Unlocking the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to NOAA Precipitation Maps
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to NOAA Precipitation Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to NOAA Precipitation Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to NOAA Precipitation Maps
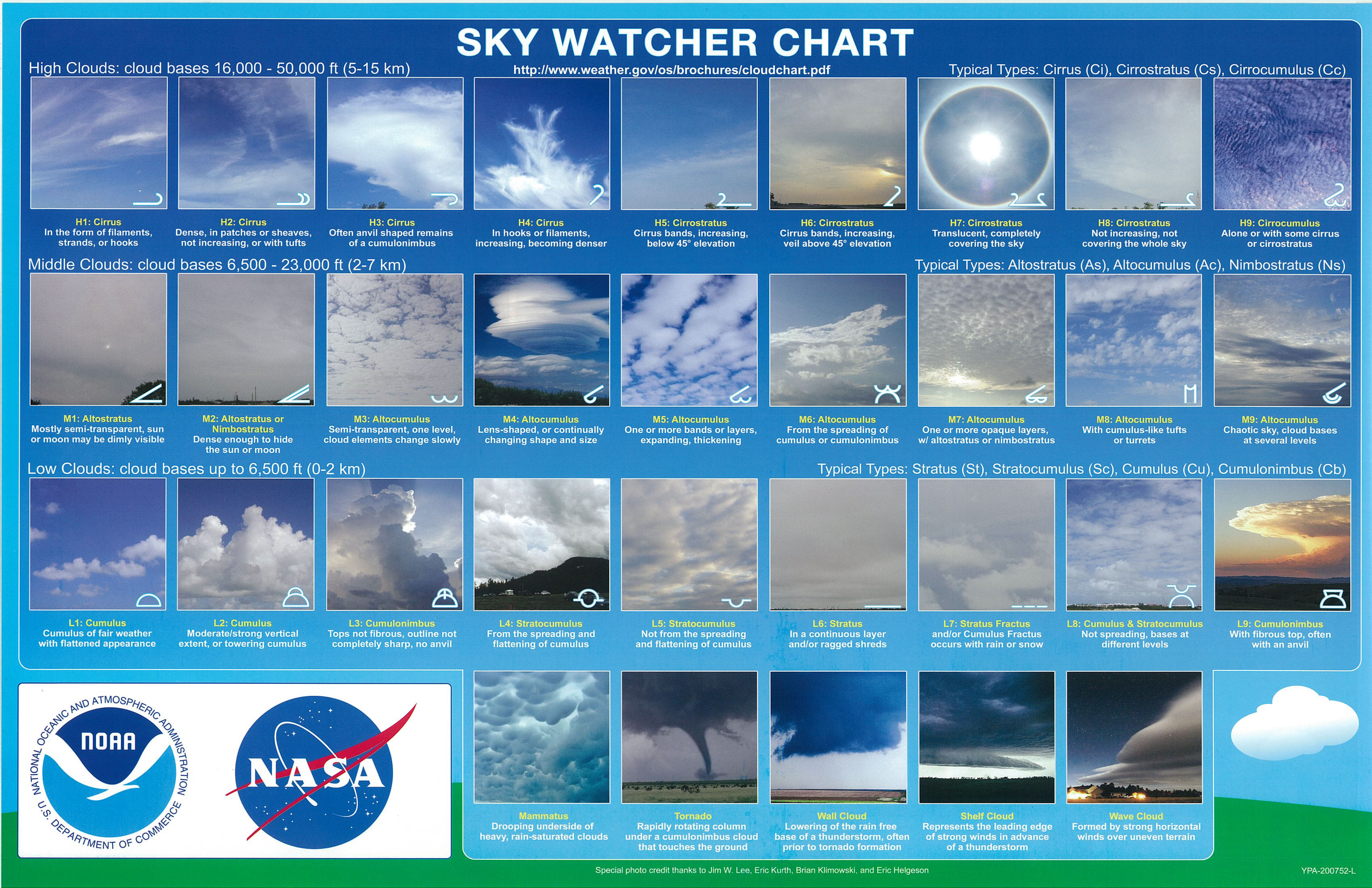
The weather, a force of nature that impacts every aspect of our lives, is constantly in motion. Understanding its nuances, especially precipitation patterns, is crucial for a wide range of activities, from agriculture and water management to transportation and public safety. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) provides invaluable insights into these patterns through its meticulously crafted precipitation maps.
A Visual Representation of Rainfall and Snowfall:
NOAA precipitation maps are powerful tools that visually depict the distribution of rainfall and snowfall across a specific region or the entire United States. These maps, often presented as color-coded grids, utilize data collected from various sources, including:
- Weather stations: Ground-based weather stations across the country provide real-time measurements of rainfall and snowfall.
- Radar: Weather radar systems, strategically positioned throughout the nation, detect precipitation through the reflection of radio waves.
- Satellites: Satellites orbiting Earth capture images of precipitation, providing a broader perspective on weather patterns.
