The Iroquois Confederacy: A Map of Unity and Strength
Related Articles: The Iroquois Confederacy: A Map of Unity and Strength
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Iroquois Confederacy: A Map of Unity and Strength. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Iroquois Confederacy: A Map of Unity and Strength
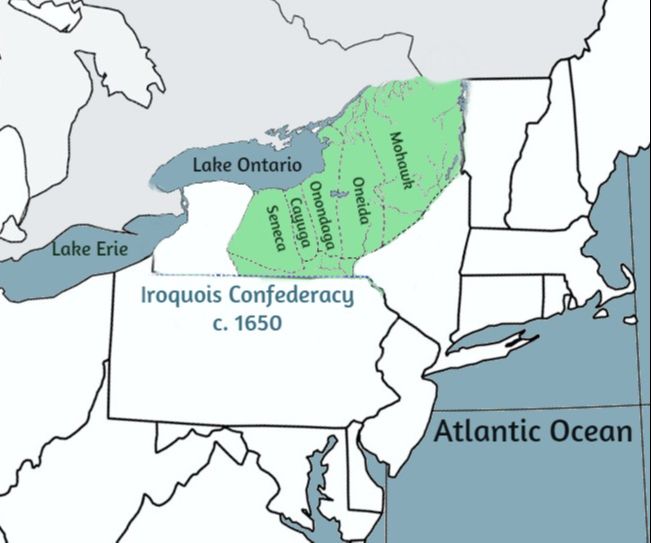
The Iroquois Confederacy, also known as the Haudenosaunee, stands as a testament to the power of unity and diplomacy in the face of adversity. This powerful alliance of six distinct Indigenous nations – the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, Seneca, and Tuscarora – thrived in the northeastern region of North America for centuries, leaving a lasting impact on the landscape and history of the continent. Understanding the Iroquois Confederacy requires a deep dive into their political structure, social organization, and geographic footprint, which can be best visualized through a map.
A Geographic Snapshot of Unity:
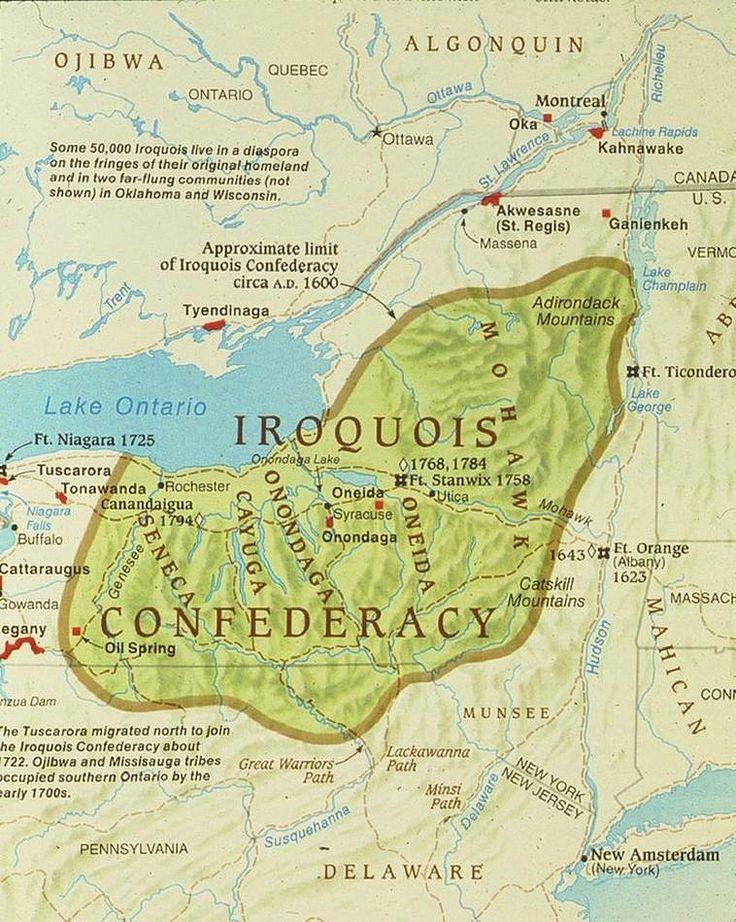
The map of the Iroquois Confederacy reveals a strategic positioning across a vast expanse of territory. Their original homeland, known as the "Long House," stretched from the St. Lawrence River in the north to the Susquehanna River in the south, encompassing parts of present-day New York, Pennsylvania, Ontario, and Quebec. This territory was rich in natural resources, including fertile farmlands, dense forests, and abundant waterways, providing the Confederacy with sustenance and facilitating trade.
