The Great Rift Valley: A Geological Tapestry Across Africa
Related Articles: The Great Rift Valley: A Geological Tapestry Across Africa
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Great Rift Valley: A Geological Tapestry Across Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Great Rift Valley: A Geological Tapestry Across Africa
/ethiopia-rift-valley-aerial-view-sb10068596hq-001-5878cd753df78c17b65b7898.jpg)
The Great Rift Valley, an immense geological feature stretching over 6,000 kilometers across eastern Africa, is a testament to the dynamic forces shaping our planet. This vast tectonic landscape, characterized by a series of valleys, volcanoes, and lakes, is a product of the ongoing separation of the African tectonic plate, a process that has been unfolding for millions of years.
A Journey Through Time: Understanding the Rift Valley’s Formation
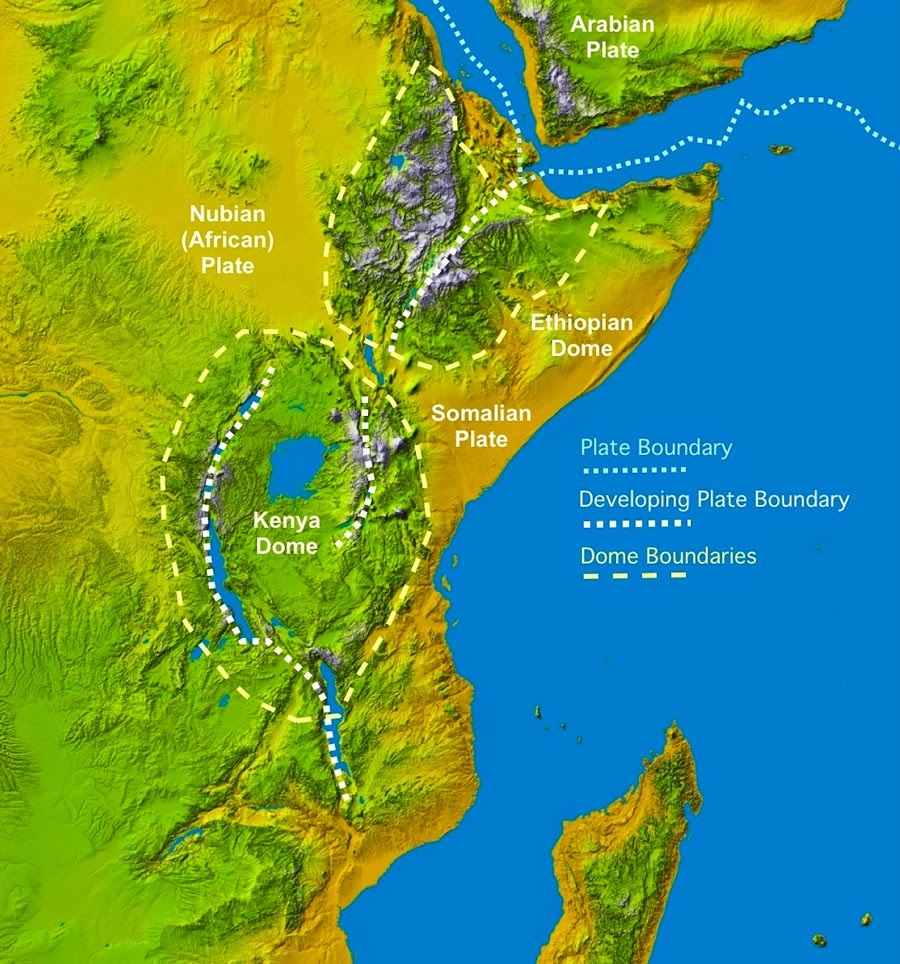
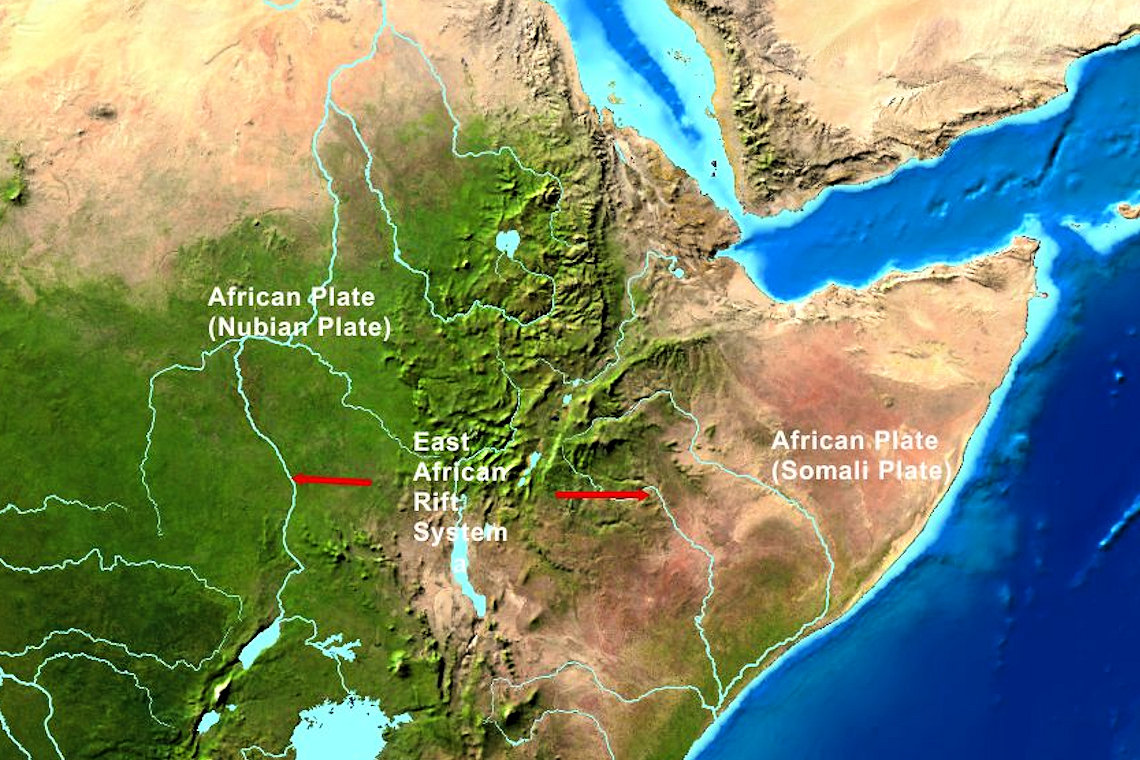
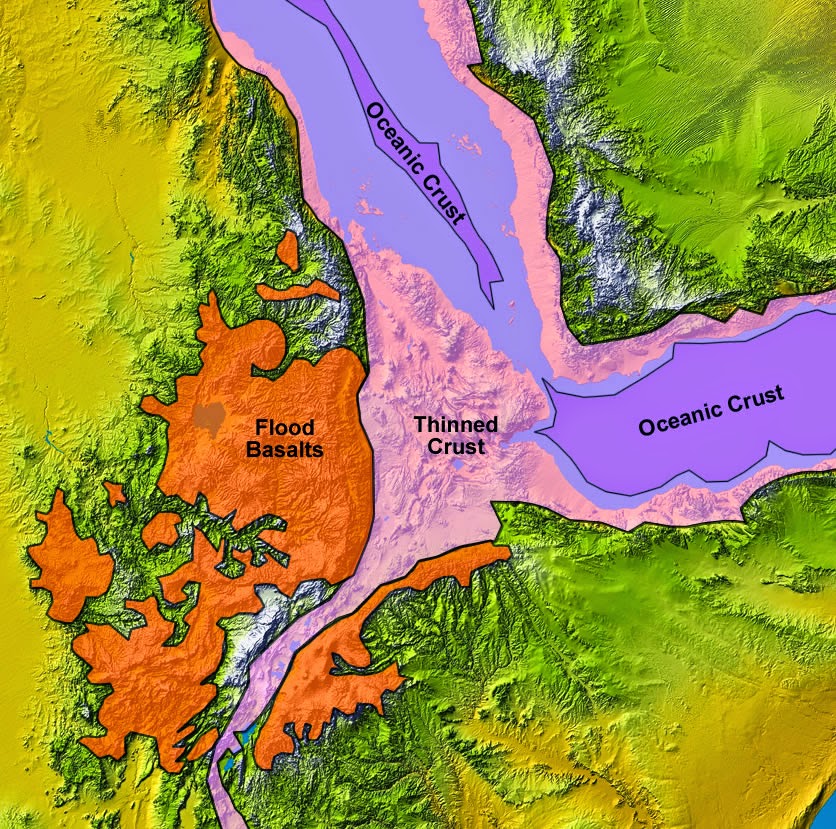
The story of the Great Rift Valley begins with the slow, relentless movement of tectonic plates. Millions of years ago, the African plate began to fracture, creating a zone of weakness that allowed magma from the Earth’s mantle to rise. This upward pressure, coupled with the tension of the separating plates, caused the Earth’s crust to stretch and thin, leading to the formation of a series of valleys, known as rift valleys.
The Rift Valley’s formation is a dynamic process, characterized by volcanic activity, earthquakes, and the gradual widening of the rift. The valley itself is not a single continuous feature, but rather a series of interconnected valleys, each with its own unique geological history and characteristics.
Mapping the Rift: A Geographical Overview
The Great Rift Valley can be broadly divided into two branches: the Eastern Rift Valley and the Western Rift Valley.
The Eastern Rift Valley: This branch, stretching from the Afar Triangle in Ethiopia to Mozambique, is a dramatic landscape of towering volcanoes, deep valleys, and vast alkaline lakes. Notable features include:
- The Ethiopian Highlands: A plateau characterized by volcanic peaks like Mount Ras Dashen, the highest mountain in Ethiopia.
