Unraveling the Landscape: A Guide to Geographic Features on Maps
Related Articles: Unraveling the Landscape: A Guide to Geographic Features on Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Landscape: A Guide to Geographic Features on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Landscape: A Guide to Geographic Features on Maps

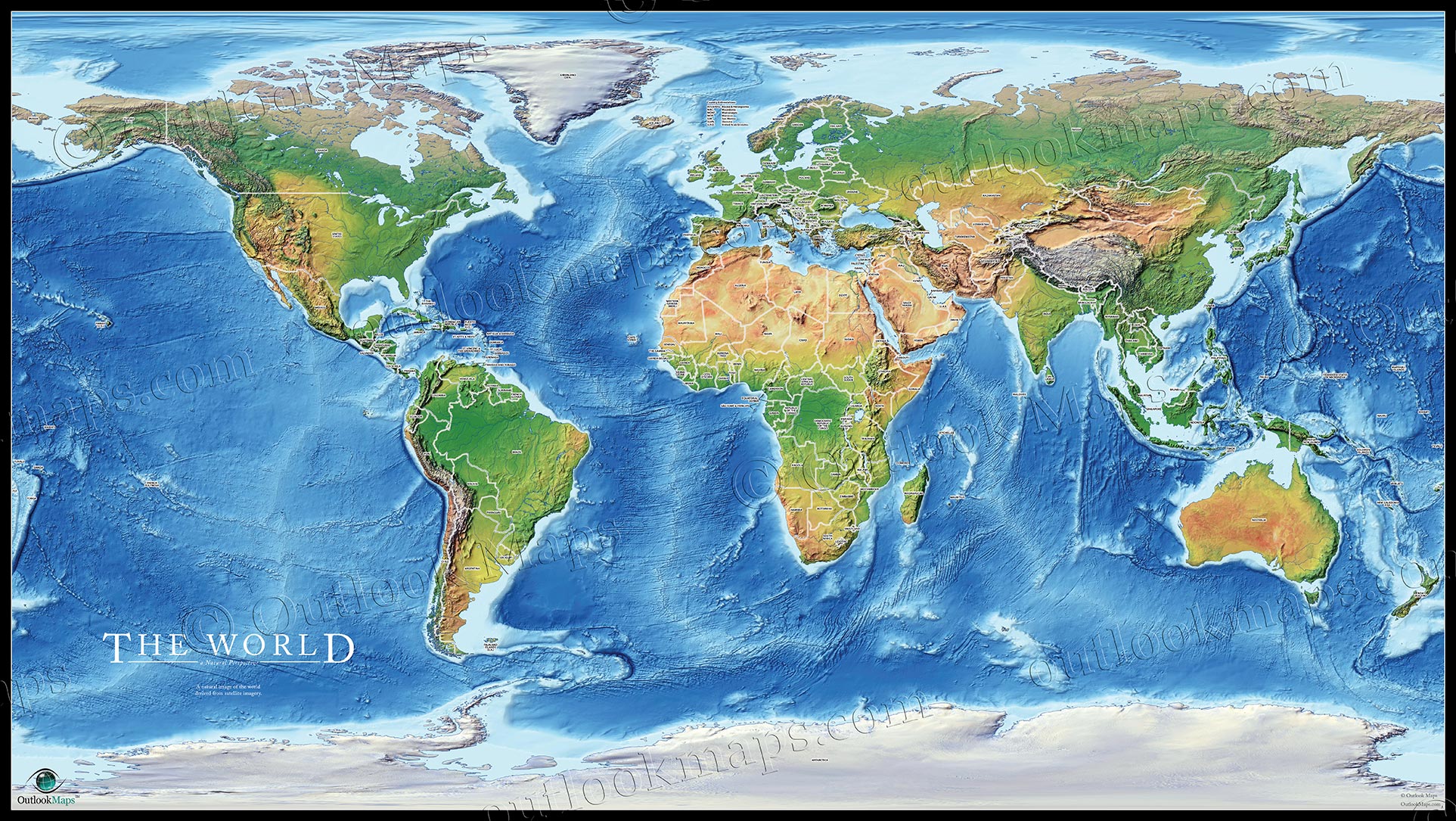
Maps are more than just static representations of the world; they are powerful tools for understanding and navigating our planet. At their core lie geographic features, the building blocks of our physical environment, each possessing unique characteristics and playing a vital role in shaping the world around us. This article delves into the diverse world of geographic features, exploring their significance in cartography, environmental studies, and human civilization.