The colors on these maps represent different precipitation intensities, allowing users to quickly discern areas experiencing heavy rainfall, light drizzle, or snowfall. The data is typically presented as accumulated precipitation over a specific period, ranging from hourly to monthly totals.
Understanding the Data and its Significance:
NOAA precipitation maps offer a wealth of information for various stakeholders:
- Farmers: Farmers rely on precipitation data to make informed decisions about planting, irrigation, and crop management. Understanding the expected rainfall patterns allows them to optimize their agricultural practices and potentially mitigate risks associated with drought or excessive rainfall.
- Water Resource Managers: Water resource managers utilize precipitation data to assess water availability and allocate resources effectively. They can track the extent of rainfall and snowfall, monitor reservoir levels, and forecast potential flooding events.
- Emergency Responders: Emergency responders rely on precipitation data to anticipate and prepare for weather-related emergencies. They can identify areas at risk of flooding, landslides, or other natural disasters, enabling them to allocate resources and prioritize response efforts.
- Transportation Professionals: Transportation professionals use precipitation data to assess road conditions and plan routes. They can anticipate potential road closures, hazardous driving conditions, and delays caused by heavy rainfall or snowfall.
- Public Safety Officials: Public safety officials utilize precipitation data to issue weather warnings and advisories. They can alert the public about potential hazards, such as flash flooding, heavy snowfall, or severe thunderstorms, promoting preparedness and safety.
Navigating the Maps: A Step-by-Step Guide:
NOAA precipitation maps are readily accessible online and offer a user-friendly interface for navigating the data. Here’s a guide to effectively utilize these maps:
- Select the desired region: Most NOAA precipitation maps allow users to zoom in on specific regions of interest, whether it’s a county, state, or the entire country.
- Choose the time period: Users can select the time period for which they want to view precipitation data, ranging from hourly to monthly totals.
- Interpret the color scale: Each map includes a color scale that indicates the intensity of precipitation, with different colors representing varying amounts of rainfall or snowfall.
- Analyze the data: Once the map is displayed, users can analyze the data to identify areas experiencing heavy precipitation, light drizzle, or snowfall. They can also track the movement of precipitation systems and anticipate future weather patterns.
Beyond Visual Representation: Accessing Additional Data:
NOAA precipitation maps provide a visual overview of precipitation patterns, but they also offer access to additional data points:
- Quantitative precipitation estimates (QPEs): QPEs provide numerical estimates of precipitation amounts, typically expressed in inches or millimeters.
- Precipitation type: NOAA maps often indicate the type of precipitation, such as rain, snow, or a mix of both.
- Precipitation duration: The maps may display the duration of precipitation events, providing insights into the length of time rainfall or snowfall occurred.
FAQs about NOAA Precipitation Maps:
1. What is the accuracy of NOAA precipitation maps?
The accuracy of NOAA precipitation maps depends on the quality and density of the data sources. While weather stations provide accurate point measurements, radar data can be affected by factors like terrain and precipitation intensity. Satellite data offers a broader perspective but can be less precise in specific locations.
2. How often are NOAA precipitation maps updated?
NOAA precipitation maps are typically updated in real-time or at regular intervals, depending on the data source and the specific map type. Some maps are updated hourly, while others are updated every few hours or even daily.
3. Are NOAA precipitation maps available for historical data?
Yes, NOAA offers access to historical precipitation data through various platforms, allowing users to analyze past precipitation patterns and trends.
4. How can I receive alerts about significant precipitation events?
NOAA provides various tools and services to receive alerts about significant precipitation events. These include email notifications, mobile app alerts, and weather radio broadcasts.
5. Can I customize NOAA precipitation maps to meet my specific needs?
Some NOAA precipitation map platforms allow users to customize the maps by selecting specific time periods, regions, and data parameters.
Tips for Using NOAA Precipitation Maps Effectively:
- Understand the limitations of the data: Be aware that precipitation maps represent estimates based on available data, and they may not capture every detail of precipitation patterns.
- Consider multiple data sources: For a more comprehensive understanding, analyze data from multiple sources, including weather stations, radar, and satellites.
- Correlate precipitation data with other factors: Combine precipitation data with other relevant information, such as terrain, soil type, and land use, to gain a more complete picture.
- Consult with experts: If you require specialized information or analysis, consult with meteorologists or other experts who can provide insights and guidance.
Conclusion:
NOAA precipitation maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding and predicting precipitation patterns, offering insights crucial for various sectors. By visualizing rainfall and snowfall distribution, these maps empower decision-makers to make informed choices, manage risks, and ensure the well-being of communities and the environment. As technology continues to evolve, NOAA precipitation maps are expected to become even more sophisticated, providing even greater accuracy and detail, further enhancing our understanding of the intricate dance of precipitation in the atmosphere.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of the Sky: A Comprehensive Guide to NOAA Precipitation Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!