, is located directly on the equator. The country offers a range of experiences, from the bustling capital city of Quito to the Galapagos Islands, a renowned wildlife sanctuary.
- Explore the Amazon Rainforest: The Amazon rainforest is a must-visit for any nature enthusiast. You can take guided tours, go on wildlife expeditions, or simply immerse yourself in the beauty of this unique ecosystem.
- Learn about the indigenous cultures: South America is home to a diverse array of indigenous cultures. Visiting indigenous communities and learning about their traditions and way of life can provide a deeper understanding of the continent’s rich heritage.
Conclusion:
The equator’s passage through South America is a defining geographical feature that has shaped the continent’s climate, biodiversity, and human settlements. From the lush rainforests of the Amazon to the towering Andes mountains, South America offers a diverse and fascinating journey for those seeking to explore the wonders of this equatorial world. Understanding the continent’s relationship with the equator provides a deeper appreciation for its unique natural and cultural heritage.


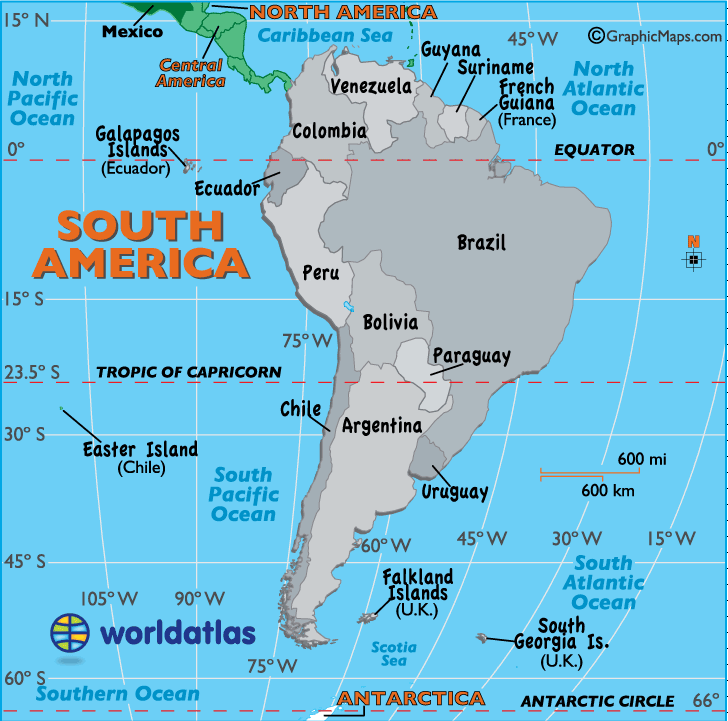


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/countries-that-lie-on-the-equator-1435319_V2-01-28e48f27870147d3a00edc1505f55770.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!