The Abbasid Caliphate: A Map of Power and Influence
Related Articles: The Abbasid Caliphate: A Map of Power and Influence
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Abbasid Caliphate: A Map of Power and Influence. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Abbasid Caliphate: A Map of Power and Influence
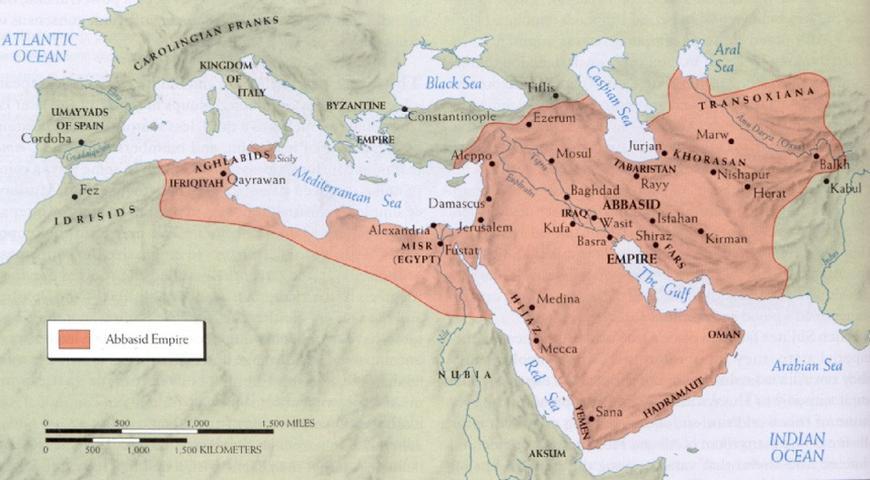
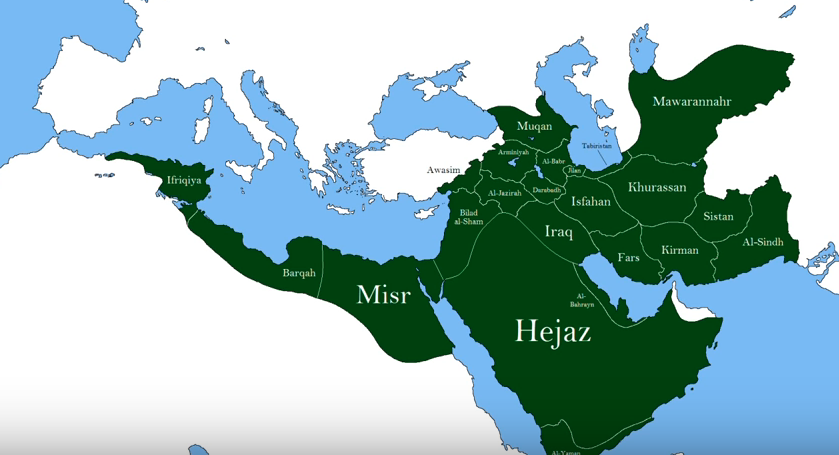
The Abbasid Caliphate, a powerful Islamic dynasty that ruled much of the Middle East and beyond for over five centuries, left an indelible mark on history. A study of the Abbasid Caliphate map reveals not only the vast geographical extent of their dominion but also the complex interplay of political, cultural, and economic factors that shaped their rise and fall. This article delves into the intricacies of the Abbasid Caliphate map, examining its evolution, key features, and lasting significance.