Understanding Geographic Features:
Geographic features are the defining elements of a landscape, encompassing both natural and man-made structures. These features can be broadly classified into two categories:
1. Natural Geographic Features:
These features are shaped by natural processes, reflecting the dynamic forces of nature over time. They include:
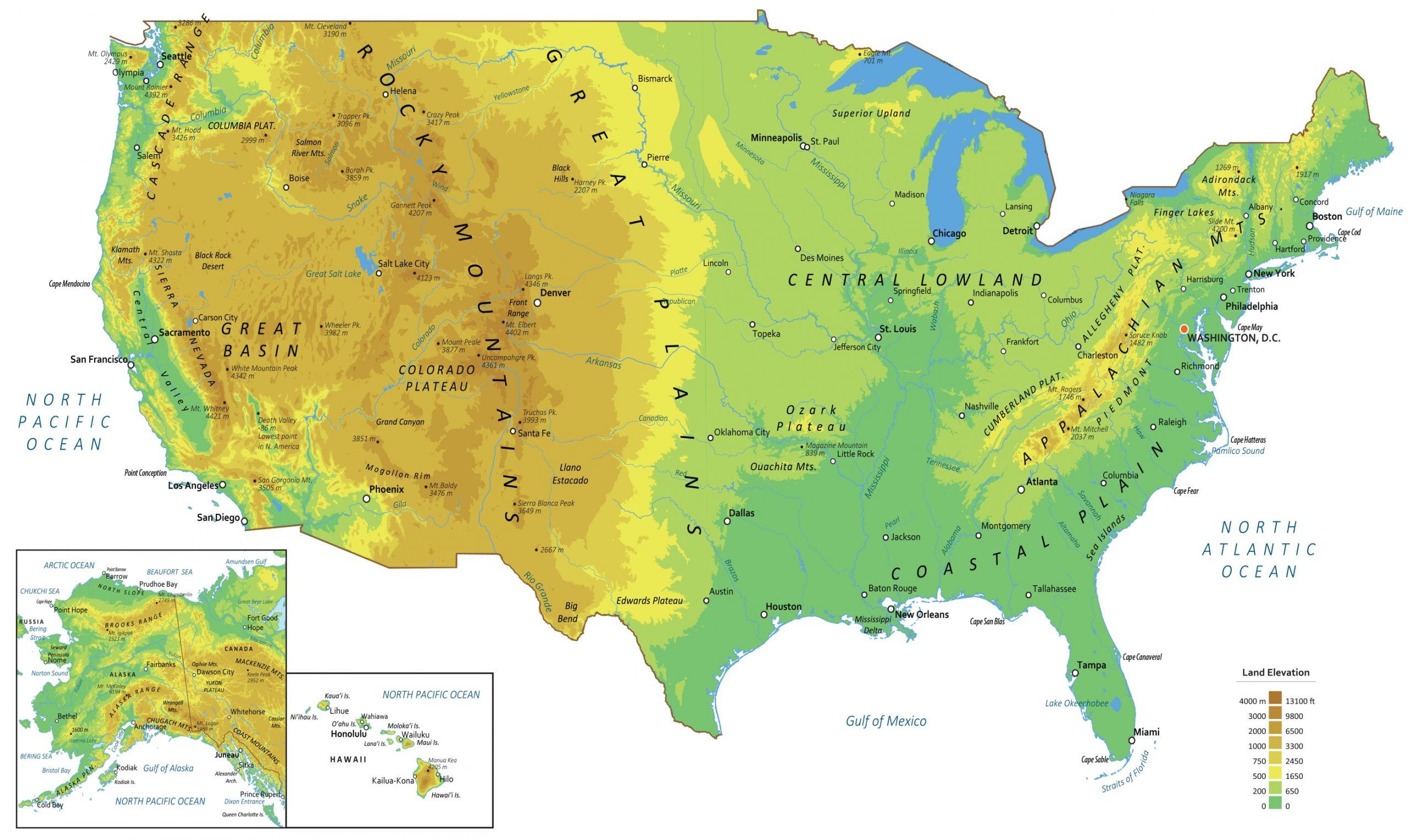
- Landforms: The physical shape of the Earth’s surface, including mountains, valleys, plains, plateaus, hills, and deserts. These landforms are sculpted by erosion, deposition, tectonic activity, and volcanic eruptions.
- Water Bodies: Encompassing oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, and glaciers, these features influence climate patterns, support biodiversity, and provide vital resources for human societies.
- Vegetation: The plant life covering the Earth’s surface, including forests, grasslands, tundra, and deserts. Vegetation patterns are influenced by climate, soil conditions, and human activity.
- Climate Zones: Defined by distinct patterns of temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions, climate zones influence the distribution of vegetation, animal life, and human settlements.
2. Man-Made Geographic Features:
These features are constructed by humans, reflecting our ingenuity and impact on the environment. They include:
- Settlements: Human settlements, ranging from small villages to sprawling cities, are the centers of human activity and cultural development.
- Infrastructure: Transportation networks (roads, railways, airports), communication systems, and energy infrastructure are vital for connecting communities and facilitating economic growth.
- Agricultural Areas: Farmlands, orchards, and pastures are crucial for food production and supporting human populations.