- The Afar Triangle: A unique geological formation where the African, Arabian, and Somali plates meet, resulting in intense volcanic activity and the formation of the Danakil Depression, one of the hottest and lowest places on Earth.
- The Kenyan Rift Valley: Home to iconic landmarks like Mount Kenya and the Great Rift Valley Lakes, including Lake Nakuru, renowned for its flamingo populations.
- The Tanzanian Rift Valley: Featuring the renowned Ngorongoro Crater, a collapsed volcano that forms a natural wildlife sanctuary, and Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa’s highest mountain.
The Western Rift Valley: This branch, located in Central Africa, is characterized by a series of deep lakes, including Lake Tanganyika, the world’s second deepest lake, and Lake Malawi, known for its diverse fish populations.
The Rift Valley: A Cradle of Life and a Hotspot of Biodiversity
The Great Rift Valley is not merely a geological marvel; it is also a haven for biodiversity. The unique landscapes, including the volcanic soils, abundant water resources, and varied climates, have fostered a remarkable array of plant and animal life.
- The Rift Valley Lakes: These diverse ecosystems, ranging from freshwater to alkaline lakes, support a rich tapestry of aquatic life, including fish, crocodiles, hippos, and numerous bird species.
- The Volcanic Landscapes: The fertile volcanic soils support a wide range of vegetation, from dense forests to grasslands, providing habitats for a variety of mammals, birds, and reptiles.
- The Rift Valley’s Unique Flora and Fauna: The region is home to iconic species like the African wild dog, the black rhinoceros, the mountain gorilla, and numerous bird species, including the shoebill stork and the secretary bird.
The Rift Valley’s Importance: A Hub for Human History and Development
The Great Rift Valley has played a pivotal role in the history of humankind. Archaeological evidence suggests that early hominids originated in the region, and the valley’s rich resources have sustained human settlements for millennia.
- The Cradle of Humankind: The Rift Valley’s volcanic ash deposits have preserved a wealth of fossils, providing crucial insights into human evolution.
- Agriculture and Trade: The valley’s fertile soils and abundant water resources have supported agricultural development and trade networks for centuries.
- Modern Development: Today, the Rift Valley is a center for tourism, agriculture, and mineral extraction.
FAQs: Understanding the Great Rift Valley
Q: What is the Great Rift Valley?
A: The Great Rift Valley is a vast geological feature stretching across eastern Africa, formed by the separation of the African tectonic plate. It is characterized by a series of valleys, volcanoes, and lakes.
Q: How was the Great Rift Valley formed?
A: The Rift Valley formed due to the movement of tectonic plates. The African plate began to fracture, allowing magma to rise from the Earth’s mantle. This upward pressure, combined with the tension of the separating plates, caused the Earth’s crust to stretch and thin, creating the valleys.
Q: What are the major features of the Great Rift Valley?
A: The Rift Valley is characterized by:
- Volcanoes: Numerous active and dormant volcanoes, including Mount Kenya, Mount Kilimanjaro, and Mount Nyiragongo.
- Lakes: A series of lakes, including Lake Tanganyika, Lake Victoria, and Lake Malawi, some of which are the deepest in the world.
- Valleys: Deep, wide valleys, often characterized by steep cliffs and dramatic landscapes.
Q: What is the significance of the Great Rift Valley?
A: The Rift Valley is significant for its:
- Geological Importance: It provides a unique window into the processes of plate tectonics and the formation of continents.
- Biodiversity: It supports a diverse range of plant and animal life, including many endangered species.
- Human History: It is considered the cradle of humankind, with numerous fossil discoveries providing insights into human evolution.
Tips for Exploring the Great Rift Valley
- Choose your focus: The Rift Valley is vast, so focus on specific areas that interest you, such as wildlife viewing, volcanic landscapes, or cultural experiences.
- Consider the time of year: The best time to visit depends on your interests. The dry season (June-October) is ideal for wildlife viewing, while the rainy season (November-May) offers lush landscapes and fewer crowds.
- Be prepared for diverse conditions: The Rift Valley’s climate varies significantly, from the hot and dry plains to the cooler highlands. Pack appropriate clothing and footwear.
- Respect the environment: Be mindful of your impact on the environment, especially when visiting sensitive ecosystems.
- Engage with local communities: Learn about the cultures and traditions of the people who live in the Rift Valley.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Earth’s Dynamics
The Great Rift Valley is a captivating testament to the dynamic forces that shape our planet. Its dramatic landscapes, diverse ecosystems, and rich human history make it a region of unparalleled beauty and significance. Understanding the Rift Valley’s geological formation, biodiversity, and cultural importance provides a deeper appreciation for the intricate connections between Earth’s processes and the evolution of life. As the African plate continues to separate, the Rift Valley will continue to evolve, leaving an enduring legacy for future generations to explore and understand.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Great Rift Valley: A Geological Tapestry Across Africa. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!