The map clearly depicts the location of each of the six nations within the Confederacy:
- Mohawk: Situated in the north, they occupied the Mohawk Valley, a strategic corridor connecting the Great Lakes to the Atlantic coast.
- Oneida: Nestled between the Mohawk and Onondaga, they controlled the central portion of the Confederacy’s territory.
- Onondaga: Holding the central position, they served as the heart of the Confederacy, responsible for maintaining order and mediating disputes.
- Cayuga: Located south of the Onondaga, they occupied the Cayuga Lake region, known for its rich agricultural resources.
- Seneca: Situated in the southwestern corner of the Confederacy, they controlled the Genesee River Valley, a strategic location for trade and defense.
- Tuscarora: Joining the Confederacy in the early 18th century, they settled in the southern region, near the Seneca territory.
The map highlights the strategic placement of each nation, demonstrating how their geographic location contributed to their political and economic power. Their proximity to key waterways and trade routes allowed them to control the flow of goods and information, fostering a thriving economy and establishing a network of alliances.
Beyond Geography: The Political Structure of the Confederacy:
The map of the Iroquois Confederacy is not merely a geographic representation but a visual embodiment of a complex political structure. The Confederacy was governed by a Grand Council, comprised of fifty chiefs, representing the six nations. This council held the power to declare war, make treaties, and settle disputes. Each nation had a specific role and responsibility within the Confederacy, ensuring a balance of power and fostering a sense of unity.
The Onondaga, known as the "Keepers of the Fire," held a unique position as the central arbiters of the Confederacy. They were responsible for maintaining the sacred fire, a symbol of the Confederacy’s enduring spirit, and for mediating disputes among the nations. This system of governance, based on consensus and diplomacy, enabled the Confederacy to thrive for centuries, effectively managing internal conflict and projecting power onto the wider geopolitical landscape.
The Importance of the Iroquois Confederacy:
The map of the Iroquois Confederacy serves as a powerful reminder of the enduring legacy of this remarkable alliance. Their achievements in diplomacy, governance, and military prowess left an indelible mark on the history of North America.
- A Model of Unity and Governance: The Iroquois Confederacy stands as a testament to the power of unity and diplomacy. Their system of governance, based on consensus and shared decision-making, provided a model for peaceful coexistence and effective conflict resolution.
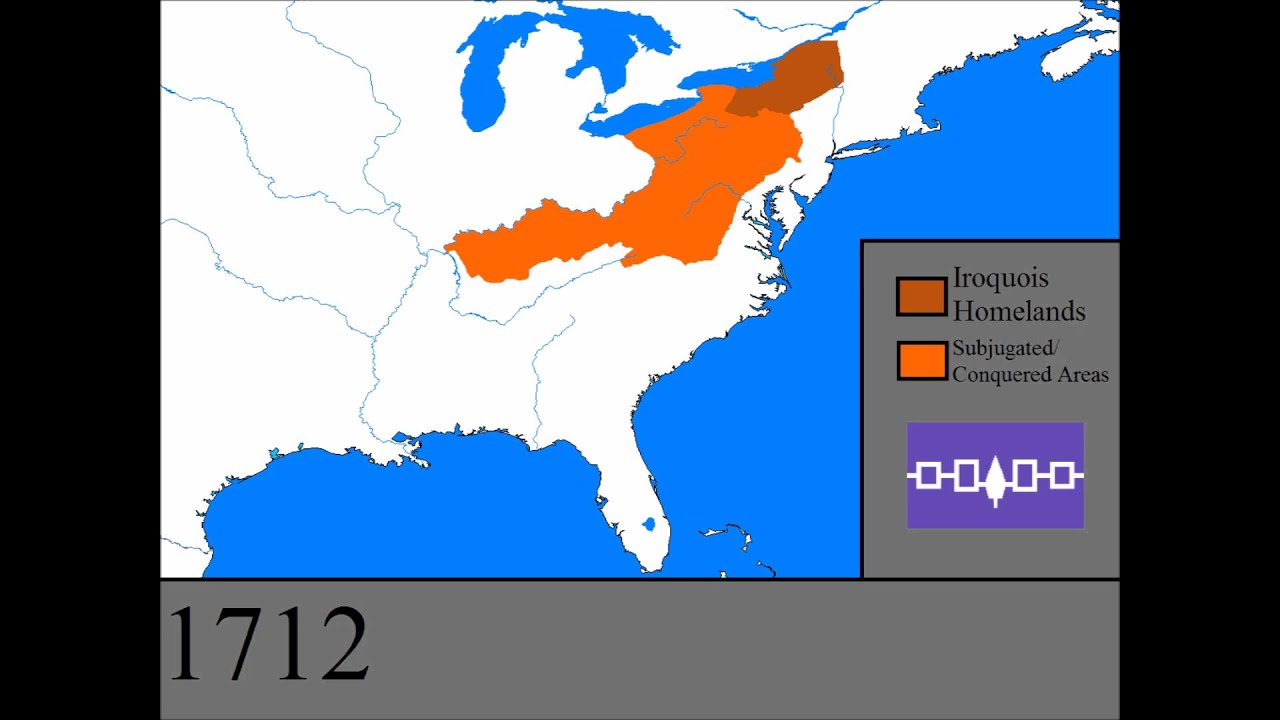
- A Force to be Reckoned With: The Confederacy’s military strength was renowned throughout the continent. Their skilled warriors and strategic alliances enabled them to maintain control over their vast territory and influence the balance of power in the region.
