The Greenbelt: A Vital Framework for Sustainable Urban Development
Related Articles: The Greenbelt: A Vital Framework for Sustainable Urban Development
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Greenbelt: A Vital Framework for Sustainable Urban Development. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Greenbelt: A Vital Framework for Sustainable Urban Development
.jpg?1534511942)
The concept of a greenbelt, a ring of protected land surrounding a city or urban area, has gained significant traction in urban planning and development strategies worldwide. Greenbelts serve as crucial buffers against urban sprawl, promoting sustainable growth and ensuring the preservation of natural ecosystems. This article explores the multifaceted role of greenbelts, highlighting their importance in safeguarding biodiversity, improving air quality, mitigating climate change, and enhancing the quality of life for urban residents.
Understanding the Greenbelt: A Protective Barrier
Greenbelts are characterized by their distinct land-use designations, typically encompassing a range of natural landscapes, such as forests, meadows, wetlands, and agricultural lands. These areas are legally protected from development, preventing the encroachment of urban infrastructure and preserving the natural character of the surrounding countryside.
Benefits of Greenbelts: A Multifaceted Impact
The benefits of greenbelts extend far beyond their aesthetic appeal, contributing significantly to environmental sustainability and urban well-being:
1. Protecting Biodiversity and Ecosystems: Greenbelts act as vital corridors for wildlife movement, connecting fragmented habitats and allowing for the dispersal of species. They provide refuge for endangered and threatened species, safeguarding biodiversity and preserving the intricate balance of ecosystems.
2. Enhancing Air Quality: Trees and vegetation within greenbelts act as natural air filters, absorbing pollutants and releasing oxygen. This process helps to improve air quality, reducing respiratory ailments and promoting public health.
3. Mitigating Climate Change: Greenbelts play a crucial role in mitigating climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Trees and other vegetation absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, storing it in their tissues and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
4. Regulating Water Flow and Preventing Flooding: Greenbelts act as natural sponges, absorbing rainfall and slowing down water runoff. This helps to prevent flooding, improve water quality, and recharge groundwater supplies.
5. Providing Recreation and Open Space: Greenbelts offer valuable recreational opportunities for urban residents, providing spaces for hiking, cycling, picnicking, and other outdoor activities. This access to nature promotes physical and mental well-being, reducing stress and improving overall quality of life.
6. Preserving Agricultural Land: Greenbelts often include agricultural lands, ensuring the continued production of food and protecting valuable farmland from development. This helps to secure food security and maintain the viability of local agricultural economies.
7. Promoting Sustainable Urban Development: Greenbelts act as a physical barrier to urban sprawl, preventing the encroachment of development into surrounding natural areas. This encourages denser, more sustainable urban development, reducing reliance on car travel and promoting walkability and public transportation.
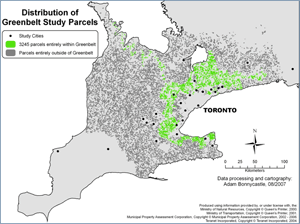
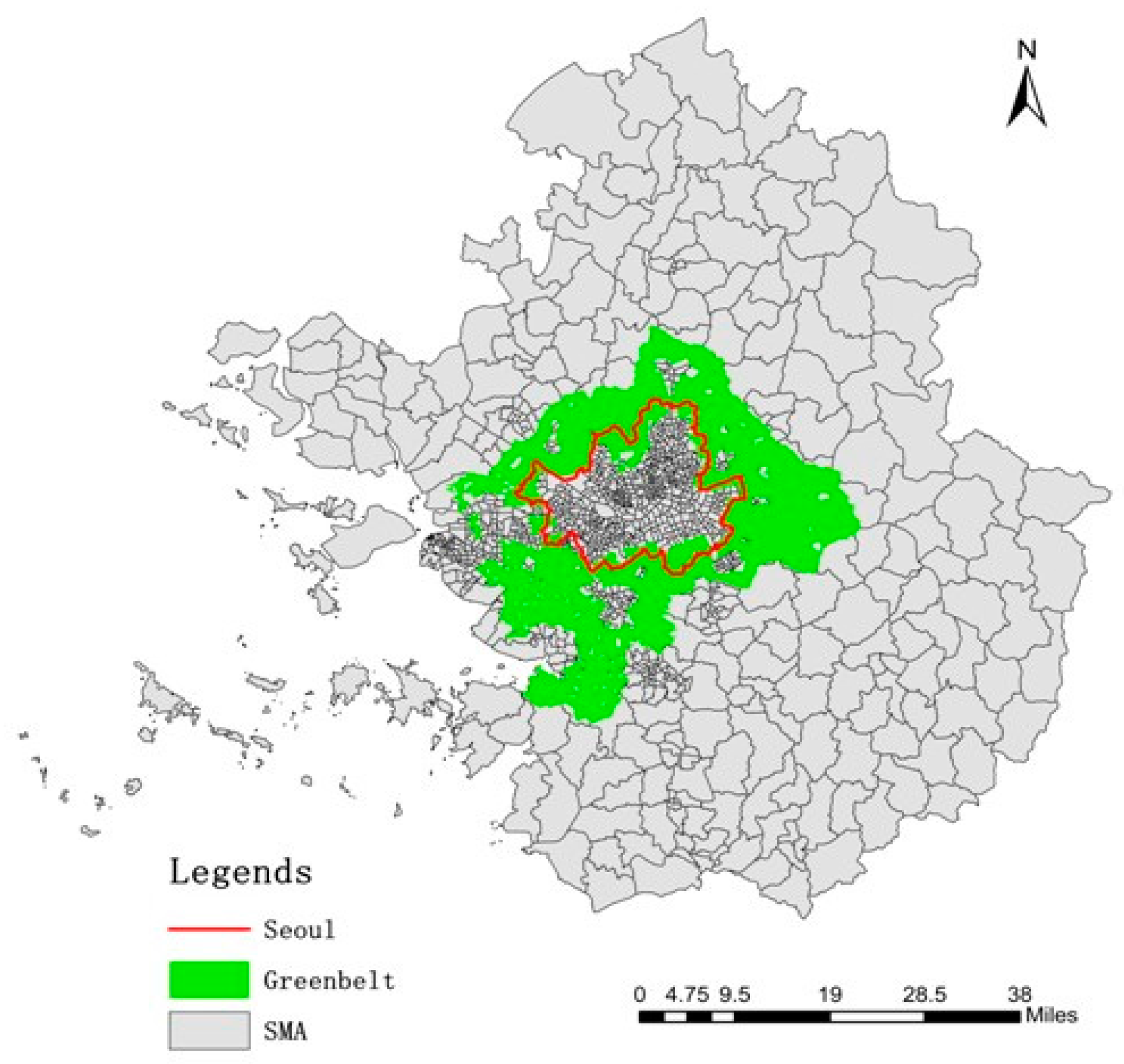
Mapping the Greenbelt: A Visual Representation of Sustainability
