The Mississippi River: A Lifeline Traced on the World Map
Related Articles: The Mississippi River: A Lifeline Traced on the World Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Mississippi River: A Lifeline Traced on the World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Mississippi River: A Lifeline Traced on the World Map
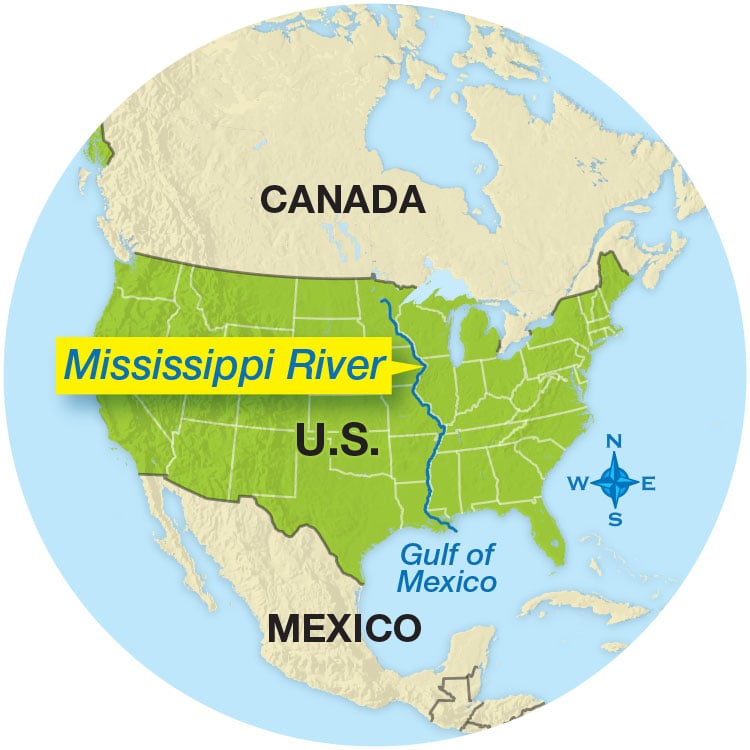
The Mississippi River, a colossal artery coursing through the heart of North America, stands as a testament to the enduring power of nature and the ingenuity of humanity. Its vast network of tributaries, stretching across a sprawling landscape, has shaped the continent’s history, culture, and economy. Understanding the Mississippi River’s reach on a world map provides a crucial lens through which to appreciate its profound significance.
A River of Superlatives:
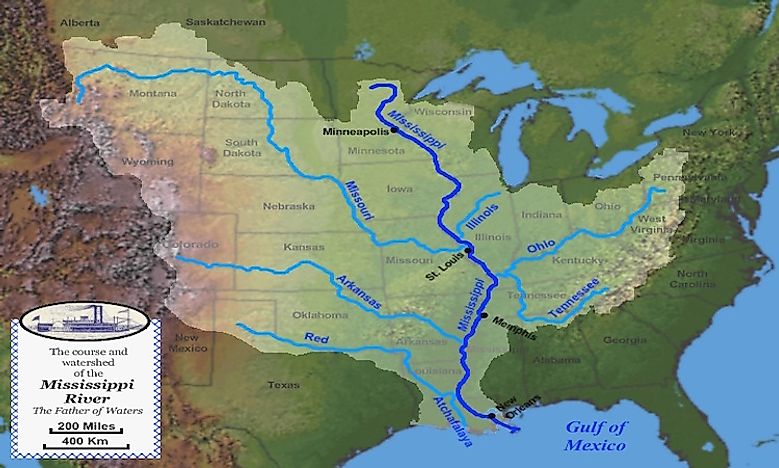
The Mississippi River, originating in Lake Itasca, Minnesota, and flowing south for over 2,300 miles to the Gulf of Mexico, is the second-longest river in North America and the third-longest in the world. Its drainage basin, encompassing a staggering 1.2 million square miles, encompasses 31 states and two Canadian provinces, making it the fourth-largest drainage basin globally. This vast expanse encompasses diverse landscapes, from the rolling hills of the Appalachian Mountains to the fertile plains of the Midwest, and includes major metropolitan centers like Minneapolis, St. Louis, and New Orleans.