- A Legacy of Resilience: The Iroquois Confederacy faced numerous challenges throughout its history, including European colonization and warfare. Despite these hardships, they persevered, adapting to changing circumstances and preserving their unique culture and traditions.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How did the Iroquois Confederacy come to be?
The Iroquois Confederacy originated in the 15th century, when five nations – the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, and Seneca – united under the leadership of the legendary Peacemaker. Their alliance was forged through a shared vision of unity and peace, aiming to end the constant warfare that plagued their ancestors.
2. What was the role of the Grand Council in the Confederacy?
The Grand Council, comprised of fifty chiefs representing the six nations, served as the supreme governing body of the Confederacy. They held the power to declare war, make treaties, and settle disputes. The Grand Council operated on the principle of consensus, ensuring that all nations had a voice in decision-making.
3. What impact did the Iroquois Confederacy have on European colonization?
The Iroquois Confederacy played a significant role in shaping the course of European colonization in North America. They engaged in both alliances and conflicts with European powers, influencing the balance of power and the outcome of major wars. Their strength and influence forced European colonists to recognize their power and negotiate treaties.
4. What is the current status of the Iroquois Confederacy?
The Iroquois Confederacy continues to exist today, with its six nations maintaining a strong sense of identity and cultural heritage. They have faced numerous challenges, including assimilation policies and the loss of traditional lands, but they continue to advocate for their rights and self-determination.
Tips for Understanding the Iroquois Confederacy:
- Engage with the map: Studying the map of the Iroquois Confederacy is crucial to understanding their geographic footprint and the strategic placement of each nation.
- Explore primary sources: The writings of early European explorers and missionaries provide valuable insights into the Iroquois Confederacy’s culture, politics, and social organization.
- Learn about their oral traditions: The Iroquois Confederacy has a rich oral tradition that provides a deeper understanding of their history, beliefs, and values.
- Visit Iroquois communities: Visiting contemporary Iroquois communities offers a chance to experience their culture firsthand and learn from their elders.
Conclusion:
The map of the Iroquois Confederacy is not just a visual representation of a geographic area; it serves as a powerful symbol of unity, strength, and resilience. It highlights the importance of diplomacy, consensus, and shared governance in fostering peace and prosperity. The Iroquois Confederacy stands as a testament to the enduring spirit of Indigenous peoples and their ability to adapt and thrive in the face of adversity. Their legacy continues to inspire and inform us, reminding us of the power of unity and the importance of preserving cultural heritage.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Iroquois Confederacy: A Map of Unity and Strength. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!