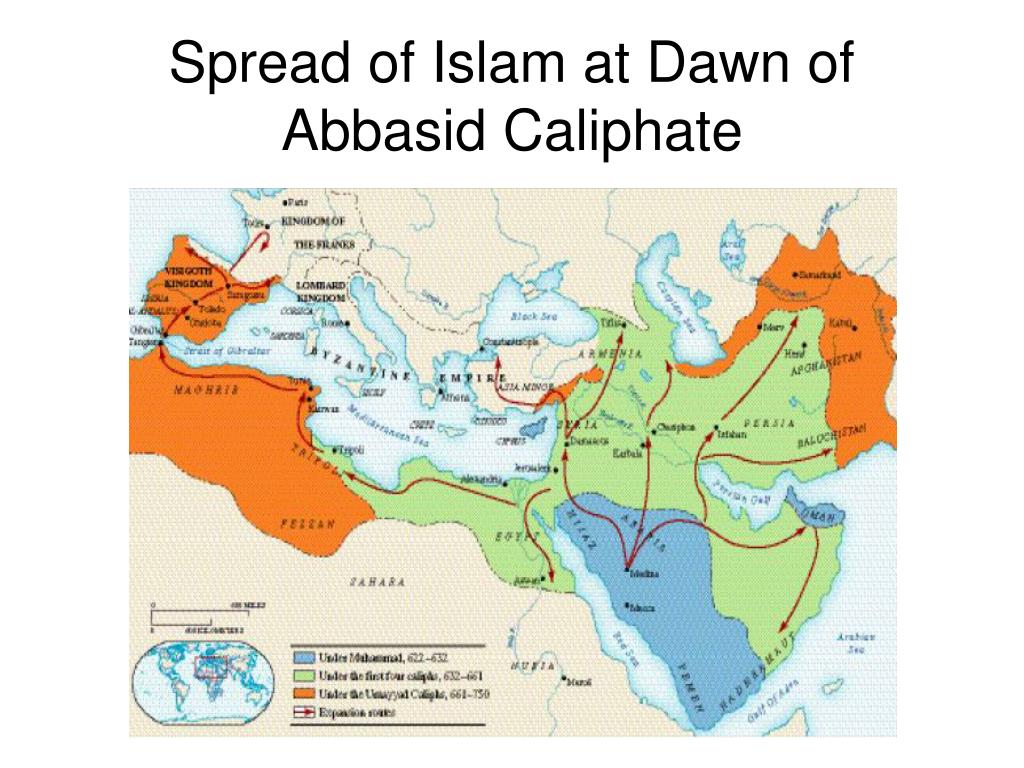
From Damascus to Baghdad: The Shift in Power
The Abbasid Caliphate emerged from the fertile ground of Umayyad rule, overthrowing the dynasty in 750 CE. The Abbasids, descendants of the Prophet Muhammad’s uncle, Abbas, consolidated their power by establishing their capital in Baghdad, a strategically located city on the Tigris River. This move marked a significant shift in the center of Islamic power, moving from Damascus to Baghdad, and ushered in a new era of cultural and intellectual flourishing.
A Map of Expansion and Consolidation
The Abbasid Caliphate map initially encompassed the territories formerly controlled by the Umayyads, including Syria, Palestine, Egypt, and North Africa. However, the Abbasid Caliphate map expanded rapidly under the reign of Harun al-Rashid (786-809 CE), reaching its zenith in terms of territorial extent. At its peak, the Caliphate encompassed a vast territory stretching from modern-day Spain in the west to parts of Central Asia in the east, including the Arabian Peninsula, Persia, Mesopotamia, and parts of Anatolia.
Key Features of the Abbasid Caliphate Map:
- The Golden Age of Islam: The Abbasid Caliphate witnessed a cultural and intellectual renaissance known as the "Golden Age of Islam." This period saw significant advancements in science, mathematics, astronomy, medicine, philosophy, and literature. The map of the Abbasid Caliphate reflected this intellectual flourishing, as centers of learning like Baghdad, Damascus, and Cordoba became hubs of knowledge and scholarship.
- Trade and Commerce: The Abbasid Caliphate map highlights the importance of trade routes that crisscrossed the empire. The Silk Road, connecting the East to the West, passed through Abbasid territories, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures. This commercial activity contributed significantly to the Caliphate’s economic prosperity and cultural dynamism.
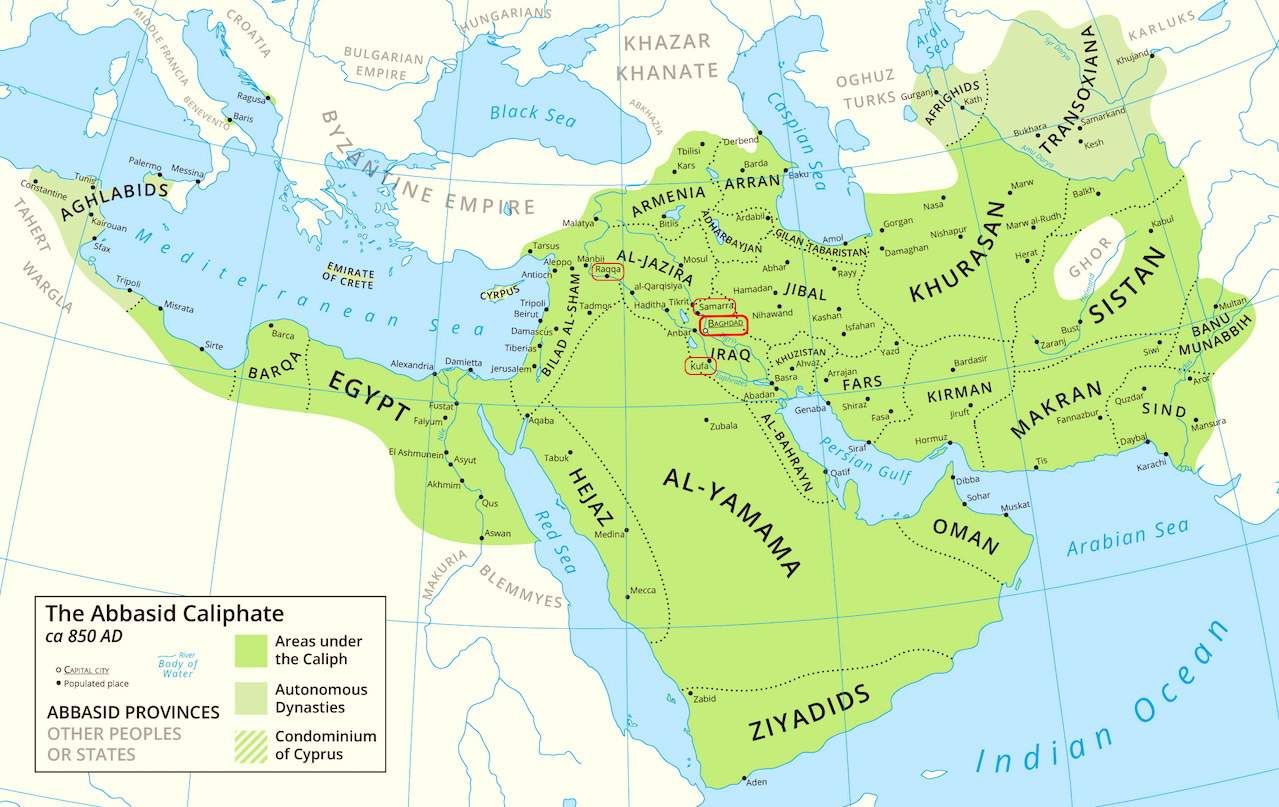
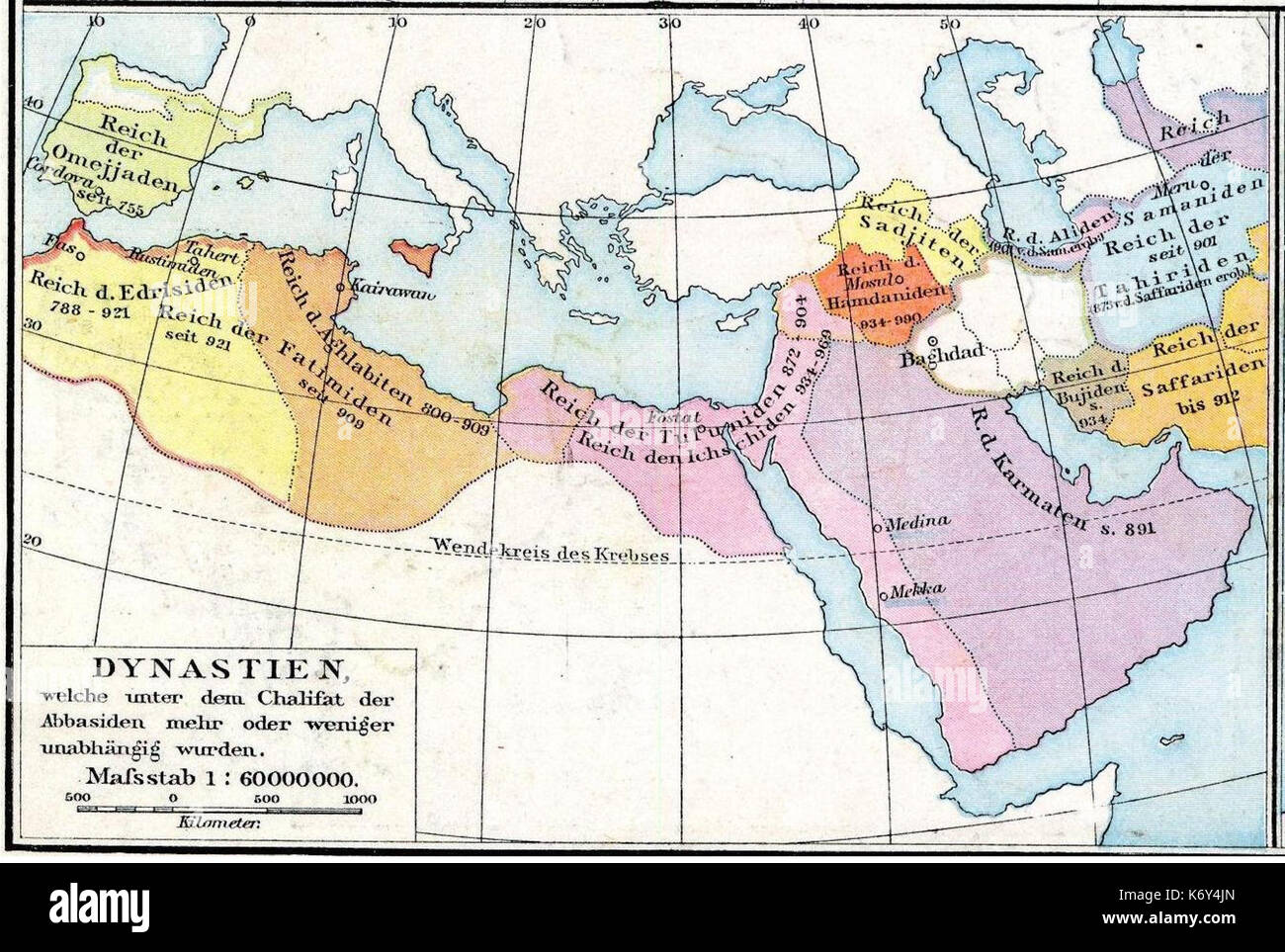
- Political Fragmentation: Despite its vastness, the Abbasid Caliphate map also reveals the inherent instability within the empire. Political fragmentation began to emerge in the 9th century CE, with regional governors asserting their independence and challenging the authority of the Caliph. This process of decentralization ultimately contributed to the Caliphate’s decline.
