Understanding Map Distance: Navigating the Straight Path
Related Articles: Understanding Map Distance: Navigating the Straight Path
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Map Distance: Navigating the Straight Path. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Map Distance: Navigating the Straight Path

The concept of map distance, specifically the straight-line distance between two points, is fundamental to various disciplines, from geography and cartography to transportation and logistics. This seemingly simple concept holds significant practical and theoretical value, enabling us to understand and measure distances on a map and translate them into real-world distances.
Defining Map Distance
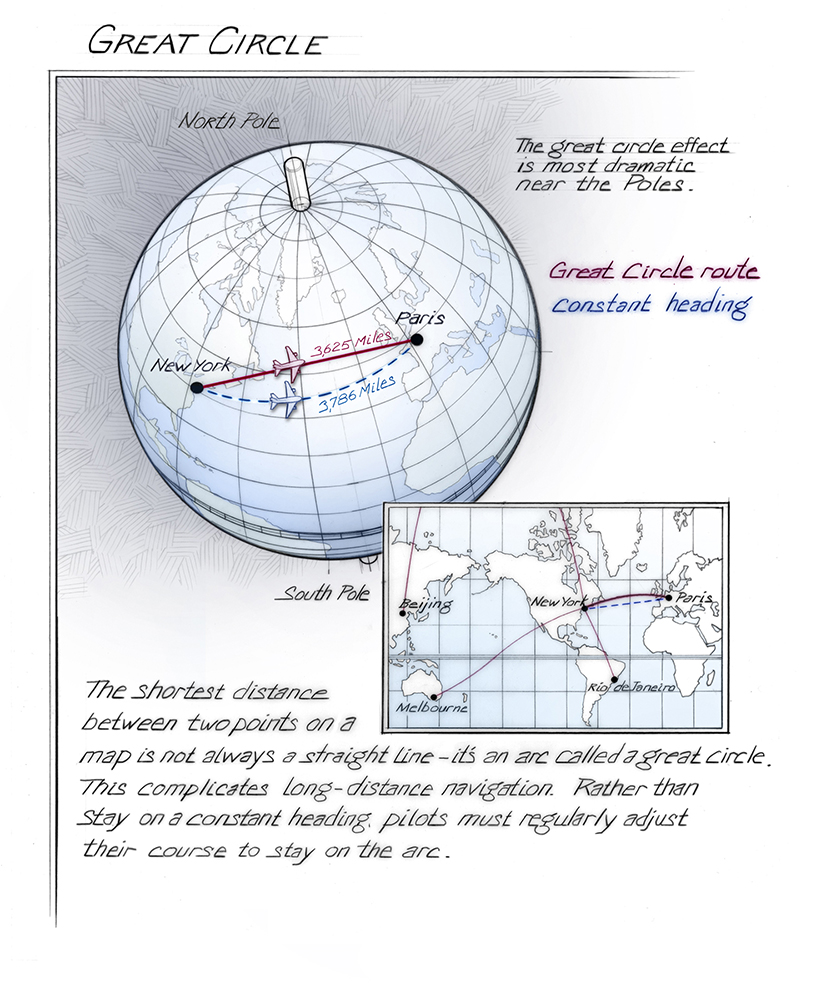
Map distance, in its simplest form, represents the shortest distance between two points on a map, measured along a straight line. This line, known as a geodesic, is the shortest path between two points on a curved surface like the Earth. It’s important to distinguish map distance from real-world distance, which considers the actual terrain and obstacles present on the ground.
The Importance of Map Distance
Map distance plays a crucial role in various applications, including:
- Navigation: Determining the shortest route between two points, crucial for drivers, pilots, and sailors.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Analyzing spatial data and understanding the relationships between different geographical features.
- Cartography: Creating accurate maps and projections that accurately represent distances.
- Urban Planning: Assessing the accessibility of different areas and planning efficient transportation networks.
- Resource Management: Determining the distances between resources and their potential users for efficient allocation.
