Unveiling the Power of Normal Maps: Enhancing Visual Fidelity in 3D Environments
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Normal Maps: Enhancing Visual Fidelity in 3D Environments
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Normal Maps: Enhancing Visual Fidelity in 3D Environments. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Normal Maps: Enhancing Visual Fidelity in 3D Environments

In the realm of 3D graphics, the pursuit of realism has driven the development of numerous techniques. One such technique, often employed to significantly enhance visual fidelity, is the use of normal maps. These digital maps, containing surface normal information, empower artists and developers to imbue 3D models with intricate detail and a sense of depth, all without the computational burden of high-polygon models.
Understanding the Essence of Normal Maps
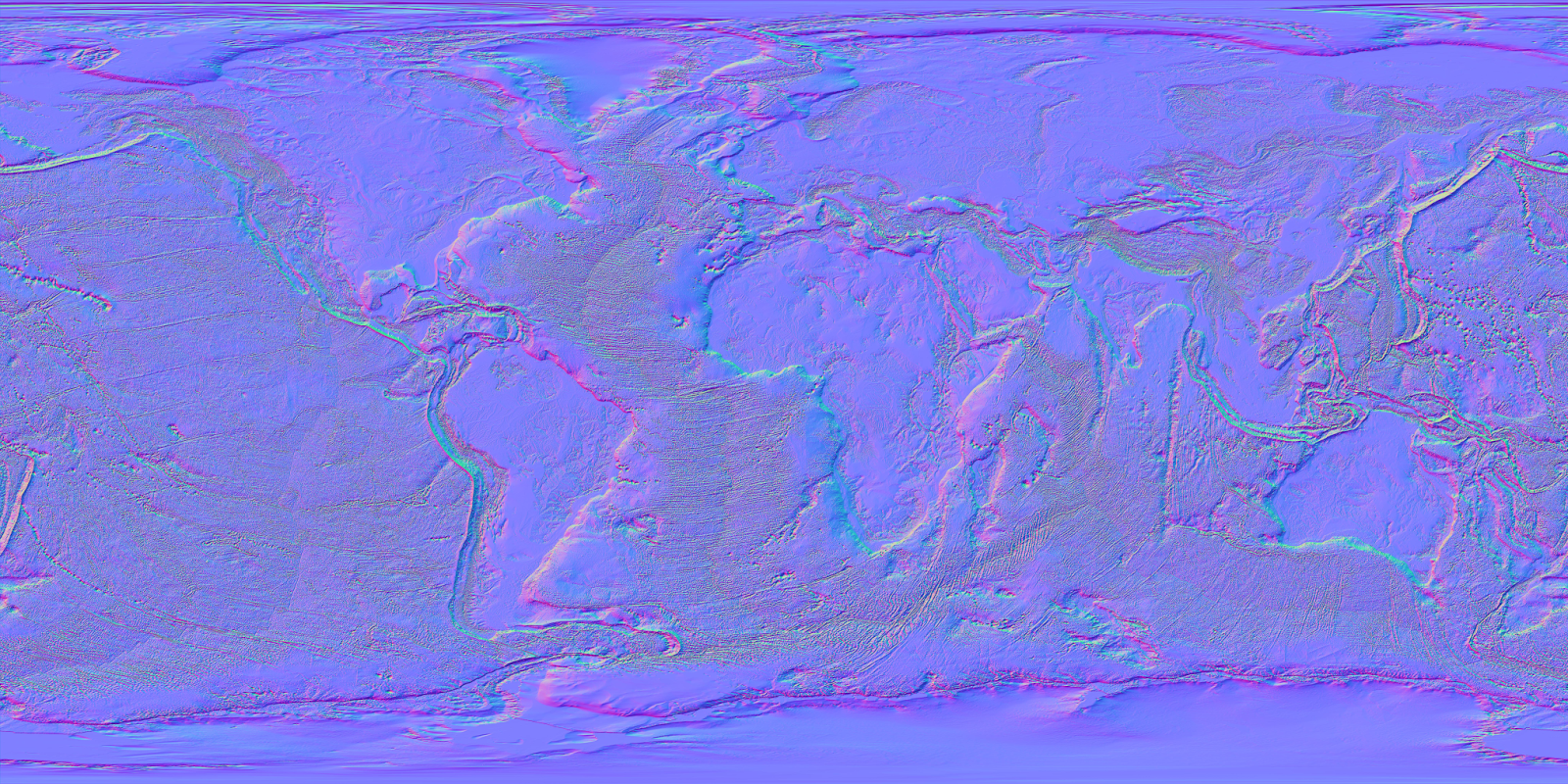
At its core, a normal map is a 2D image that encodes the direction of surface normals for each pixel of a 3D model. These normals, essentially vectors perpendicular to the surface at each point, dictate how light interacts with the surface, shaping the visual appearance of shadows, highlights, and reflections.
