The Enigmatic Geography of Russia: A Vast Landscape of Diverse Terrain and Climate
Related Articles: The Enigmatic Geography of Russia: A Vast Landscape of Diverse Terrain and Climate
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Enigmatic Geography of Russia: A Vast Landscape of Diverse Terrain and Climate. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enigmatic Geography of Russia: A Vast Landscape of Diverse Terrain and Climate

Russia, the largest country in the world by land area, is a land of extremes, encompassing a staggering diversity of landscapes, climates, and resources. Its geography is a defining characteristic, influencing its history, culture, and economic development. Understanding the complexities of Russia’s map is crucial for comprehending its unique position on the world stage.
A Vast and Diverse Landscape:
Russia stretches across eleven time zones, spanning over 11,000 kilometers from east to west and 4,000 kilometers from north to south. Its vastness is unparalleled, encompassing 17.1 million square kilometers, encompassing over 1/8th of the Earth’s inhabited landmass. This sheer size creates a mosaic of diverse landscapes, from the frozen tundra of the Arctic to the fertile steppes of the south, the dense forests of Siberia to the rolling hills of the European part of the country.
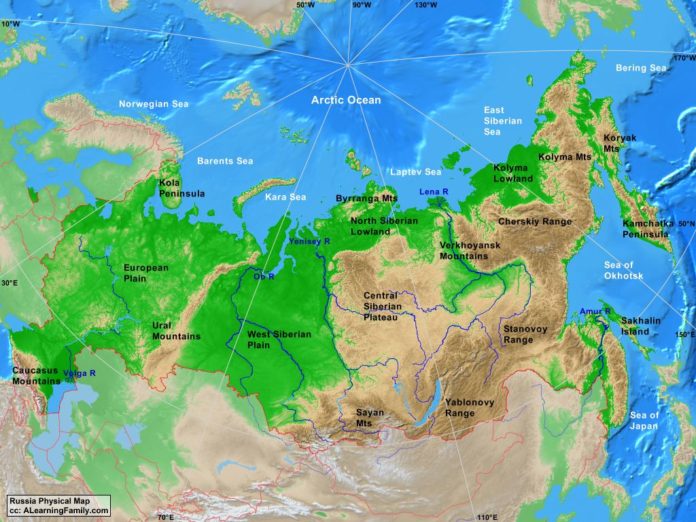
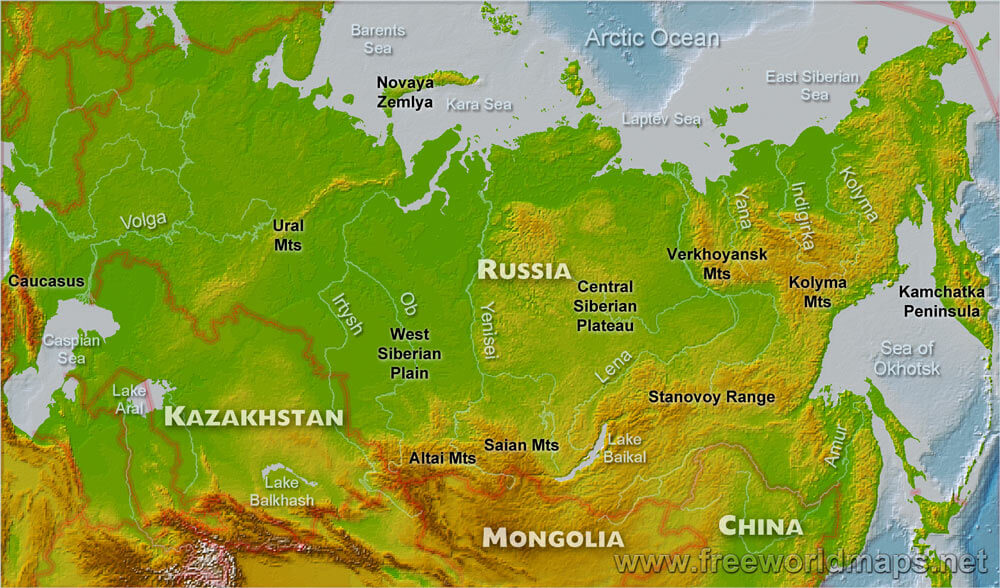
The European Plain:
The westernmost region of Russia, known as the European Plain, is a vast expanse of flat, fertile land. This region is home to the majority of Russia’s population and its major cities, including Moscow, St. Petersburg, and Nizhny Novgorod. The European Plain is characterized by its rich agricultural lands, providing the country with a significant portion of its food production.