- Industrial Zones: Factories, mines, and other industrial facilities play a significant role in economic development but can also have environmental consequences.
Importance of Geographic Features on Maps:
Maps are essential tools for understanding and interacting with the world around us. Geographic features on maps serve several crucial purposes:
- Spatial Awareness: Maps provide a visual representation of the distribution and relationships between geographic features, enhancing our understanding of spatial patterns and connections.
- Navigation and Orientation: Maps guide us through unfamiliar landscapes, aiding in navigation and orientation, especially for travelers, explorers, and emergency responders.
- Resource Management: Maps are invaluable for managing natural resources, identifying areas suitable for agriculture, forestry, mining, and other economic activities.
- Environmental Planning: Maps help us understand the distribution of ecosystems, identify areas prone to natural hazards, and develop effective strategies for environmental protection.
- Historical and Cultural Insights: Maps provide insights into the historical development of human settlements, migration patterns, and cultural influences.
FAQs by Geographic Features on Maps:
1. What are the different types of mountains?
Mountains are classified based on their formation processes, resulting in distinct characteristics. Fold mountains, formed by the collision of tectonic plates, are characterized by their elongated shape and parallel ridges. Volcanic mountains, formed by the eruption of magma, are characterized by their conical shape and often exhibit volcanic features like craters and lava flows. Block mountains, formed by the uplift and faulting of crustal blocks, have steep slopes and flat summits.
2. How do rivers shape the landscape?
Rivers are powerful agents of erosion and deposition, shaping the landscape through a continuous cycle of carving valleys, transporting sediments, and forming deltas. Erosion occurs as the flowing water wears away at the riverbed and banks, while deposition occurs when the river’s energy decreases, causing sediments to settle and build up.
3. What are the different types of forests?
Forests are classified based on their dominant tree species, climate conditions, and geographical location. Tropical rainforests are characterized by high rainfall, dense vegetation, and a rich biodiversity. Temperate forests, found in mid-latitude regions, have distinct seasons and support a variety of deciduous and coniferous trees. Boreal forests, located in high-latitude regions, are dominated by coniferous trees and experience long, cold winters.
4. How do cities impact the environment?
Cities have a significant impact on the environment, both positive and negative. Urban areas consume large amounts of resources, produce significant amounts of waste, and contribute to air and water pollution. However, cities also offer opportunities for innovation in sustainable development, promoting energy efficiency, waste reduction, and green infrastructure.
5. How are maps used in disaster preparedness?
Maps play a crucial role in disaster preparedness by providing valuable information about potential hazards, evacuation routes, and resource availability. They help emergency responders understand the affected area, coordinate rescue efforts, and plan for post-disaster recovery.
Tips by Geographic Features on Maps:
- Use a variety of map types: Different map types, such as topographic maps, road maps, and thematic maps, provide different perspectives and insights into geographic features.
- Pay attention to scale: The scale of a map determines the level of detail and the area covered. Choose a map with an appropriate scale for your needs.
- Understand map symbols: Map symbols represent different geographic features, so it is essential to understand their meaning.
- Use map legends: Map legends provide a key to the symbols used on the map, making it easier to interpret the information.
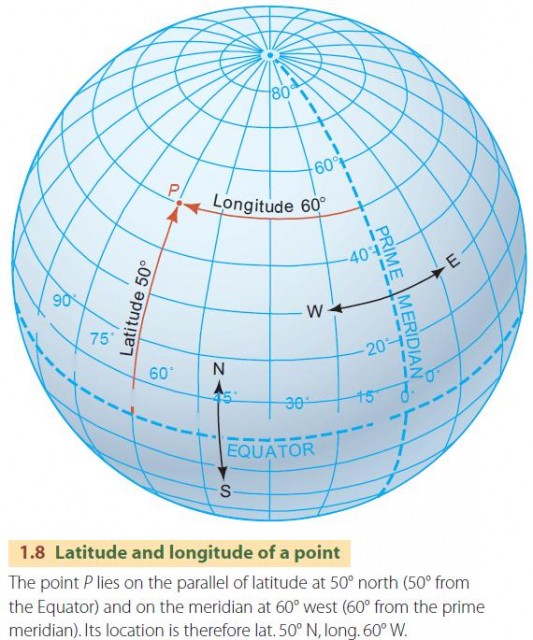
- Consider map projections: Map projections distort the Earth’s surface to represent it on a flat plane. Choosing an appropriate projection is crucial for accurate representation.
Conclusion by Geographic Features on Maps:
Geographic features are the fundamental elements that define our planet’s landscape. Maps provide a powerful tool for understanding these features, their interrelationships, and their impact on human societies. By leveraging the information contained within maps, we can navigate the world, manage resources, plan for the future, and appreciate the intricate beauty and complexity of our planet.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Landscape: A Guide to Geographic Features on Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!