Imagine a smooth, flat surface. Light would interact with it uniformly, resulting in a predictable, flat appearance. Now, imagine adding intricate details – grooves, bumps, and creases – to this surface. Light interacts with these details differently, creating subtle shadows and highlights that add depth and realism. This is where normal maps come into play.
Instead of explicitly modeling these details with high-polygon meshes, normal maps capture the essence of these surface variations, allowing for a significant reduction in polygon count while retaining the visual impact of intricate detail. This reduction in complexity leads to performance improvements, especially crucial for real-time applications like games and interactive environments.
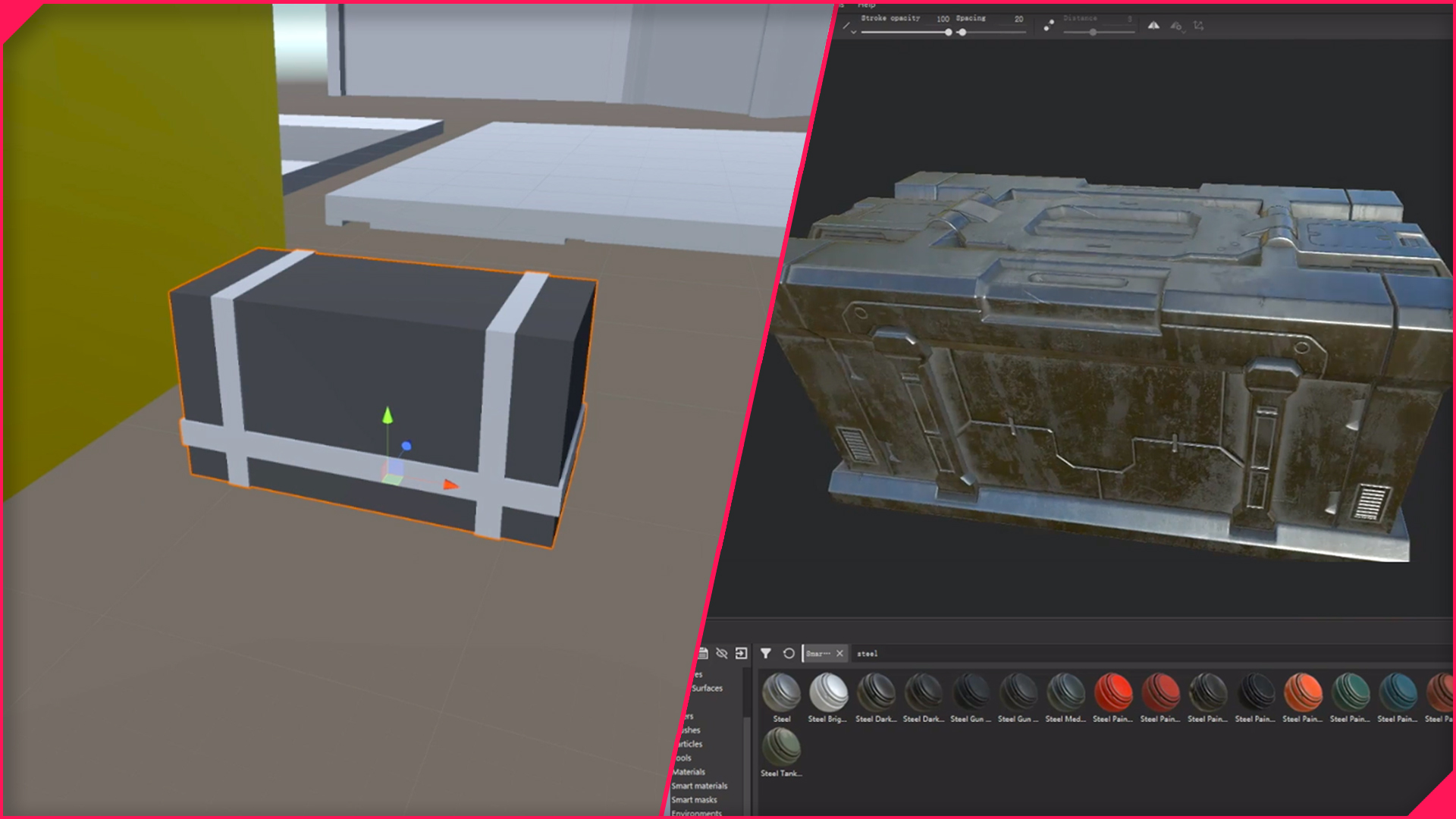
Normal Map Creation: A Journey from 3D Model to Digital Map
