The Power of ELAC Maps: Navigating the Landscape of Language Learning
Related Articles: The Power of ELAC Maps: Navigating the Landscape of Language Learning
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Power of ELAC Maps: Navigating the Landscape of Language Learning. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of ELAC Maps: Navigating the Landscape of Language Learning

The field of language learning is constantly evolving, with new methodologies and approaches emerging to enhance the learning experience. One such innovation that has gained significant traction is the ELAC Map, a powerful tool designed to guide educators and learners through the complex landscape of language acquisition. This article delves into the intricacies of ELAC Maps, exploring their structure, benefits, and applications.
Understanding the ELAC Map: A Framework for Language Development
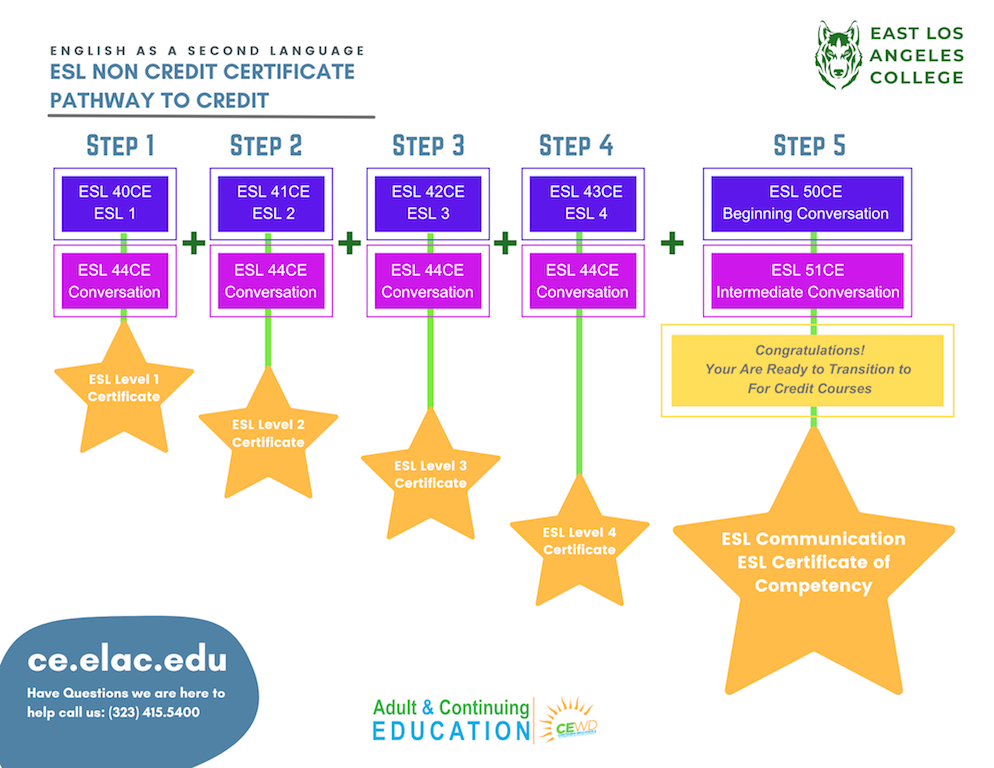
ELAC stands for "English Language Acquisition Continuum." An ELAC Map, therefore, is a visual representation of the progression of language development, outlining the stages a language learner traverses from initial exposure to fluency. This map serves as a comprehensive framework for understanding the developmental process, providing educators with valuable insights into the unique needs of each learner.
The Key Components of an ELAC Map
ELAC Maps typically consist of five key components:
- Language Domains: These encompass the various aspects of language, including listening, speaking, reading, and writing. Each domain is further broken down into specific skills and abilities.
- Developmental Stages: The map outlines distinct developmental stages, each characterized by specific linguistic capabilities. These stages are often marked by benchmarks and milestones that indicate progress.
- Linguistic Features: Each stage is associated with specific linguistic features, such as vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation. These features evolve as learners progress through the stages.