The Ural Mountains:
Marking the boundary between Europe and Asia, the Ural Mountains are a significant geological feature. This ancient mountain range, stretching for over 2,000 kilometers, is rich in mineral resources, including iron, copper, and nickel. The Urals serve as a natural barrier, influencing the climate and vegetation on either side.
Siberia:
Beyond the Urals lies Siberia, a vast and sparsely populated region encompassing over 75% of Russia’s landmass. Siberia is dominated by the West Siberian Plain, a flat, low-lying region with extensive swamps and wetlands. Further east, the Central Siberian Plateau rises, characterized by its rugged terrain and harsh climate. Siberia is renowned for its vast forests, known as taiga, which hold a significant portion of the world’s timber reserves.
The Russian Far East:
The Russian Far East, bordering China, North Korea, and Mongolia, is a region of dramatic landscapes, including the Kamchatka Peninsula, known for its active volcanoes and geothermal activity. This region is characterized by its mountainous terrain, dense forests, and a harsh continental climate.
Climate and Resources:
Russia’s vast territory experiences a wide range of climates, influenced by its latitude, proximity to the ocean, and complex terrain. The north is dominated by a frigid Arctic climate, while the south enjoys a more temperate continental climate. This diverse climate supports a wide range of vegetation, from the tundra and taiga of the north to the steppes and forests of the south.
Russia is richly endowed with natural resources, including vast reserves of oil, natural gas, coal, and timber. Its mineral wealth is also significant, with deposits of iron ore, nickel, copper, and diamonds. These resources have played a crucial role in shaping the country’s economy and its global influence.
Geographic Challenges and Opportunities:
Russia’s vast size and diverse geography present both challenges and opportunities. The harsh climate and challenging terrain have historically hindered development and transportation, particularly in Siberia and the Far East. However, these vast expanses also offer potential for resource extraction, agricultural development, and tourism.
The country’s long borders with numerous countries, including China, Mongolia, and Ukraine, present both opportunities for trade and cooperation, as well as potential security concerns. Russia’s geographic position, straddling Europe and Asia, has historically made it a crossroads of cultural and economic exchange.
Navigating the Complexities of Russia’s Geography:
Understanding Russia’s geography is essential for comprehending its history, culture, and political landscape. Its vastness and diversity have shaped its unique identity and its role in the world. From the fertile European Plain to the rugged Siberian wilderness, Russia’s map tells a story of both beauty and challenges, highlighting the country’s immense potential and its complex geopolitical position.
FAQs about Russia’s Geography:
-
What is the highest mountain in Russia? Mount Elbrus, located in the Caucasus Mountains, is the highest mountain in Russia and Europe, reaching a height of 5,642 meters.
-
What is the largest river in Russia? The Ob River, flowing through Western Siberia, is the largest river in Russia by volume and the seventh longest in the world.
-
What is the largest lake in Russia? Lake Baikal, located in Siberia, is the largest freshwater lake by volume in the world, holding over 20% of the world’s unfrozen freshwater.
-
What is the largest city in Russia? Moscow, the capital of Russia, is the largest city by population, with over 12 million inhabitants.
-
What are the main geographical features of Russia? Russia’s main geographical features include the European Plain, the Ural Mountains, Siberia, the Russian Far East, and the Caucasus Mountains.
-
What are the main climate zones in Russia? Russia experiences a wide range of climates, including the Arctic, subarctic, humid continental, and steppe climates.
-
What are the main natural resources of Russia? Russia is rich in natural resources, including oil, natural gas, coal, timber, iron ore, nickel, copper, and diamonds.
Tips for Studying Russia’s Geography:
-
Utilize online maps and atlases: Interactive maps can provide detailed information about Russia’s geography, including physical features, climate zones, and major cities.
-
Explore geographical documentaries and films: Visual media can offer a deeper understanding of Russia’s diverse landscapes and its unique geographical challenges.
-
Read books and articles on Russian geography: There are numerous resources available that provide comprehensive insights into the country’s geography, history, and culture.
-
Engage with experts: Consult with geographers, historians, and political scientists to gain deeper knowledge about Russia’s complex geographical landscape.
Conclusion:
Russia’s vast and diverse geography is a defining characteristic of the country, influencing its history, culture, and economic development. Understanding the complexities of its map is crucial for comprehending its unique position on the world stage. From the fertile plains of the west to the rugged mountains of the east, Russia’s landscape presents both challenges and opportunities, shaping its identity and its role in global affairs. By studying Russia’s geography, we gain a deeper appreciation for its unique character and its enduring influence on the world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enigmatic Geography of Russia: A Vast Landscape of Diverse Terrain and Climate. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!