The creation of a normal map involves a multi-step process that bridges the gap between a 3D model and its digital representation. This process typically involves the following steps:
-
High-Poly Model Creation: The initial stage involves creating a detailed 3D model, often referred to as the "high-poly" model. This model serves as the source for capturing the intricate surface details that will be encoded in the normal map.
-
Baking the Normal Map: The high-poly model is then "baked" into a lower-resolution model, often called the "low-poly" model. This baking process extracts the surface normal information from the high-poly model and transfers it to the low-poly model.
-
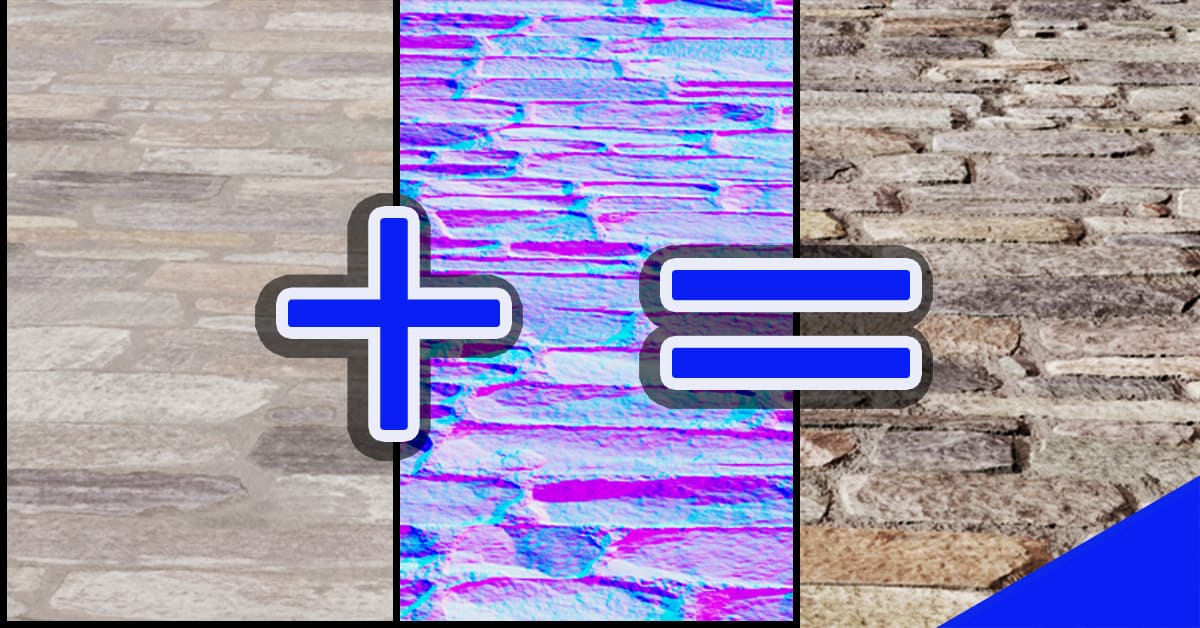
Normal Map Generation: Software tools are employed to generate the actual normal map from the baked data. These tools typically use color channels to represent the direction of the surface normals, with different colors signifying different directions.