- Dynastic Struggles: The Abbasid Caliphate map reflects the constant power struggles within the dynasty. Rival claimants to the Caliphate, often supported by ambitious provincial governors, engaged in internecine warfare that weakened the empire’s central authority. These internal conflicts further contributed to the Caliphate’s fragmentation.
- The Rise of New Powers: The Abbasid Caliphate map also reflects the emergence of new powerful entities within its borders. The rise of the Turkish Mamluks in Egypt, the emergence of the Fatimid Caliphate in North Africa, and the establishment of independent Islamic kingdoms in Spain and Persia all signaled the weakening of Abbasid control.
The Decline and Fall of the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate, despite its initial grandeur, faced a gradual decline and eventual collapse. Internal conflicts, external threats, and the rise of new powers contributed to its demise. The Caliphate map, once a symbol of power and unity, became fragmented and ultimately dissolved in the 13th century CE. The Mongol invasion under Hulagu Khan, culminating in the sack of Baghdad in 1258 CE, marked the symbolic end of the Abbasid Caliphate.
The Lasting Legacy of the Abbasid Caliphate
Despite its eventual fall, the Abbasid Caliphate left an enduring legacy. The cultural achievements of the Golden Age of Islam, the advancements in science and technology, and the spread of Islamic knowledge throughout the world are all testaments to the Caliphate’s lasting impact. The Abbasid Caliphate map serves as a reminder of the dynamic interplay of political, cultural, and economic forces that shaped the history of the Middle East and beyond.
FAQs about the Abbasid Caliphate Map:
Q: What was the largest extent of the Abbasid Caliphate?
A: At its peak, the Abbasid Caliphate encompassed a vast territory stretching from modern-day Spain in the west to parts of Central Asia in the east, including the Arabian Peninsula, Persia, Mesopotamia, and parts of Anatolia.
Q: What factors contributed to the decline of the Abbasid Caliphate?
A: The decline of the Abbasid Caliphate was attributed to a combination of factors, including internal conflicts, external threats, the rise of new powers, and economic instability.
Q: What was the significance of Baghdad as the Abbasid capital?
A: Baghdad’s strategic location on the Tigris River, its access to trade routes, and its cultural and intellectual dynamism made it an ideal location for the Abbasid Caliphate’s capital.
Q: How did the Abbasid Caliphate contribute to the spread of Islamic knowledge?
A: The Abbasid Caliphate established centers of learning, supported scholars and translators, and facilitated the exchange of knowledge through trade routes, contributing significantly to the spread of Islamic knowledge throughout the world.
Q: What are some of the lasting legacies of the Abbasid Caliphate?
A: The Abbasid Caliphate left behind a lasting legacy, including the cultural achievements of the Golden Age of Islam, advancements in science and technology, and the spread of Islamic knowledge.
Tips for Understanding the Abbasid Caliphate Map:
- Study the key geographic features: The Abbasid Caliphate map highlights the importance of trade routes, major cities, and natural barriers that shaped the empire’s development.
- Examine the political divisions: The map reveals the fragmentation of the Caliphate into regional provinces and the emergence of independent kingdoms.
- Consider the cultural and intellectual centers: The map highlights the cities that became hubs of scholarship, scientific advancements, and artistic expression.
- Analyze the impact of external threats: The map reveals the challenges posed by neighboring empires and nomadic tribes.
- Understand the dynamic nature of the empire: The map reflects the constant shifts in power, territorial control, and cultural influence.
Conclusion:
The Abbasid Caliphate map is a powerful tool for understanding the rise and fall of a dynamic and influential empire. It reveals the complex interplay of political, cultural, and economic forces that shaped the history of the Middle East and beyond. The map serves as a reminder of the Abbasid Caliphate’s enduring legacy, its contributions to the Golden Age of Islam, and its lasting impact on the world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Abbasid Caliphate: A Map of Power and Influence. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!