Maps of greenbelts serve as essential tools for understanding the spatial extent and characteristics of these protected areas. These maps provide valuable information for planning and decision-making, ensuring that development occurs in a sustainable manner and respects the ecological integrity of the greenbelt.
Key Features of Greenbelt Maps:
- Land Use Boundaries: Greenbelt maps clearly delineate the boundaries of protected areas, separating them from surrounding urban and agricultural lands.
- Natural Features: Maps should highlight key natural features within the greenbelt, such as forests, wetlands, rivers, and agricultural lands.
- Infrastructure: Existing infrastructure within the greenbelt, such as roads, trails, and public facilities, should be indicated on the map.
- Conservation Zones: Maps may identify specific conservation zones within the greenbelt, highlighting areas of particular ecological significance.
- Development Restrictions: Maps should indicate any restrictions on development within the greenbelt, such as building height limits or limitations on land use.
FAQs on Greenbelts:
Q: Why are greenbelts important for cities?
A: Greenbelts play a vital role in safeguarding biodiversity, improving air quality, mitigating climate change, and enhancing the quality of life for urban residents. They act as buffers against urban sprawl, promoting sustainable growth and preserving natural ecosystems.
Q: How are greenbelts established?
A: Greenbelts are typically established through legislation or local planning policies, which designate specific areas as protected from development. These policies may involve land acquisition, conservation easements, or other legal mechanisms.
Q: What are the challenges facing greenbelts?
A: Greenbelts face various challenges, including pressure from development, inadequate funding for maintenance, and lack of public awareness about their importance.
Q: How can I support greenbelts?
A: You can support greenbelts by advocating for their protection, volunteering with local conservation groups, and supporting organizations that work to preserve natural areas.
Tips for Implementing Greenbelts:
- Conduct thorough ecological assessments: Prioritize the preservation of ecologically significant areas and ensure that greenbelt boundaries are aligned with natural features.
- Involve stakeholders: Engage with local communities, landowners, and other stakeholders in the planning and implementation of greenbelts.
- Develop clear land-use regulations: Establish clear and enforceable regulations to prevent development within the greenbelt and ensure its long-term protection.
- Promote sustainable transportation: Encourage the use of public transportation, cycling, and walking to reduce reliance on cars and minimize environmental impact.
- Invest in green infrastructure: Support the development of green infrastructure, such as parks, trails, and green roofs, to enhance the aesthetic appeal and recreational value of greenbelts.
Conclusion:
Greenbelts are essential components of sustainable urban development, providing a multitude of benefits for both the environment and urban populations. By preserving natural areas, regulating urban growth, and fostering a connection between urban and rural landscapes, greenbelts play a crucial role in creating vibrant, resilient, and healthy cities for future generations. As urban areas continue to expand, the importance of greenbelts will only grow, making their protection and management a critical priority for sustainable urban planning.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Greenbelt: A Vital Framework for Sustainable Urban Development. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!