- Assessment Tools: The map incorporates various assessment tools, such as standardized tests, classroom observations, and informal assessments, to measure learner progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Instructional Strategies: The map provides a framework for developing appropriate instructional strategies tailored to the needs of learners at different stages of development.
Benefits of ELAC Maps: A Multifaceted Approach to Language Learning
ELAC Maps offer numerous benefits to both educators and learners, fostering a more effective and personalized learning experience.
For Educators:
- Individualized Instruction: ELAC Maps provide a clear understanding of each learner’s strengths and weaknesses, enabling educators to tailor instruction to individual needs.
- Targeted Intervention: By identifying specific areas where learners require support, educators can implement targeted interventions to address gaps in understanding.
- Progress Monitoring: The map facilitates continuous monitoring of learner progress, allowing educators to track growth and adjust instruction accordingly.
- Collaboration and Communication: ELAC Maps serve as a common language for educators, fostering effective communication and collaboration across different grade levels and teaching teams.
For Learners:
- Clear Expectations: The map provides learners with a clear understanding of the learning goals and the developmental stages they will progress through.
- Increased Motivation: The visual representation of progress motivates learners to strive for mastery and celebrate their achievements.
- Self-Assessment: Learners can use the map to self-assess their progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Personalized Learning: The map allows learners to engage in activities and resources tailored to their individual needs and learning styles.
ELAC Maps in Action: Applications in Diverse Settings
ELAC Maps find application in a wide range of educational settings, supporting language development across different age groups and learning environments.
- English Language Learner (ELL) Programs: ELAC Maps are an essential tool in ELL programs, providing a framework for assessing and supporting learners with diverse linguistic backgrounds.
- Mainstream Classrooms: Educators in mainstream classrooms can utilize ELAC Maps to identify and support students who may be struggling with language acquisition.
- Teacher Training Programs: ELAC Maps play a crucial role in teacher training programs, equipping future educators with the knowledge and skills necessary to support language development.
FAQs about ELAC Maps
1. What is the difference between an ELAC Map and a language proficiency scale?
While both tools assess language development, ELAC Maps provide a more comprehensive framework. They not only outline proficiency levels but also incorporate developmental stages, linguistic features, assessment tools, and instructional strategies.
2. How can educators use ELAC Maps to differentiate instruction?
By understanding the specific linguistic needs of each learner, educators can differentiate instruction by providing varied activities, resources, and support mechanisms tailored to individual learning styles and developmental stages.
3. Are ELAC Maps standardized across all educational institutions?
While the general principles of ELAC Maps are consistent, specific implementations may vary depending on the educational institution and the language being learned.
4. How often should ELAC Maps be reviewed and updated?
ELAC Maps should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure they remain relevant and aligned with current research and best practices in language acquisition.
5. How can parents be involved in the use of ELAC Maps?
Educators can involve parents by providing them with information about the ELAC Map, explaining the stages of language development, and discussing strategies to support their child’s language learning at home.
Tips for Utilizing ELAC Maps Effectively
- Collaborate with colleagues: Engage in regular discussions with colleagues to share best practices and develop a shared understanding of the ELAC Map.
- Incorporate formative assessments: Use formative assessments to monitor learner progress and adjust instruction accordingly.
- Provide clear and concise feedback: Offer specific and actionable feedback that helps learners understand their strengths and areas for improvement.
- Foster a supportive and inclusive learning environment: Create a classroom atmosphere where learners feel safe to take risks, make mistakes, and learn from each other.
- Celebrate learner achievements: Recognize and celebrate learner progress to encourage motivation and a sense of accomplishment.
Conclusion: A Roadmap for Language Success
ELAC Maps serve as a powerful roadmap for navigating the intricate journey of language acquisition. By providing a comprehensive framework for understanding language development, these maps empower educators to tailor instruction, monitor progress, and foster a supportive learning environment. Through their multifaceted approach, ELAC Maps contribute significantly to the success of language learners, paving the way for greater communication, understanding, and cultural appreciation.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of ELAC Maps: Navigating the Landscape of Language Learning. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!