Measuring Map Distance
Measuring map distance involves several methods, each with its own advantages and limitations:
- Rulers and Scales: Using a ruler and the map’s scale, one can directly measure the distance between two points on the map. This method is simple but prone to inaccuracies due to the map’s projection and distortion.
- Map Projections: Different map projections distort distances in different ways. Understanding the specific projection used for a map is crucial for accurate distance measurement.
- Geographic Coordinate Systems: Using latitude and longitude coordinates, one can calculate the great circle distance between two points on the Earth’s surface. This method is highly accurate but requires specialized software or tools.
- Online Tools and Software: Numerous online tools and software programs allow users to input coordinates or select points on a map to calculate the straight-line distance between them. These tools offer convenience and often provide additional information like travel time and elevation changes.
Factors Affecting Map Distance
It’s important to acknowledge that map distance is not always an accurate representation of real-world distance. Several factors can influence the discrepancy:
- Terrain: The presence of hills, valleys, and other topographical features can significantly affect the actual distance traveled compared to the straight-line distance on a map.
- Obstacles: Buildings, rivers, lakes, and other obstacles can force routes to deviate from a straight line, increasing the actual distance traveled.
- Map Projection: Different map projections distort distances differently, especially at higher latitudes or across large areas.
- Scale: The scale of a map determines the level of detail and accuracy in representing distances. Smaller scale maps (showing larger areas) are less accurate for measuring distances than larger scale maps (showing smaller areas).
Applications of Map Distance
The concept of map distance finds practical applications in a wide range of fields:
- Transportation: Determining the shortest routes for vehicles, airplanes, and ships, optimizing travel time and fuel consumption.
- Logistics: Planning efficient delivery routes for goods and services, minimizing transportation costs and maximizing delivery efficiency.
- Emergency Response: Quickly assessing the distance between an incident location and available resources, facilitating timely and efficient response.
- Environmental Studies: Analyzing the spatial distribution of natural resources, pollution sources, and other environmental factors.
- Real Estate: Determining the proximity of properties to amenities, schools, and other important locations for real estate valuation and development.
FAQs about Map Distance
Q: What is the difference between map distance and real-world distance?
A: Map distance represents the shortest distance between two points on a map, measured along a straight line. Real-world distance considers the actual terrain and obstacles present on the ground, making it often longer than map distance.
Q: How can I accurately measure map distance?
A: Using a ruler and the map’s scale is a simple method, but online tools and software programs offer more accurate measurements, especially when considering map projections and geographic coordinates.
Q: Why is map distance important in navigation?
A: Map distance helps determine the shortest route between two points, allowing for efficient navigation and minimizing travel time and distance.
Q: Can map distance be used to calculate travel time?
A: While map distance provides a basis for estimating travel time, it doesn’t account for factors like traffic, road conditions, and speed limits.
Q: How does map distance relate to geographic coordinates?
A: Geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) can be used to calculate the great circle distance between two points on the Earth’s surface, providing a highly accurate measure of map distance.
Tips for Using Map Distance
- Understand the Map Scale: Ensure you are using the correct scale for the map you are working with.
- Consider Map Projection: Be aware of the map projection used and its potential distortions in distance.
- Factor in Terrain and Obstacles: Account for real-world factors like hills, valleys, and obstacles that can affect the actual distance traveled.
- Utilize Online Tools: Leverage online tools and software programs for accurate and convenient map distance calculations.
- Compare with Real-World Distances: When possible, compare map distances with real-world distances to assess accuracy and adjust for any discrepancies.
Conclusion
Map distance, specifically the straight-line distance between two points, plays a crucial role in various applications, from navigation and transportation to GIS analysis and urban planning. Understanding the concept of map distance, its limitations, and its applications is essential for accurate spatial analysis and informed decision-making in numerous fields. While map distance provides a valuable starting point for measuring distances, it’s important to consider real-world factors and utilize appropriate tools for accurate and comprehensive analysis.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Map Distance: Navigating the Straight Path. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!