Beyond the Basics: Types of Normal Maps and Their Applications
Normal maps are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different types of normal maps cater to specific needs and applications:
-
Tangent Space Normal Maps: These are the most common type, where the normal vectors are defined relative to the tangent space of the 3D model. This allows for efficient and accurate rendering, as the normal vectors are aligned with the surface.
-
Object Space Normal Maps: These maps define the normal vectors relative to the world space, offering greater flexibility but potentially requiring more complex calculations.
-
Bump Maps: These maps are a simplified form of normal maps, often used for subtle surface variations. They use grayscale values to represent the height of the surface, leading to a more limited representation of normal directions.
The Advantages of Utilizing Normal Maps
The use of normal maps offers numerous advantages, making them a valuable tool for artists and developers alike:
-
Enhanced Visual Fidelity: Normal maps significantly enhance the visual realism of 3D models by introducing intricate surface details without the computational burden of high-polygon models.
-
Performance Optimization: By reducing the polygon count, normal maps contribute to improved performance, especially in real-time applications. This allows for smoother rendering and higher frame rates.
-
Artistic Flexibility: Normal maps provide artists with greater control over surface details, enabling them to experiment with different textures and effects without needing to modify the underlying model.
-
Memory Efficiency: Normal maps are relatively small in size compared to high-polygon models, leading to reduced memory consumption and faster loading times.
Frequently Asked Questions about Normal Maps
Q: What is the difference between a normal map and a bump map?
A: While both normal maps and bump maps aim to enhance surface detail, they differ in their approach. Normal maps encode the direction of surface normals, providing a more detailed and accurate representation of surface variations. Bump maps, on the other hand, use grayscale values to represent surface height, offering a simpler and less detailed representation.
Q: Can I create a normal map from a photograph?
A: Yes, it is possible to create a normal map from a photograph using specialized software. These tools analyze the depth and texture of the photograph to generate a normal map that can be applied to a 3D model.
Q: How do I use a normal map in a game engine?
A: Most game engines provide support for normal maps. You typically need to import the normal map as a separate texture and assign it to the material of the 3D model. The engine will then use the normal map information to calculate lighting and shading effects.
Tips for Using Normal Maps Effectively
-
Choose the Right Resolution: The resolution of the normal map should be appropriate for the level of detail required and the target platform. Higher resolutions offer greater detail but can impact performance.
-
Optimize for Compression: Normal maps can be compressed to reduce file size without sacrificing visual quality. Use lossless compression formats like PNG or DDS for optimal results.
-
Avoid Artifacts: Artifacts, such as banding or noise, can appear in normal maps. Ensure proper settings and techniques are used during the baking and generation process to minimize these issues.
-
Experiment with Different Textures: Normal maps can be combined with other textures, such as diffuse and specular maps, to create a more comprehensive and realistic visual appearance.
Conclusion: The Future of Normal Maps in 3D Graphics
Normal maps have become an indispensable tool in the world of 3D graphics, enabling artists and developers to achieve stunning visual fidelity without sacrificing performance. Their versatility, efficiency, and ease of use make them a valuable asset for creating immersive and engaging 3D experiences. As technology continues to advance, normal maps are likely to play an even more prominent role in shaping the future of 3D graphics, pushing the boundaries of realism and immersion in virtual environments.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Normal Maps: Enhancing Visual Fidelity in 3D Environments. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!