Historical Significance:
The Mississippi River has played a pivotal role in shaping American history, serving as a vital transportation route for explorers, traders, and settlers. From the early explorations of French fur traders to the westward expansion of the United States, the river facilitated movement, trade, and cultural exchange. Its banks witnessed the rise of bustling river towns and the development of the steamboat, a technological marvel that revolutionized commerce and transportation. The river’s strategic importance was further highlighted during the Civil War, serving as a crucial supply line for both the Union and Confederate armies.
Economic Lifeline:
The Mississippi River remains a vital economic artery for the United States, supporting a wide range of industries. Its vast waterway facilitates the transportation of agricultural products, manufactured goods, and energy resources, contributing significantly to the nation’s economic prosperity. The river is home to numerous ports and harbors, connecting major cities and facilitating international trade. Its agricultural significance is undeniable, with the fertile lands along its banks producing vast quantities of crops, including corn, soybeans, wheat, and cotton. The river also supports a thriving fishing industry, providing sustenance and livelihoods for communities along its course.
Ecological Significance:
The Mississippi River’s ecological significance is profound, supporting a diverse array of flora and fauna. Its waters provide habitat for numerous fish species, migratory birds, and mammals, including the iconic American alligator. The river’s floodplains, characterized by rich soils and abundant vegetation, create vital breeding grounds for various wildlife. However, the river faces significant environmental challenges, including pollution, habitat loss, and invasive species.
Challenges and Conservation:
The Mississippi River’s immense size and influence come with significant challenges. Its watershed is susceptible to pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and urban sewage. The river’s flow is heavily regulated by dams and levees, impacting natural flood cycles and altering habitats. Climate change poses a further threat, with increased precipitation and rising temperatures potentially exacerbating flood risks and altering the river’s flow patterns.
Efforts are underway to address these challenges and ensure the long-term health of the Mississippi River. Conservation initiatives focus on reducing pollution, restoring habitats, and mitigating the impacts of climate change. Collaboration among federal, state, and local governments, as well as private organizations, is essential to achieve these goals.
Exploring the Mississippi River on a World Map:
A Mississippi River world map serves as a powerful tool for understanding its vast reach and influence. It visually depicts the river’s course, its tributaries, and the diverse landscapes it traverses. The map highlights the river’s connection to major cities, ports, and agricultural regions, providing a comprehensive overview of its economic and cultural significance.
FAQs about the Mississippi River:
Q: What is the length of the Mississippi River?
A: The Mississippi River is approximately 2,320 miles (3,734 kilometers) long.
Q: Where does the Mississippi River begin and end?
A: The Mississippi River originates at Lake Itasca in Minnesota and flows south to the Gulf of Mexico.
Q: What are the major tributaries of the Mississippi River?
A: The Mississippi River has numerous tributaries, including the Missouri River, the Ohio River, the Arkansas River, and the Red River.
Q: What are the major cities located along the Mississippi River?
A: Major cities located along the Mississippi River include Minneapolis, St. Louis, Memphis, and New Orleans.
Q: What are the primary industries supported by the Mississippi River?
A: The Mississippi River supports various industries, including agriculture, transportation, energy production, and tourism.
Q: What are the major environmental challenges facing the Mississippi River?
A: The Mississippi River faces significant environmental challenges, including pollution, habitat loss, and the impacts of climate change.
Tips for Understanding the Mississippi River:
- Explore a Mississippi River world map: Use a world map to visualize the river’s course, tributaries, and surrounding landscapes.
- Research the history of the river: Learn about the role the river played in American history, from exploration to westward expansion.
- Discover the economic importance of the river: Investigate the industries and activities supported by the Mississippi River.
- Understand the ecological significance of the river: Explore the diverse flora and fauna that depend on the river’s ecosystem.
- Learn about conservation efforts: Research initiatives aimed at protecting and restoring the Mississippi River.
Conclusion:
The Mississippi River, a majestic waterway etched onto the world map, stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of nature, history, and human endeavor. Its vast reach, diverse landscapes, and profound influence have shaped the continent’s destiny, providing a lifeline for transportation, commerce, and sustenance. Recognizing the Mississippi River’s importance and addressing the challenges it faces are crucial for ensuring its continued vitality and the well-being of the communities it sustains. By understanding the river’s significance and engaging in conservation efforts, we can preserve this vital resource for future generations.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Mississippi River: A Lifeline Traced on the World Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!